* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gene Therapy and Transgenic Animals
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
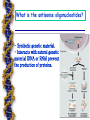
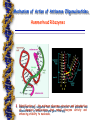
Anti-mRNA Strategies What is the antisense oligonucleotides? - Synthetic genetic material. - Interacts with natural genetic material (DNA or RNA) prevent the production of proteins. Antisense Oligonucleotides are unmodified or chemically modified ssDNA, RNA or their analogs. They are 13-25 nucleotides long and are specifically designed to hybridize to the corresponding RNA by Watson-Crick binding Mechanism of Action of Antisense Oligonucleotides. 1. Translational Arrest by Blocking the Ribosome. animation Antisense RNA technology The antisense RNA procedure for blocking or reducing the level of expression of a specific gene. Mechanism of Action of Antisense Oligonucleotides. 2. Activation of RNase H The enzyme RNase H is a nonspecific endonuclease and catalyzes the cleavage of RNA via a hydrolytic mechanism. Mechanism of Action of Antisense Oligonucleotides. Ribozymes – Ribozymes are RNA molecules that catalyze biochemical reactions. – Ribozymes cleave singlestranded regions in RNA through transesterification or hydrolysis reactions that result in cleavage of phosphordiester bonds animation Types of Ribozymes Tetrahymena Group I intron Hammerhead ribozyme Hairpin ribozyme Hepatitis delta virus ribozyme Rnase P Mechanism of Action of Antisense Oligonucleotides. Hammerhead Ribozymes 2. of sequence the minimum ribozyme structure into and plasmids introduction 1. Identification Ribozyme-coding has been incorporated and of chemical modifications that retain ribozyme activity and administered, in effect ribozyme gene therapy. enhancing stability to nucleases. Basic features of Hammerhead ribozyme 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Single strand of RNA. Three helical stem regions. Unpaired loops at the ends of two helices. Helices radiate out from central unpaired core of nucleotides. Cleavage site is next to a small, unpaired "U-turn" loop. Limitations of Practical Applications of Antisense Oligonucleotides 1. Accessible sites of the target RNA for oligonucleotide binding have to be identified. 2. Antisense agents have to be protected against nucleolytic attack. 3.Cellular uptake and correct intracellular localization. Medicinal Chemistry of Antisense Oligonucleotides One of the major challenges for antisense approaches is the stabilization of oligonucleotides, as unmodified oligodeoxynucleotides are rapidly degraded in biological fluids by nucleases. Application of Antisense Oligonucleotides 1.Functional Genomics and Target Validation: Antisense oligonucleotides can be used to selectively manipulate the expression of chosen gene or genes. The process results in : – A pharmaceutical copmound understood mechanism of action. with a well- – Well characterized distribution and a safe side effect profile which could be used as a human therapeutic. Application of Antisense Oligonucleotides 2. Potential Therapeutic Oligonucleotides Applications of Antisense – A wide variety of potential therapeutic applications of antisense oligonucleotides has been reported in the last few years. – Major areas of these therapeutic applications include: 2.1. Antiviral 2.2. Antibacterial 2.3. CNS Therapeutics: Antisense Oligonucleotides will address unmet medical needs for CNS diseases. 2. Potential Therapeutic Applications of Antisense Oligonucleotides 2.4. Inflammation Therapeutics: e.g. Colitis, Lupus, Lung inflammation, Skin inflammation, Transplantation rejection, Reperfusion injury, Rheumatoid Arthritis and Ocular disease. Cardiovascular Therapeutics: e.g. prevention of restenosis, myocardial infarction, rejection in heart transplantation, hypertension and atherosclerosis. 2.5. 2.6. Regulation of Apoptosis: which will address treatment of cancer, psoriasis,fibrosis, atherosclerosis, restenosis and others 2. Potential Therapeutic Applications of Antisense Oligonucleotides 2.7. Anticancer: 2.8. Other Therapeutic Applications potentials: diabetes, pain and analgesia, psoriasis, myasthenia gravis, hair loss…etc – The most recent antisense application as therapeutic tool is aimed to treat the SARS and bird Flu Clinical Trials of Antisense Oligonucleotides – One antisense oligonucleotide (fomivirsen) has been approved. – Currently, there are near to 50 antisense compounds in trials for various diseases, up to 10 of which are in phase III, with an additional 20 in Phase II. Future of Antisense-Based Biotechnology – The clinical experience to date should be considered part of the beginning of the story of antisense treatment, with more clinical trials of new antisense drugs soon expected. The promise – Currently over of 30antisense-based pharmaceutical and biotechnology is therefore stronger biotechnology companies have declared an interest in or have an active than ever.drug development program already under way in antisense-based therapeutics –The fuller story, yet to be written, promises to be rich. THANKS FOR LISTENING