* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Metabolic Pathways and Energy Production
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
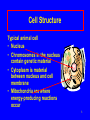
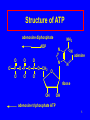
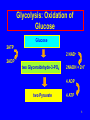
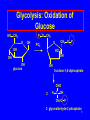
Metabolic Pathways and Energy Production Metabolism and ATP Energy Important Coenzymes Glycolysis 1 Metabolism All the chemical reactions that occur in the cells of our bodies. Catabolic reactions • Break down large molecules • Provide energy for ATP catabolic anabolic Anabolic reactions • Use small molecules to build large ones • Require energy 2 Cell Structure Typical animal cell • Nucleus • Chromosomes in the nucleus contain genetic material • Cytoplasm is material between nucleus and cell membrane • Mitochondria are where energy-producing reactions occur 3 ATP • Energy is released as food is oxidized • Used to form ATP from ADP and Pi ADP + Pi + Energy ATP • In cells, energy is provided by the hydrolysis of ATP ATP ADP + Pi + Energy 4 Structure of ATP adenosine diphosphate ADP O - O O O - O N O N P O P O P O CH2 - NH2 - N adenine N O O ribose OH OH adenosine triphosphate ATP 5 Digestion of Foods Digestion is the first step of catabolism • Carbohydrates glucose, fructose, galactose • Proteins amino acids • Lipids glycerol fatty acids 6 Coenzymes • Substances that connect metabolic pathways • In reduction, coenzymes accept H atoms • In oxidation, coenzymes remove H atoms FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide) FAD + -CH2-CH2- FADH2 + -CH=CH- NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) NAD+ + -CH-OH NADH + H+ + -C=O 7 Glycolysis: Oxidation of Glucose Glucose 2ATP 2 NAD+ 2ADP two Glyceraldehyde-3-PO4 2NADH + 2H+ 4 ADP two Pyruvate 4 ATP 8 Glycolysis: Oxidation of Glucose P O CH2 HO CH2 O OH CH2 O P O PO4 OH HO OH OH OH glucose OH fructose-1,6-diphosphate CHO 2 H C OH CH2O P 2 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate 9 Glycolysis: Oxidation of Glucose 2 ADP + 2 Pi 2 ATP CHO CHO 2 2 H C OH H C O CH3 CH2O P 2 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate 2 NAD+ 2 pyruvate 2 NADH + 2 H+ 10 Glycolysis: Oxidation of Glucose Glycolysis generates 2 ATP molecules and 2 NADH + 2 H+ Two ATP used in adding phosphate groups to glucose and fructose-6-phosphate (- 2 ATP) Four ATP generated in direct transfer to ADP by two 3C molecules (+ 4 ATP) Glucose + 2 ADP + 2 Pi + 2 NAD+ 2pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 H+ 11 Pathways for Pyruvate Aerobic conditions O || CH3–C –COO- + NAD+ + CoA pyruvate O || CH3–C –CoA + CO2 + NADH + H+ acetyl CoA 12 Pathways for Pyruvate Anaerobic conditions (No O2 available) Reduce to lactate to replenish NAD+ for glycolysis O || CH3–C –COO- + NADH + H+ OH | CH3–CH –COO- + NAD+ pyruvate lactate enzyme: lactate dehydrogenase 13 Lactate in Muscles • Strenuous exercise leads to anaerobic conditions • Oxygen in muscles is depleted • Lactate builds up as glycolysis continues • Muscles tire and become painful • Breathing rate increases • Rest repays oxygen debt • Lactate re-forms pyruvate in liver 14 Learning Check M1 Match the following with the terms below: (1) Catabolic reactions (2) Coenzymes (3) Glycolysis (4) Lactate A. Produced during anaerobic conditions B. Reactions that convert glucose to pyruvate C. Metabolic reactions that break down large molecules to smaller molecules + energy D. Substances that remove or add H atoms in oxidation and reduction reactions 15 Solution M1 Match the following with the terms below: (1) Catabolic reactions (2) Coenzymes (3) Glycolysis (4) Lactate A. 4 Produced during anaerobic conditions B. 3 Reactions that convert glucose to pyruvate C. 1 Metabolic reactions that break down large molecules to smaller molecules + energy D. 2 Substances that remove or add H atoms in oxidation and reduction reactions 16