* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mitosis Flip Book
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
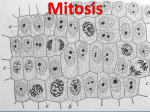
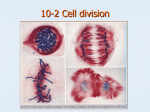
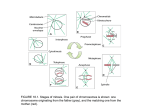
MITOSIS FLIP BOOK ALEXIS TUCKER EARLY PROPHASE The nuclear membrane and the nucleolus start to disappear. The spindle fibers start to form. LATE PROPHASE The nucleus has completely disappeared. The spindle fibres have fully formed, and they attach themselves to the centromeres. METAPHASE The spindle fibres tug the X shaped chromosomes into a line across the middle of the cell. ANAPHASE The spindle fibres begin to contract and shorten which pulls the centromere apart to let the sister chromatids move to the opposite sides of the cell. Once they separate, each chromatid is a chromosome. TELOPHASE The spindle fibres begin to disappear, and a nuclear membrane forms around the chromosomes. A nucleolus appears within each nucleus. There are two nuclei in the cell, now it’s about to divide. CYTOKINESIS This is the final stage in mitosis. Cytokinesis separates the nuclei into two daughter cells which are identical to the original cell.