Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones
... © 2013 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part. ...
... © 2013 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part. ...
Alkenes 4 - ChemWeb (UCC)
... mercurinium or bromonium cation bond-breaking of the C-Hg or C-Br bond is more advanced than bond-formation with the incoming nucleophile. Hence the SN2 transition state for this reaction has partial carbocationic (i.e. SN1) character and therefore nucleophilic attack is at the most substituted carb ...
... mercurinium or bromonium cation bond-breaking of the C-Hg or C-Br bond is more advanced than bond-formation with the incoming nucleophile. Hence the SN2 transition state for this reaction has partial carbocationic (i.e. SN1) character and therefore nucleophilic attack is at the most substituted carb ...
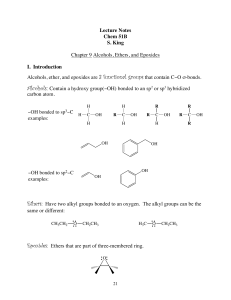
Don`t forget to study the generic functional groups and the common
... Only a rhodium catalyst allows hydrogenation of H2/Rh an aromatic ring at standard pressure and temperature. Carboxylic acids are not reduced by hydrogen. ...
... Only a rhodium catalyst allows hydrogenation of H2/Rh an aromatic ring at standard pressure and temperature. Carboxylic acids are not reduced by hydrogen. ...
Chapter 6 Addition Reactions to Alkenes
... and therefore more electron rich carbon. In the present case, the addition of the electrophile (the boron) and the nucleophile (the hydride) are concerted, so that there is no real carbocation but there is some build-up of positive charge in the transition state. There is a four-center transition st ...
... and therefore more electron rich carbon. In the present case, the addition of the electrophile (the boron) and the nucleophile (the hydride) are concerted, so that there is no real carbocation but there is some build-up of positive charge in the transition state. There is a four-center transition st ...
Organic Chemistry
... Because tertiary and secondary carbocations are more stable than primary carbocations, Markovnikov addition is observed in the electrophilic addition of HX to alkenes, so the product formed is the one with the halogen substituent upon the more highly substituted carbon. Also, rearrangement (hydride ...
... Because tertiary and secondary carbocations are more stable than primary carbocations, Markovnikov addition is observed in the electrophilic addition of HX to alkenes, so the product formed is the one with the halogen substituent upon the more highly substituted carbon. Also, rearrangement (hydride ...
Reactions of Alkenes
... transition state for attack of water on bromonium ion has carbocation character; more stable transition state (left) has positive charge on more highly substituted carbon ...
... transition state for attack of water on bromonium ion has carbocation character; more stable transition state (left) has positive charge on more highly substituted carbon ...
The Carbonyl Group - Angelo State University
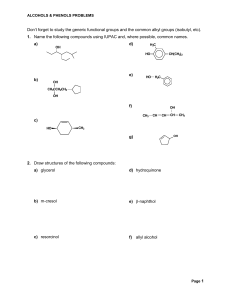
... • Draw structural formulas for the following molecules: – 4-chloro-2-phenylpentanal ...
... • Draw structural formulas for the following molecules: – 4-chloro-2-phenylpentanal ...
Alkenes and Alkynes I
... Use a high concentration of a strong and nonpolarizable base, such as an alkoxide. (Because a weak and polarizable base would not drive the reaction toward a bimolecular reaction, thereby allowing unimolecular processes (such as SN1 or E1 reactions) to compete. Ch. 7 - 25 ...
... Use a high concentration of a strong and nonpolarizable base, such as an alkoxide. (Because a weak and polarizable base would not drive the reaction toward a bimolecular reaction, thereby allowing unimolecular processes (such as SN1 or E1 reactions) to compete. Ch. 7 - 25 ...
Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 2202--2220 - RSC Publishing
... Nyhlén and Privalov a few years ago.30 Just recently, this gap was closed by the groups of Stephan31 and Ashley.32 Stephan and co-workers had already found that 1,1-diphenylethylene is reduced to the corresponding alkane when treated with dihydrogen in the presence of catalytic amounts of B(C6F5)3 ...
... Nyhlén and Privalov a few years ago.30 Just recently, this gap was closed by the groups of Stephan31 and Ashley.32 Stephan and co-workers had already found that 1,1-diphenylethylene is reduced to the corresponding alkane when treated with dihydrogen in the presence of catalytic amounts of B(C6F5)3 ...
Project Overview
... Use a high concentration of a strong and nonpolarizable base, such as an alkoxide. (Because a weak and polarizable base would not drive the reaction toward a bimolecular reaction, thereby allowing unimolecular processes (such as SN1 or E1 reactions) to compete. Ch. 7 - 26 ...
... Use a high concentration of a strong and nonpolarizable base, such as an alkoxide. (Because a weak and polarizable base would not drive the reaction toward a bimolecular reaction, thereby allowing unimolecular processes (such as SN1 or E1 reactions) to compete. Ch. 7 - 26 ...
Chiral Enolate Equivalents
... Despite this impressive track record, the weak reactivity of enolates in general confines the range of usable electrophiles to aldehydes, some primary or activated alkyl halides, unsaturated carbonyls, electrophilic halogens, oxaziridines, aza compounds, and a handful of other reactive electrophile ...
... Despite this impressive track record, the weak reactivity of enolates in general confines the range of usable electrophiles to aldehydes, some primary or activated alkyl halides, unsaturated carbonyls, electrophilic halogens, oxaziridines, aza compounds, and a handful of other reactive electrophile ...
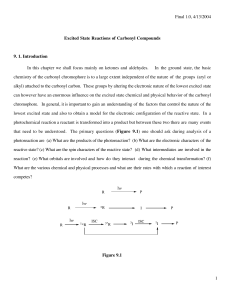
Excited State Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds
... state still the carbon (of C=O) is more electron rich than the oxygen. As indicated by the IR frequency of the C=O stretching, the double bond character in the T1 (pp*) state is reduced but not to the same degree as in T1 (np*) state. The C=O stretching frequencies for 4-methoxy acetophenone in S0 a ...
... state still the carbon (of C=O) is more electron rich than the oxygen. As indicated by the IR frequency of the C=O stretching, the double bond character in the T1 (pp*) state is reduced but not to the same degree as in T1 (np*) state. The C=O stretching frequencies for 4-methoxy acetophenone in S0 a ...
Iodomethylzinc_iodid.. - Groupe Charette
... oxygen functions proximal to the alkene. First discovered in 1959,20 this reaction has been often utilized in synthetic efforts21 and the reaction itself has been the subject of several investigations.22 For example, cyclopropanation of 2-cyclohexen-1-ol provides the syn-cyclopropane almost exclusiv ...
... oxygen functions proximal to the alkene. First discovered in 1959,20 this reaction has been often utilized in synthetic efforts21 and the reaction itself has been the subject of several investigations.22 For example, cyclopropanation of 2-cyclohexen-1-ol provides the syn-cyclopropane almost exclusiv ...
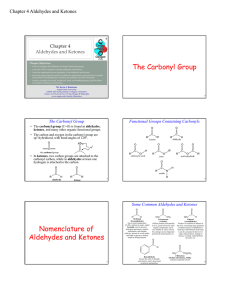
The Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones
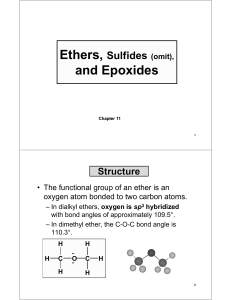
... aldehydes and ketones do not form hydrogen bonds with themselves. • Aldehydes and ketones therefore have boiling points that are in between those of alcohols and hydrocarbons of the same molecular weight: – Alcohols form hydrogen bonds, and have high ...
... aldehydes and ketones do not form hydrogen bonds with themselves. • Aldehydes and ketones therefore have boiling points that are in between those of alcohols and hydrocarbons of the same molecular weight: – Alcohols form hydrogen bonds, and have high ...
- University at Albany
... Silver (I) and copper (I) salts react with terminal alkynes to form silver and copper acetylides. Silver and copper acetylides are much less basic and less nucleophilic than their sodium counterpart. Thus, they don’t have much synthetic utility. Silver and copper acetylides are not very soluble, ...
... Silver (I) and copper (I) salts react with terminal alkynes to form silver and copper acetylides. Silver and copper acetylides are much less basic and less nucleophilic than their sodium counterpart. Thus, they don’t have much synthetic utility. Silver and copper acetylides are not very soluble, ...











![[Ru(Triphos)H2(CO)] Characterisation - Durham e](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017676948_1-4352644236c53cc416f065328f560d26-300x300.png)