* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
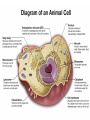
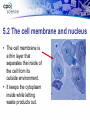
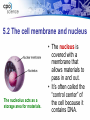
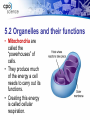
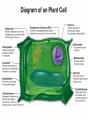
Chapter Five: Cell Structure and Function • 5.2 Cells: A Look Inside Page # Description 64Notes 5.2 Cells: A Look Inside Date Assigned 12/3 Point Value 10 My Score 5.2 Cells: A Look Inside • A cookie factory is like a cell. • An analogy is a way of explaining something complicated using an easier example. • A cookie factory is a good analogy for understanding all the cell parts and their functions. 5.2 Cells: A Look Inside • Every cell part has a job or function. • This chart shows how a cell is like a cookie factory 5.2 The cell membrane and nucleus • The cell membrane is a thin layer that separates the inside of the cell from its outside environment. • It keeps the cytoplasm inside while letting waste products out. 5.2 The cell membrane and nucleus The nucleolus acts as a storage area for materials. • The nucleus is covered with a membrane that allows materials to pass in and out. • It’s often called the “control center” of the cell because it contains DNA. 5.2 Organelles and their functions • Mitochondria are called the “powerhouses” of cells. • They produce much of the energy a cell needs to carry out its functions. • Creating this energy is called cellular respiration. 5.2 Organelles and their functions • A vacuole is the storage area of the cell. • Vacuoles store water, food, and waste. 5.2 Organelles and their functions • Ribosomes are the protein factories of the cell. • When ribosomes make proteins, they release them into the ER. 5.2 Organelles and their functions • The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a series of tunnels throughout the cytoplasm. • They transport proteins from one part of the cell to another. 5.2 Organelles and their functions • Golgi bodies receive proteins and other compounds from the ER. • They package these materials and distribute them to other parts of the cell. 5.2 Organelles and their functions • Lysosomes contain enzymes that can break things down. • Lysosomes pick up bacteria, food, and old organelles and break them into small pieces that can be reused. 5.2 Organelles and their functions • The cytoskeleton is a series of fibers made from proteins. • It provides structure to the cell and gives it its shape. 5.2 How plant cells are different 1. Plant cells have chloroplasts, but animal cells do not. A chloroplast is an organelle that contains a green pigment called chlorophyll. 5.2 How plant cells are different 2. Plant cells have a large central vacuole that stores cell sap. 5.2 How plant cells are different 3. Plant cells have a cell wall, but animal cells do not. Cell walls provide structure and support for the plant.