* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Elimination reactions under acidic conditions
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition wikipedia , lookup
Vinylcyclopropane rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Diels–Alder reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
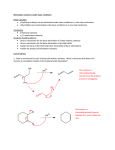
Elimination reactions under acidic conditions Major concepts Alcohols may be dehydrated under acid catalyzed conditions to give alkenes. This is an example of an elimination reaction. The mechanism of the dehydration of an alcohol to form an alkene is exactly the opposite of the addition of water to an alkene to form an alcohol (microscopic reversibility) Sulfuric acid pulls water away from the reaction and makes the elimination thermodynamically favorable. The more stable alkene is formed preferentially, which is generally the more substituted alkene (Zaitsev product)or the conjugated alkene. Vocabulary Elimination reactions Dehydration Microscopic reversibility Zaitsev product Students should be able to: Draw a mechanism and energy diagram for elimination of an alcohol under acidic conditions Explain how additions of water to an alkene and elimination of an alcohol are opposite mechanisms Describe how to shift equilibrium in favor of elimination or addition Predict the major product according to alkene stability Daily Problems 1. Provide a mechanism for these elimination reactions of alcohols under acidic conditions. 2. Draw an energy diagram for this elimination. Explain the role of sulfuric acid in making it downhill overall. E rxn coord 3. In which direction is this reaction favored? Explain your reasoning. The reaction is favored towards the left. Since there is water added to the reaction, the more favorable product is produced more, which is the left most product due to the maximum amount of sigma bonds. 4. In each of these reactions, there is more than one alkene that could form. Draw out all possible products, and then circle the one you would predict to be the major product. (Don’t worry about cis/trans isomers.) 5. In this reaction, the less substituted alkene is the major product. Explain. The less substituted alkene is the major product because the double bond formed is in conjugation with the existing double bond from the starting materials. Conjugation is very stabilizing! Cumulative problems You have learned three types of reactions: acid/base, addition, and elimination. Can you think about them all at the same time? 6. Predict the products of these reactions. (Hint: What type of reaction is it?) elimination elimination 7. Provide the reagents. (Hint: What type of reaction is it?) H-I addition H2SO4 elimination H2O/ H+ addition Extension problem 8. Eliminations can also happen under basic conditions, but only if there is a carbonyl appropriately placed. Here is an example reaction and a mechanism. Here is an example that doesn’t work, with a mechanism. The difference is the first step of each reaction. Explain why the first step works in the top reaction but not the bottom reaction. (Hint: Think about the stability of the intermediate.) The first acid/base reaction works because the anion made is stabilized by resonance and the final product of the reaction is conjugated. The second does not work because OH is a bad leaving group and the breaking of two sigma bonds and making of one pi and one sigma bond is unfavorable.