* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure and Function Study Guide – Honors Biology What are
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
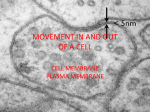
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
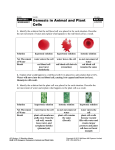
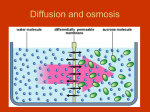
Cell Structure and Function Study Guide – Honors Biology 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. What are the 3 parts of the cell theory? What types of cells does this theory apply to? What are the parts that are found in ALL cells? What is the difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? What are some examples of each? What is the name for a unicellular eukaryote? Why is it important for cells to have a large surface area? What is the difference between chromosomes and chromatin? What are the functions of the following organelles? A. Cell membrane B. Cytoplasm C. Chloroplast D. Cytoskeleton – what are parts of the cytoskeleton? E. Mitochondria F. Golgi body G. Ribosomes H. Nucleus I. Lysosome J. Cell wall K. Rough ER L. Smooth ER Vacuole (central vacuole) What organelle(s) are found only in plants? Animals? Label cells and their parts (prokaryote and eukaryote) How do cells contact one another in animal cells? What is the plasmodesmata in plants? Why is it needed? What are flagella? What does it look like? What types of organisms have them? What is a phospholipid? What cell organelle does it make up? What are the parts? What is the meaning of selectively permeable? Channels and pumps within the cell membrane are made up of what? Types of passive transport: osmosis, diffusion, facilitated diffusion – explain each. What is the goal of passive transport? What would happen to cells (osmosis) in hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic? Be able to read an example and explain what type of osmosis and what happens to the cell. What is the normal environment for plant cells? IV solutions for humans? What is cytolysis (animal cells)? Plasmolysis (plant cells)? What is the difference between active and passive transport? What are some examples of active? What is the difference between endocytosis and exocytosis? What are 3 types of endocytosis? What happens in each? What is an example of phagocytosis? What are the 5 levels of organization from smallest to largest? What are some examples of organs? Organ systems? What is the meaning of cell specialization? Provide some examples. 29. You should also be able to answer questions about lab activities and be able to label the cell organelles. o o o Baggie lab – how did this lab represent the cell membrane and the meaning of selectively permeable? Draw a diagram of what happened Gummy bear lab – how did this lab represent osmosis? What was the hypertonic solution? Hypotonic? What happened to the gummy bears in each? Cell Size lab- how did this lab demonstrate the relationship between cell size, surface area and transport of materials? Label all letters in the animal cell. A B C D E F G H I J K L M Label the plant cell below with the following parts: Chloroplast Cell wall Cytoplasm Ribosomes Golgi body Central vacuole Plasmodesmata Rough ER Smooth ER Mitochondria Nucleus Nuclear membrane Nucleolus