* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Metabotropic Neurot
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Spike-and-wave wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
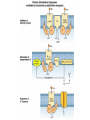
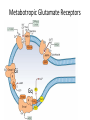
Metabotropic Neurotransmitter Receptors Dopamine Receptors Dopamine receptors • D1, D5 types • D1 highest expressed DA receptor – Coupled to Gas • D2,3,4 types • D2 is the site of action for anti-psychotic drugs – Coupled to Gai and Gao • Primary AC in striatum is AC5 – Activated by Gas and PKC – Inhibited by Gai/o and Ca2+ D2 autoreceptor • D2 can be alternatively spliced to D2s and D2l • D2s acts as the inhibitory pre-synaptic autoreceptor – Inhibits synthesis and release of DA • D2l functions as an inhibitory post-synaptic receptor Adrenergic Receptors • a1-adrenergic receptors – 3 types, all coupled to Gaq/11 (PLC pathway) • a2-adrenergic receptors – 3 types, coupled to Gai/o (inhibit AC) – Found pre-synaptically, acts as autoreceptor • b-adrenergic receptors – 3 types, coupled to Gas (activate AC) – Often found on glia, where they reduce glutamate uptake and regulate glucose utilization Functional Roles of adrenergic receptors • Hypothalamic – A1 in MPO area mediate wakefulness • Amygdala and HPC – A1 and B receptor activation promotes long term memory consolidation – A2 activation enhance working memory in PFC – A1 activation in PFC inhibits its function CA Receptor Regulation • Agonist induced down regulation – Receptors are internalized after prolonged treatment with agonists • Reuptake inhibitors • Drugs like amphetamine • Denervation Supersensitivity (203 lab) – Physical ablation or chemical antagonism of receptor activation leads to increased receptor density and sensitivity Muscarinic Ach Receptors mAchR localization • M1-abundant post-synaptic (dendritic) receptor in the brain • M2 enriched in thalamus and brainstem, low levels elsewhere – Pre-synaptic autoreceptor • M3 low levels in cortex and HPC • M5 low levels in VTA, SN midbrain • M4 high levels in striatum (pre-synaptic) Implications for disease • AD-loss of cholinergic neurons • Schizophrenia- reduced levels of M1 and M4 – Genetic and pharmacological links • Parkinson’s disease – Links to nicotine protection – Regulation of pre-synaptic DA release – Balance of Ach and DA in Striatum regulates movement • Drug Addiction-M5 antagonists in VTA Serotonin Receptors Serotonin Receptors 5-HT1A • Gi/o coupled • Cortex and hippocampus • Post-synaptic and somatodendritic autoreceptor functions – As autoreceptors, mechanism is via activation of K+ channels • Function in feeding, sexual behaviors, and body temperature, ACTH release • Agonists of 5-HT1A treat anxiety, and perhaps depression and schizophrenia too 5-HT2 Family • Gq coupled • 5-HT2A post-synaptic receptor found highest in PFC on both GABA and Glutamate neurons • Homeostatic functions (temperature) • Roles in cognition and mental illness – Antagonists are anti-psychotic – Agonists are hallucinogenic 5-HT 4,6,7 receptors • Gs coupled • 5-HT4 – Multiple splice isoforms – Not well studied • 5-HT6 – Target of anti-psychotic drugs and anti-depressants (striatum) – Antagonists increase Ach transmission, improve learning and memory • 5-HT7 – Sleep, circadian rhythms and mood (SCN) – Target of anti-psychotic drugs Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors Gi Gq Functional Roles for mGluR • All 3 classes inhibit L-type voltage sensitive Ca2+ channels • mGluR activation also closes K+ channels, leading to slow repolarization (prolong excitation) HPC and cortex • Opposite effect in cerebellum • Pre-synaptic mGluRs are inhibitory-on both Glutamate and GABA neurons (Ca2+ channel) Studies in knock-out mice • mGlu1 -/- mice-cerebellar ataxia – mGlu1 necessary for pruning of climbing fiberPurkinje cell synapses during development – LTD is defective, poor motor learning • mGlu2 -/- mice- impaired LTD in HPC Metabotropic GABA receptors • 2 members, R1 and R2, have been cloned • Function as a dimer, R1 binding GABA, R2 binding the G protein • 4 known associated subunits regulate localization, function, and pharmacology • Inhibitory – Open K+ channels – Block Ca2+ channels (presynaptic inhibition) – Inhibit AC