* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell: Organelles and Functions
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
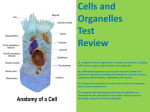
The Cell: Organelles and Functions Organelles Membrane Bound Subunits that carry out Specialized Functions Cell Membrane Form: Proteins and Phospholipids Function: Form for cell Controls access Cytoplasm Water and Dissolved Substances Nucleus Form: Nuclear envelope surrounds chromatin Function: Cellular “Command Center” Difference between chromatin and chromosomes? Nucleolus Specialized region for producing Ribosomes Dense region inside of nucleus Endoplasmic Reticulum Form: Network of Membrane-Lined Channels Function: 1. Transport of cellular products Processing of cellular products - Lipids to cell membrane - Proteins for export Golgi Complex Form Membrane folds outside of ER Make carbohydrates and finish export proteins Ribosome Form Mesh of RNA and protein Lysosome Form Membrane-bound sack of enzymes What is an enzyme? Function: Digest particles for food and protection Mitochondria Form Double layer of membrane with wrinkled inside Function Makes ATP, releases energy from food Chloroplast Capture energy from sunlight to make simple sugar and starch Vacuole YouTube MicroSafari Paramecium Form: Membrane bound sacks Function: Consumption and excretion Cytoskeleton Microfilaments - protein: actin - outside support of cell - “skin” of a building - allow for cell movement Microtubules - protein: tubulin - support inside of cell - “girders” of cell support the inside - movement of things inside of cell YouTube - Amoeba under microscope IV Centrosome Form: Mass of protein Function: Generates centrioles during mitosis Cilia and Flagella Form: “Hair” or “Whip-like” extensions from the cell made of microtubules Function: Locomotion Types of Cellular Life Unicellular Life Prokaryotes - Eubacteria and Archaebacteria - Single cell, widely distributed life Unicellular Life Protists - Unicellular eukaryotic life - Protozoans : Animal-like protists - Algae : Plant-like protists Cell Specialization and Multicellular Organisms Specialization increases efficiency Use more energy = bigger body Bigger body = higher survivability Higher survivability = more surviving offspring Specialization In Cells Organ Types and Organelles Organism Organ Cell Organelle Levels of organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism