* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
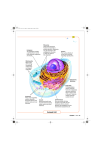
The Cell Cell Types & Cell Parts Cell Types Cell Types Eukaryote Have Nucleus Plant Animal Prokaryote No Nucleus Fungi Protista Bacteria Kindgom Monera Prokaryotic Cells or Prokaryotes The Bacteria Capsule • A protective covering • Made up of polysaccharides • Keep the bacterium from drying out & to protect it • The capsule is a major virulence factor in the major disease-causing bacteria, • E.g. Escherichia coli and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Cell Wall • Gives the cell its shape • Surrounds the plasma membrane, protecting it from the environment. • Helps to anchor appendages (pili and flagella) • Responsible for keeping the cell from bursting when there are large differences in osmotic pressure between the cytoplasm and the environment. Nucleoid • A region of cytoplasm where the chromosomal DNA is located. • It is not a membrane bound nucleus • Most bacteria have a single, circular chromosome • Small circular DNA strands, called plasmids, are also found in the cytoplasm. Pili • Small hairlike projections emerging from the outside cell surface. • Assist the bacteria in attaching to other cells and surfaces, such as teeth, intestines, and rocks. • Without pili, bacteria lose their ability to infect because they're unable to attach to host tissue. Prokaryotic Ribosomes • Site of protein synthesis • Bacterial ribosomes are never bound to other organelles Bacterial Shapes Bacterial Arrangements Eukaryotic Cells Or Eukaryotes Nucleus & Membrane Bound Organelles Animal Cell Cytoplasm Centriole Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Vacuole Cell Membrane Nucleolus Nucleus Mitochondria Ribosome Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Nuclear Membrane Golgi Apparatus Lysosome Plant Cell Smooth Nucleus Nucleolus Chloroplast Endoplasmic Reticulum Nuclear Membrane Golgi Apparatus Cell Wall Cell Membrane Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Vacuole Mitochondria Ribosome Cytoplasm Cell Membrane • Controls what enters and leaves cell • Protects and supports the cell • Made of a Phospholipid Bi-layer • Proteins – act as channels, carriers, or pumps to pass molecules into or out of the cell • Cholesterol molecules prevent phospholipids from sticking to each other • Fluid Mosaic Phospholipid Bilayer Cell Membrane Cell Membrane • Carbohydrate chains • Act like chemical ID cards – allows cells to recognize each other. Cell Wall • Plants, algae, some bacteria • Helps support and protect cell • 2 or more layers thick – Outer layer is where cells meet – gluey substance – pectin – Primary cell wall is next – made of cellulose Nucleus • large dark structure • Not all cells have a nucleus – Eukaryotes – Prokaryotes • Information center and holds DNA (genetic code) • Chromosomes – DNA and Proteins – Genetic code Nucleolus • Inside Nucleus • Made of RNA • Makes Ribosomes – Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis Cytoplasm • Jelly like substance • Holds organelles • Most chemical reactions happen here Cytoplasm • Made up of * Proteins including enzymes * Vitamins * Ions * Nucleic acids and their precursors * Amino acids and their precursors * Sugars, carbohydrates and their derivatives * Fatty acids and their derivatives • These are all part of continuous chemical reactions. Mitochondria • Powerhouse of the cell • Break down sugars for energy – Convert ADP to ATP • 2 Membranes – Outer surrounds mitochondria – Inner increases surface area – more efficient Mitochondrion Chloroplast • Only in plant cells • Have Chlorophyll • Convert Sun energy into chemical energy Chloroplast Ribosome • Composed of RNA and protein • some attached to membranes, some free • smallest organelles · 25 nanometers (1 billionth of a meter) Endoplasmic Reticulum • Network of channels – ER • Transports materials through the inside of the cell • Rough ER – Has Ribosomes covering it • Smooth ER – NO RIBOSOMES ON IT (Detoxifies) • Synthesized proteins are moved to Golgi Apparatus for modification Golgi Apparatus or Golgi body • Looks like flattened stack of pancakes • Modifies, collects, packages, and distributes proteins Lysosomes The Cleanup Crew • Lysosomes help digest particles – contain enzymes and chemicals necessary for digestion • Break down organelles that have outlived their usefulness • Formed by Golgi Apparatus • Only in Animal Cells Cellular Junctions