* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELLS : the Structural and Functional Units of All Life Forms
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
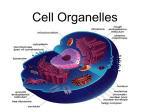
CELLS : the Structural and Functional Units of All Life Forms Microscopes are used to view objects too small to be seen clearly with the human eye CLM- compound light microscopes use many lenses and a beam of light to magnify objects up to 3000X. Require a translucent specimen. See in micrometers SEM – scanning electron microscopes, use beam of electrons, object must be stained with heavy metal, see the outside surface in 3D, 100,000X, nanometers TEM - transmission electron microscope, electron beam, heavy metal stain, through thin slices, powerful Scanning Tunneling Electron Microscope – can be used to guide electrons into specimen, “virtual tour” , can see macromolecules ( not atoms ) Cytology Cytology is the study of cells ‘cyto’ means cell, ‘ology’ is the study of Cell fractionation – uses centrifuge to take cells apart and separate their organelles based on density Centrifuge – 80,000 rpm, spins cells in liquid to break them apart. Cell Types Prokaryotic cells Small Found only in bacteria (Archea and Eubacter kingdoms) Cell membrane, cytoplasm, DNA without a nuclear membrane and special ribosomes No internal membranes or membrane bound organelles Eukaryotic cells Larger Found in plants, animals, fungi and protista Contain cell membrane, cytoplasm, DNA inside of a nucleus Many organelles bounded by membranes. Surface area to volume ratio Surface area is represented by cell membrane (product in and out) – this unit is ‘squared’ A sphere is the shape with the largest surface area to volume ratio Volume is represented by cytoplasm (site of all reactions) – this unit is ‘cubed’ Need to match supply with demand and import with export, energy amts and pollution also need to be considered IT is more EFFICIENT to have many, small cells than fewer large cells. Cell Membrane Fluid mosaic model phospholipid bilayer Amphopathic Selectively permeable More PROKARYOTIC information Pro (before) and karyon (kernal or center) Small, 0.1 mm (micrometers) to 10 mm Found only in bacteria (Eubacteria and Archeabcter) Cell membrane, cytoplasm, DNA without a nuclear membrane and special ribosomes No internal membranes or membrane bound organelles DNA is in the form of one circular chromosome Few hundred genes Region is called nucleiod Ribosomes are 70 s MAY contain capsules, pili, flagella and plasmids More EUKARYOTE information Eukaryotic cells Larger Found in plants, animals, fungi and protista Contain cell membranes, cytoplasm, DNA inside of a nucleus Many organelles bounded by membranes. Organelles vary greatly from kingdom to kingdom. Eukaryotic nucleus Nuclei is plural of nucleus; “center” Function of nucleus is to control everyday activity of the cell and to control cell reproduction (of information) Nuclear membrane is similar to plasma membrane Membrane is porous to certain nutrients Contains DNA in the form of many chromosomes Chromosomes can’t leave, membrane must dissolve during cell division. Cells can be multinucleate or coenocytic Eukaryotic Organelles Cytoplasm is fluid and organelles Cytosol refers to just the solution ALL cells have ribosomes (slight dif.) ALL cells have DNA (euk. contained) Organelles like ribosomes are solid Many eukaryotic organelles are membranes bound. (packages) List of organelles – Cell membrane Nucleus Nuclear membrane, chromosomes, chromatin, centrioles, nucleolus, spindle fibers Ribosomes ( attached and free ) Membrane bound organelles “surrounded by membrane” Cilia, flagella, plasmodesmata Mitochondrion, chloroplast, plastid, vacuole, Golgi apparatus, smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) and rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER), lysosomes, Other Microtubules, microfilaments (actin), etc.