* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quiz 7 Name: 1. After ATP fuels the Na+/K+ pump at the cell
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
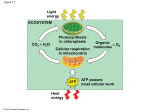
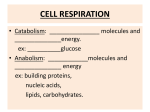
Quiz 7 Name:_____________________ 1. After ATP fuels the Na+/K+ pump at the cell membrane in an animal cell, where do the “used-up” ADP and Pi go? A) ADP and Pi accumulate in the cytosol and don’t form ATP again B) ADP and Pi are regenerated to ATP by the Na+/K+ pump running in reverse C) ADP and Pi are regenerated to ATP in the chloroplast D) ADP and Pi are regenerated to ATP in the mitochondrion E) C and D 2. Cells use the energy of energy-rich food molecules to form ATP. Which of the following represents a state of high energy? A) the C-H bonds in food molecules B) the H (electrons and H+) loaded onto NADH C) the proton gradient across the mitochondrial membrane D) the ATP formed E) all of the above 3. Which molecules can be utilized (directly or after some breakdown) in the cellular respiration pathway to generate ATP energy? A) amino acids and proteins B) glycerol and fatty acids C) glucose and sucrose D) starch and glycogen E) all of the above 4. What is needed to keep glycolysis reaction running? A supply of A) only glucose B) only glucose and ADP C) glucose, ADP, phosphate (Pi), and NAD+ D) only glucose, ADP, and NAD+ E) only glucose and NAD+ 5. When O2 is absent, mitochondrial electron transport stops and NADH can no longer drop off electrons. Predict what happens in the absence of O2: A) Glycolysis continues to produce ATP irrespective of what happens to NADH. B) Glycolysis stops unless NADH is used for something else. 6. During intense exercise, as muscles go into anaerobiosis (O2-deprived energy creation), the body will increase its consumption of A) fats. B) proteins. C) carbohydrates. D) all of the above 7. Which of the following statements is NOT true for NAD+? A) In the absence of NAD+, glycolysis can still function. B) NAD+ is converted to NADH during both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. C) NADH has more energy than NAD+. D) NADH can transfer electrons into the mitochondrial electron transport chain. 8. Cellular respiration harvests the most chemical energy from which of the following? A) glycolysis B) fermentation C) generating carbon dioxide and oxygen in the mitochondrial electron transport chain D) the mitochondrial part of cellular respiration (citric acid cycle, electron transport, and ATP synthase) 9. Which does not take place in the cytosol? A) alcohol fermentation B) glycolysis C) citric acid cycle E) lactic acid fermentation 10. All three classes of polymers (proteins, fats, and carbohydrates) can provide the energy for mitochondrial ATP synthesis because they all contain A) Glucose B) Carbon-hydrogen bonds C) Carbon-oxygen bonds D) Phosphate E) Glycerol