* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download psychology - History of - 2013
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and psychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals wikipedia , lookup
Index of psychology articles wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical psychology wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Humanistic psychology wikipedia , lookup
Gestalt psychology wikipedia , lookup
Developmental psychology wikipedia , lookup
International psychology wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Social psychology wikipedia , lookup
Experimental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
Political psychology wikipedia , lookup
Subfields of psychology wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cross-cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Music psychology wikipedia , lookup
History of psychology wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Operant conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Hidden personality wikipedia , lookup
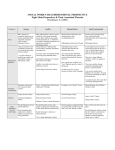
The scientific study of behavior and mental processes that is tested through scientific research. Four Goals of Psychology: 1. Describe 2. Explain 3. Predict 4. Influence Wilhelm Wundt (18321920) Father of Psychology 1st Laboratory of Psychology Structuralist ◦ a psychologist who studied the basic elements that make up conscious mental experiences. Introspection - “inner experiences” William James (1842-1910) 1st Psychology Class at Harvard Influenced by Darwin’s Survival of the Species Influenced Motivation & Emotion Functionalist - a psychologist who studied the function (rather than the structure) of consciousness. Why do we run away if we notice that we are in danger? William James Because we are afraid of what will happen if we don't. (1842-1910) obvious (and Class incorrect)at answer to a seemingly trivial 1st This Psychology Harvard question has been the central concern of a century-old debate about Influenced by Darwin’s Survival the nature of our emotions. of the Species William James conceived of an emotion in terms of a Influenced & occurrence Emotionof an arousing sequence of eventsMotivation that starts with the stimulus (the sympathetic nervous system or the parasympathetic Functionalist nervous system); and ends with a passionate feeling, a conscious - a psychologist emotional experience. who studied the function (rather than the structure) of consciousness. A major goal of emotion research is still to elucidate this stimulus-to-feeling sequence — to figure out what processes come between the stimulus and the feeling. Sir Francis Galton (1822-1911) World Traveler Cousin of Charles Darwin - Heredity - coined the phrase “nature versus nurture” “Wouldn’t the world be a better place if we could get rid of less desirable people?” His theories are now discredited! Point of View: Focus is on the unconscious Sigmund Freud (1856-1939) Stage Theorist (Oral, Anal, Phallic, Latency, Genital) Studies in Hysteria Unconscious Mind Dream Interpretation Free Association Defense Mechanisms Therapist’s Role: Objective In the Western world, until the 17th century, hysteria referred to a medical condition thought to be particular to women and caused by disturbances of the uterus (from the Greek ὑστέρα "hystera" = Point of View: Focus is on the unconscious uterus), such as when a baby emerges from the Sigmund Freud (1856-1939) female birth canal. Stage Theorist (Oral, Anal, Phallic, Latency, Genital) Freudian psychoanalytic theory attributed hysterical symptoms to the subconscious mind's Studies in Hysteria attempt to protect the patient from psychic stress. Unconscious Mind Dream Interpretation Free Association Defense Mechanisms Therapist’s Role: Objective Alfred Adler (1870-1937) Carl Jung (pronounced Young) (1875–1961) Karen Horney (pronounced “Hornay”) (1885-1952) Anna Freud (1895-1982) John Bowlby (1907-1990) Margaret Mahler (1897-1985) Point of View: Behavior can be easily studied, shaped, and changed. Ivan Pavlov (1849-1936) Classical Conditioning: Pavlov’s Dogs John B. Watson (18781958) Classical Conditioning ◦ Little Albert B.F. Skinner (1904-1990) Operant Conditioning ◦ Skinner’s Rats ◦ Positive Reinforcement ◦ Negative Reinforcement Point of View: Human nature is constantly evolving and self-directed. Carl Rogers (1902-1987) ◦ Unconditional Positive Regard, Empathy, Congruence Abraham Maslow (1908-1970) ◦ Hierarchy of Needs ◦ Father of Modern Management Psychology Rollo May (1909-1994) ◦ Existential Psychology Point of View: Focus on how we process, store, and use information, & how information influences our thinking, language, problem solving, & creativity. Albert Ellis (1913-2007) ◦ Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT) form of cognitive behavior therapy (CBT) & was first expounded by Ellis in the mid 1950s; development continued until his death in 2007. Aaron Beck (1921) ◦ Founder of Cognitive Therapy seeks to help the patient overcome difficulties by identifying & changing dysfunctional thinking, behavior, & emotional responses Point of View : studies the human lifespan & how changes in development affect one’s behavior and motivation. Erik Erikson (1902-1994) Jean Piaget (1896-1980) Point of View: Perception is more than the sum of its parts - it involves a “whole pattern” or, in German, a Gestalt. Fritz Perls (1893-1970) – Founder of Gestalt ◦ Laura Perls ◦ Empty Chair Technique Max Wertheimer (1880-1943) Wolfgang Kohler (1887-1967) Kurt Koffka (1886-1941) Point of View : emphasizes the impact PET scans and CAT scans Neurotransmitters Genetics of biology on behavior. Point of View : involves studying the influence of cultural and ethnic similarities and differences on behavior and social functioning. ◦ Gender, Socioeconomic Status, Immigration Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) ◦ Zone of Proximal Development the difference btwn what a learner can do w/o help & what he can do with help.