* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Cells - New Brigden School
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
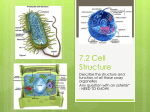
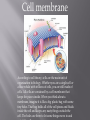
By Kelten Pratt Cell wall The cell wall is a tough rubbery wall that protects the inner organs but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and structural support and protection, in addition to acting as a filtering mechanism Golgi complex Part of the cellular endomembrane system, the Golgi apparatus packages proteins inside the cell before they are sent to their destination; it is particularly important in the processing of proteins for secretion. Ribosome s Ribosomes are cell organelles that consist of RNA and proteins. They are responsible for assembling the proteins of the cell. Depending on the protein production level of a particular cell, ribosomes may number in the Nucleus The nucleus is the cell brain it contains the cell uniqueness and tells the cell what to do. Mitochondria Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell. They are organelles that act like a digestive system which takes in nutrients, breaks them down, and creates energy rich molecules for the cell. The biochemical processes of the cell are known as cellular respiration. Many of the reactions involved in cellular respiration happen in the mitochondria. Mitochondria are the working organelles that keep the cell full of energy. cytoplasm Cytoplasm is the fluid that fills a cell. Scientists used to call the fluid protoplasm. Early on, they didn't know about the many different types of fluids in the cell. There is special fluid in the mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and nucleus. The only two 'plasms' left are cytoplasm (the fluid in the cell also called cytosol) and nucleoplasm (the fluid in the nucleus). Each of those fluids has a very different composition vacuole A vacuole is a membranebound organelle which is present in all plant and fungal cells and some protest, animal and bacterial cells. chloroplast Chloroplasts are the food producers of the cell. The organelles are only found in plant cells and some protests such as algae. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts. Chloroplasts work to convert light energy of the Sun into sugars that can be used by cells. The entire process is called photosynthesis and it all depends on the little green chlorophyll molecules in each chloroplast. Plants are the basis of all life on Earth. They are classified as the producers of the world. In the process of photosynthesis, plants create sugars and release oxygen (O2). The oxygen released by the chloroplasts is the same oxygen you breathe every day. Mitochondria work in the opposite direction. They use oxygen in the process of releasing chemical energy from sugars. Cell membrane According to cell theory, cells are the main unit of organization in biology. Whether you are a single cell or a blue whale with trillions of cells, you are still made of cells. All cells are contained by a cell membrane that keeps the pieces inside. When you think about a membrane, imagine it is like a big plastic bag with some tiny holes. That bag holds all of the cell pieces and fluids inside the cell and keeps any nasty things outside the cell. The holes are there to let some things move in and

















![Student_Work_files/how cells keep us alive[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008096061_1-3bccda7a250f4b6d053f03d6cd844694-150x150.png)