Transition Metal Reagents and Catalysts
... This process is called the Fischer±Tropsch process and attracted attention as an important method of commercial production of synthetic oil. In 1938 RoÈlen, one of Fischer's co-workers, tried the reaction of alkene with synthesis gas using a Co catalyst and found the formation of aldehydes. This rea ...
... This process is called the Fischer±Tropsch process and attracted attention as an important method of commercial production of synthetic oil. In 1938 RoÈlen, one of Fischer's co-workers, tried the reaction of alkene with synthesis gas using a Co catalyst and found the formation of aldehydes. This rea ...
Diastereoselective Allylation of Carbonyl Compounds and Imines:
... decomposition of compound 2 could occur. The allylation of chiral α-alkoxyaldehydes under these reaction conditions provided excellent yields with high stereoselectivity, a single diastereomer being observed in many cases by NMR analyses of the crude reaction product (Table 2, entries 1−3 and 5). Re ...
... decomposition of compound 2 could occur. The allylation of chiral α-alkoxyaldehydes under these reaction conditions provided excellent yields with high stereoselectivity, a single diastereomer being observed in many cases by NMR analyses of the crude reaction product (Table 2, entries 1−3 and 5). Re ...
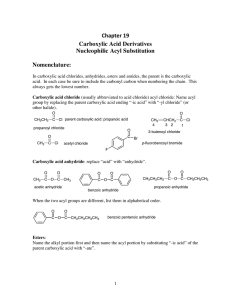
Chapter 19 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Nucleophilic Acyl
... Since a nucleophile can attack either carbonyl, symmetrical anhydrides are usually used so as to give one product. (1) Preparation of Esters (a) We can use neutral alcohols. With the neutral alcohols we usually use acid catalysis to activate the carbonyl carbon of the anhydride to nucleophilic attac ...
... Since a nucleophile can attack either carbonyl, symmetrical anhydrides are usually used so as to give one product. (1) Preparation of Esters (a) We can use neutral alcohols. With the neutral alcohols we usually use acid catalysis to activate the carbonyl carbon of the anhydride to nucleophilic attac ...
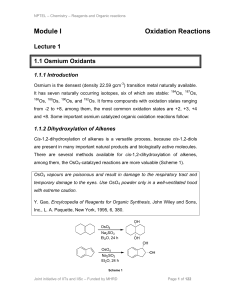
Module I Oxidation Reactions
... intermediate a that could readily co-ordinate with chiral ligand ‘L’ to afford chiral imido-osmium intermediate b (Scheme 18). The latter may react with alkene to yield c via (2+2)-cycloaddition that may rearrange to give d that could undergo hydrolysis with water to give the target hydroxylamine de ...
... intermediate a that could readily co-ordinate with chiral ligand ‘L’ to afford chiral imido-osmium intermediate b (Scheme 18). The latter may react with alkene to yield c via (2+2)-cycloaddition that may rearrange to give d that could undergo hydrolysis with water to give the target hydroxylamine de ...
Ethers, Epoxides and Sulfides
... ¾ Ether cannot form hydrogen bond with another ether molecule. ¾ Its lone pair electron can form a hydrogen bond with hydrogen bond donor with O-H or N-H. ...
... ¾ Ether cannot form hydrogen bond with another ether molecule. ¾ Its lone pair electron can form a hydrogen bond with hydrogen bond donor with O-H or N-H. ...
R - Evans - Harvard University
... of excess base was then probed by employing 1.7 equiv of diisopropylethylamine in the enolization reaction; no change in the diastereoselectivity was observed (entry D). I n contrast, when excess dibutylboryl triflate (1.7 equiv) was employed, the diastereoselectivitydecreased to 86:14 (entry E). Ev ...
... of excess base was then probed by employing 1.7 equiv of diisopropylethylamine in the enolization reaction; no change in the diastereoselectivity was observed (entry D). I n contrast, when excess dibutylboryl triflate (1.7 equiv) was employed, the diastereoselectivitydecreased to 86:14 (entry E). Ev ...
Aldehydes and Ketones The Carbonyl Group
... The Polarity of the Carbonyl Group • Since there is no hydrogen on the carbonyl oxygen, aldehydes and ketones do not form hydrogen bonds with themselves. • Aldehydes and ketones therefore have boiling points that are in between those of alcohols and hydrocarbons of the same molecular weight: – Alcoh ...
... The Polarity of the Carbonyl Group • Since there is no hydrogen on the carbonyl oxygen, aldehydes and ketones do not form hydrogen bonds with themselves. • Aldehydes and ketones therefore have boiling points that are in between those of alcohols and hydrocarbons of the same molecular weight: – Alcoh ...
Retrosynthetic Analysis of Nabumetone
... Grignard reactions that produce secondary alcohols, will require oxidation to the corresponding ketone to arrive at the desired product. Starting with the bond between the ring and the side chain, we are given two pairs of synthons as shown in Scheme 2. The synthetic equivalent to the aromatic anion ...
... Grignard reactions that produce secondary alcohols, will require oxidation to the corresponding ketone to arrive at the desired product. Starting with the bond between the ring and the side chain, we are given two pairs of synthons as shown in Scheme 2. The synthetic equivalent to the aromatic anion ...
Title Several Reactions of Isocyanide and Related Compounds
... transition metals of groups VI, VII and VIII generally form more than one type of both isocyanide and carbonyl comp lexes. ...
... transition metals of groups VI, VII and VIII generally form more than one type of both isocyanide and carbonyl comp lexes. ...
Ethers - Home - KSU Faculty Member websites
... reaction takes place in aqueous acid, the epoxide opens to a glycol. Because of its desirable solubility properties, meta-chloroperoxybenzoic acid (MCPBA) is often used for these epoxidations. O ...
... reaction takes place in aqueous acid, the epoxide opens to a glycol. Because of its desirable solubility properties, meta-chloroperoxybenzoic acid (MCPBA) is often used for these epoxidations. O ...
Glycosyl amines
... Equilibrium mixture of methyl D-xylosides originating from the Fischer glycosidation of D-xylose in methanolic solution of hydrogen chloride at 35º C. Methyl D-xylopyranoside is the major product, due to the anomeric effect, which is characteristic for the tetrahydropyran rings with an electronegati ...
... Equilibrium mixture of methyl D-xylosides originating from the Fischer glycosidation of D-xylose in methanolic solution of hydrogen chloride at 35º C. Methyl D-xylopyranoside is the major product, due to the anomeric effect, which is characteristic for the tetrahydropyran rings with an electronegati ...
19.7 Reversible Addition Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones
... 19.1 Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones 19.2 Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones 19.3 Spectroscopy of Aldehydes and Ketones 19.4 Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones 19.5 Introduction to Aldehyde and Ketone Reactions 19.6 Basicity of Aldehydes and Ketones 19.7 Reversible Addition Reactions ...
... 19.1 Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones 19.2 Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones 19.3 Spectroscopy of Aldehydes and Ketones 19.4 Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones 19.5 Introduction to Aldehyde and Ketone Reactions 19.6 Basicity of Aldehydes and Ketones 19.7 Reversible Addition Reactions ...
Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
... Esters, N,N-disubstituted amides, and nitriles are often used as solvents because they are polar, but do not have reactive hydroxyl or amino groups. We have seen that dimethylformamide (DMF) is a common aprotic polar solvent (Section 10.3). ...
... Esters, N,N-disubstituted amides, and nitriles are often used as solvents because they are polar, but do not have reactive hydroxyl or amino groups. We have seen that dimethylformamide (DMF) is a common aprotic polar solvent (Section 10.3). ...
The Grob Fragmentation
... RHS shows a Grignard mediated reaction then it undergoes a Grob fragmentation ...
... RHS shows a Grignard mediated reaction then it undergoes a Grob fragmentation ...
Organometallic Methods for Forming and Cleaving Carbon
... First and foremost, I would like to show my gratitude to Prof. Robert Madsen for accepting me in his group and for his valuable guidance and expertise during my time as a Ph.D. student. I deeply appreciate Dr. Phil. Torkil Holm for sharing his experience and for fruitful discussions. I would very mu ...
... First and foremost, I would like to show my gratitude to Prof. Robert Madsen for accepting me in his group and for his valuable guidance and expertise during my time as a Ph.D. student. I deeply appreciate Dr. Phil. Torkil Holm for sharing his experience and for fruitful discussions. I would very mu ...
Chapter - FIU Faculty Websites
... • Like gem-diol formation, the synthesis of acetals is reversible, and often, the equilibrium favors the reactants. • In acetal synthesis, since water is formed as a by-product, the equilibrium can be driven to the right by removing H2O as it is formed using distillation or other techniques. Please ...
... • Like gem-diol formation, the synthesis of acetals is reversible, and often, the equilibrium favors the reactants. • In acetal synthesis, since water is formed as a by-product, the equilibrium can be driven to the right by removing H2O as it is formed using distillation or other techniques. Please ...
Organic Chemistry
... anions are both strong bases and good nucleophiles They participate in nucleophilic substitution reactions with alkyl halides to form new C-C bonds to alkyl groups; they undergo alkylation • because alkyne anions are also strong bases, alkylation is practical only with methyl and 1° halides • with ...
... anions are both strong bases and good nucleophiles They participate in nucleophilic substitution reactions with alkyl halides to form new C-C bonds to alkyl groups; they undergo alkylation • because alkyne anions are also strong bases, alkylation is practical only with methyl and 1° halides • with ...
Alkyl Halides SN and E reactions
... elimination. In 3° substrates, only SN1 is possible. In Me° and 1° substrates, SN2 is faster. For 2° substrates, the mechanism of substitution depends upon the solvent. 2. Strong bases, like OH- and OR-, are also good nucleophiles. Substitution and elimination compete. In 3° and 2° alkyl halides, E2 ...
... elimination. In 3° substrates, only SN1 is possible. In Me° and 1° substrates, SN2 is faster. For 2° substrates, the mechanism of substitution depends upon the solvent. 2. Strong bases, like OH- and OR-, are also good nucleophiles. Substitution and elimination compete. In 3° and 2° alkyl halides, E2 ...
Reactions of Alkyl Halides (SN1, SN2, E1, and E2 reactions)
... elimination. In 3° substrates, only SN1 is possible. In Me° and 1° substrates, SN2 is faster. For 2° substrates, the mechanism of substitution depends upon the solvent. 2. Strong bases, like OH- and OR-, are also good nucleophiles. Substitution and elimination compete. In 3° and 2° alkyl halides, E2 ...
... elimination. In 3° substrates, only SN1 is possible. In Me° and 1° substrates, SN2 is faster. For 2° substrates, the mechanism of substitution depends upon the solvent. 2. Strong bases, like OH- and OR-, are also good nucleophiles. Substitution and elimination compete. In 3° and 2° alkyl halides, E2 ...