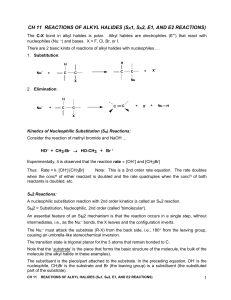
Reactions of Alkyl Halides (SN1, SN2, E1, and E2 reactions)
... elimination. In 3° substrates, only SN1 is possible. In Me° and 1° substrates, SN2 is faster. For 2° substrates, the mechanism of substitution depends upon the solvent. 2. Strong bases, like OH- and OR-, are also good nucleophiles. Substitution and elimination compete. In 3° and 2° alkyl halides, E2 ...
... elimination. In 3° substrates, only SN1 is possible. In Me° and 1° substrates, SN2 is faster. For 2° substrates, the mechanism of substitution depends upon the solvent. 2. Strong bases, like OH- and OR-, are also good nucleophiles. Substitution and elimination compete. In 3° and 2° alkyl halides, E2 ...
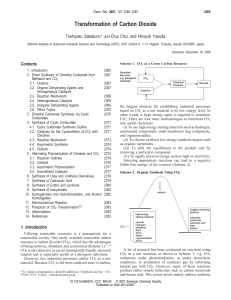
Transformation of Carbon Dioxide
... [We have formally included orthoesters in the dehydrated derivatives of alcohols, but it is difficult to synthesize orthoesters by the dehydrative condensation of alcohols and esters.] The reactivity of the substrates increases in the order of route a to d in Scheme 9. For example, epoxides or cycli ...
... [We have formally included orthoesters in the dehydrated derivatives of alcohols, but it is difficult to synthesize orthoesters by the dehydrative condensation of alcohols and esters.] The reactivity of the substrates increases in the order of route a to d in Scheme 9. For example, epoxides or cycli ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... Formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, and acetone are important commercial chemicals, synthesized by special methods. In the laboratory, aldehydes and ketones are most commonly prepared by oxidizing alcohols, but they can also be prepared by hydrating alkynes and by Friedel–Crafts acylation of arenes. Aldehyd ...
... Formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, and acetone are important commercial chemicals, synthesized by special methods. In the laboratory, aldehydes and ketones are most commonly prepared by oxidizing alcohols, but they can also be prepared by hydrating alkynes and by Friedel–Crafts acylation of arenes. Aldehyd ...
CHEM 203 Material
... Example: the C atom in CH4 has formally acquired 4 electrons, thereby assuming the oxidation state of –4. This produces a significant concentration of electronic density around the C atom. One may predict that the C atom in methane will behave as an electron donor in its reactions; that is, it will ...
... Example: the C atom in CH4 has formally acquired 4 electrons, thereby assuming the oxidation state of –4. This produces a significant concentration of electronic density around the C atom. One may predict that the C atom in methane will behave as an electron donor in its reactions; that is, it will ...
Zn(BH4)2/Al2O3: A new synthetic method for the efficient
... method is fast for the reduction of aldehydes, in the case of ketones, the need for large amounts of NaBH4 (eightfold) and the moderate yields of the products are major limitations.5c–d On the other hand, zinc tetrahydroborate, Zn(BH4)2, as a non-conventional hydride transfer agent, has been reporte ...
... method is fast for the reduction of aldehydes, in the case of ketones, the need for large amounts of NaBH4 (eightfold) and the moderate yields of the products are major limitations.5c–d On the other hand, zinc tetrahydroborate, Zn(BH4)2, as a non-conventional hydride transfer agent, has been reporte ...
Chem E2b - Organic Chemistry II What is Organic Chemistry?
... As with acidity, inductive effects are generally WEAKER than resonance effects Z = NR2, OR: Strongly Activating (resonance) Z = NHCO2R, OCO2R: Moderately Activating (inductive) Z = R (Alkyl, vinyl): Weakly Activating (inductive) Y = F, Cl, Br, I: Weakly Deactivating (inductive withdrawal/resonance d ...
... As with acidity, inductive effects are generally WEAKER than resonance effects Z = NR2, OR: Strongly Activating (resonance) Z = NHCO2R, OCO2R: Moderately Activating (inductive) Z = R (Alkyl, vinyl): Weakly Activating (inductive) Y = F, Cl, Br, I: Weakly Deactivating (inductive withdrawal/resonance d ...
Boron and Metal Catalyzed CC and CH Bond Formation
... Research efforts focused on the use of boron and metals to form new carboncarbon and carbon-hydrogen bonds are summarized in this dissertation. Several novel reactions have been developed. These include: the deoxygenation of benzylic alcohols using chloroboranes, alkenylation of benzylic alcohols us ...
... Research efforts focused on the use of boron and metals to form new carboncarbon and carbon-hydrogen bonds are summarized in this dissertation. Several novel reactions have been developed. These include: the deoxygenation of benzylic alcohols using chloroboranes, alkenylation of benzylic alcohols us ...
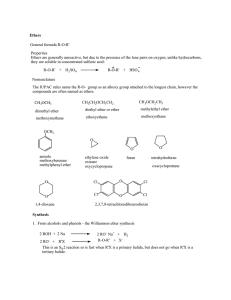
Ethers General formula R-O-R` Properties Ethers are generally
... The IUPAC rules name the R-O- group as an alkoxy group attached to the longest chain, however the compounds are often named as ethers. CH3OCH3 ...
... The IUPAC rules name the R-O- group as an alkoxy group attached to the longest chain, however the compounds are often named as ethers. CH3OCH3 ...
Document
... • A reaction is stereoselective when it forms predominantly or exclusively one stereoisomer when two or more are possible. • The E2 reaction is stereoselective because one stereoisomer is formed preferentially. Why? ...
... • A reaction is stereoselective when it forms predominantly or exclusively one stereoisomer when two or more are possible. • The E2 reaction is stereoselective because one stereoisomer is formed preferentially. Why? ...
Document
... • A reaction is stereoselective when it forms predominantly or exclusively one stereoisomer when two or more are possible. • The E2 reaction is stereoselective because one stereoisomer is formed preferentially. Why? ...
... • A reaction is stereoselective when it forms predominantly or exclusively one stereoisomer when two or more are possible. • The E2 reaction is stereoselective because one stereoisomer is formed preferentially. Why? ...
aa-2005-38-71-negishi - University of Windsor
... such as Li and Mg, which are normally considered to be “highly nucleophilic”, would be desirable from a reactivity point of view. Conversely, organometals containing highly electronegative metalloids, such as B and Si, might be expected to be of limited reactivity. Under conditions that are stoichio ...
... such as Li and Mg, which are normally considered to be “highly nucleophilic”, would be desirable from a reactivity point of view. Conversely, organometals containing highly electronegative metalloids, such as B and Si, might be expected to be of limited reactivity. Under conditions that are stoichio ...
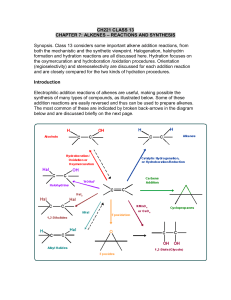
CH221 CLASS 13
... Synopsis. Class 13 considers some important alkene addition reactions, from both the mechanistic and the synthetic viewpoint. Halogenation, halohydrin formation and hydration reactions are all discussed here. Hydration focuses on the oxymercuration and hydroboration /oxidation procedures. Orientatio ...
... Synopsis. Class 13 considers some important alkene addition reactions, from both the mechanistic and the synthetic viewpoint. Halogenation, halohydrin formation and hydration reactions are all discussed here. Hydration focuses on the oxymercuration and hydroboration /oxidation procedures. Orientatio ...
PDF - Nanyang Technological University
... We used a chiral amine combined with CuBr2 as a cooperative catalytic system to develop the enantioselective reaction between 1 a and 2 a. The reaction catalyzed by (S)proline/CuBr2 in DMF gave the desired product in 63 % yield and in a 1:1 diastereomeric ratio (d.r.), with virtually no enantioselec ...
... We used a chiral amine combined with CuBr2 as a cooperative catalytic system to develop the enantioselective reaction between 1 a and 2 a. The reaction catalyzed by (S)proline/CuBr2 in DMF gave the desired product in 63 % yield and in a 1:1 diastereomeric ratio (d.r.), with virtually no enantioselec ...
Document
... • With base, the nucleophile is ¯OH, and the mechanism follows the usual two steps: nucleophilic attack followed by protonation. • The reaction rate increases in the presence of base because the base converts H2O into ¯OH, a stronger ...
... • With base, the nucleophile is ¯OH, and the mechanism follows the usual two steps: nucleophilic attack followed by protonation. • The reaction rate increases in the presence of base because the base converts H2O into ¯OH, a stronger ...
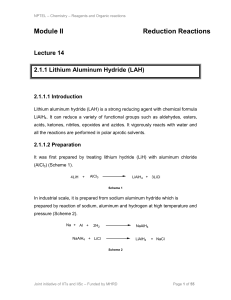
Module II Reduction Reactions
... The reduction of aromatic compounds to 1,4-cyclohexadiene compounds in presence of alkali metal liquid ammonia and an alcohol is called Birch reduction. A variety of aromatic compounds containing electron donating or electron withdrawing groups could be readily converted to the corresponding 1,4cycl ...
... The reduction of aromatic compounds to 1,4-cyclohexadiene compounds in presence of alkali metal liquid ammonia and an alcohol is called Birch reduction. A variety of aromatic compounds containing electron donating or electron withdrawing groups could be readily converted to the corresponding 1,4cycl ...
Palladium and Ruthenium Catalyzed Reactions By Bryan Jaksic
... provide a simple method for the formation of substituted alkynes, a commonly found functionality within important organic molecules. These reactions are generally believed to be catalyzed by a Pd(0)L2 species which are generated in situ from a palladium precatalyst and are often co-catalyzed by CuI ...
... provide a simple method for the formation of substituted alkynes, a commonly found functionality within important organic molecules. These reactions are generally believed to be catalyzed by a Pd(0)L2 species which are generated in situ from a palladium precatalyst and are often co-catalyzed by CuI ...
Enol esters: Versatile substrates in synthesis of fine and specialty
... an overview of enol and vinyl esters as substrates and intermediates, by exploring their application on small and large scale. The asymmetric hydroformylation/Wittig olefination tandem process of Z-enol acetates yields γhydroxy-α,β-unsaturated carbonyl motifs present in antifungal bioactive compound ...
... an overview of enol and vinyl esters as substrates and intermediates, by exploring their application on small and large scale. The asymmetric hydroformylation/Wittig olefination tandem process of Z-enol acetates yields γhydroxy-α,β-unsaturated carbonyl motifs present in antifungal bioactive compound ...
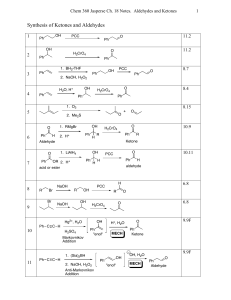
Synthesis of Ketones and Aldehydes
... Classification of Mechanisms Associated With Ketone/Aldehyde Reactions. • There may seem to be a dizzying number of mechanisms this chapter. But all of them simplify into some combination of acid- or base-catalyzed addition reaction, elimination reaction and/or substitution reaction. • To predict wh ...
... Classification of Mechanisms Associated With Ketone/Aldehyde Reactions. • There may seem to be a dizzying number of mechanisms this chapter. But all of them simplify into some combination of acid- or base-catalyzed addition reaction, elimination reaction and/or substitution reaction. • To predict wh ...
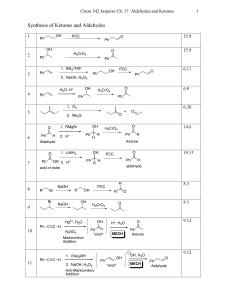
Synthesis of Ketones and Aldehydes
... Classification of Mechanisms Associated With Ketone/Aldehyde Reactions. • There may seem to be a dizzying number of mechanisms this chapter. But all of them simplify into some combination of acid- or base-catalyzed addition reaction, elimination reaction and/or substitution reaction. • To predict wh ...
... Classification of Mechanisms Associated With Ketone/Aldehyde Reactions. • There may seem to be a dizzying number of mechanisms this chapter. But all of them simplify into some combination of acid- or base-catalyzed addition reaction, elimination reaction and/or substitution reaction. • To predict wh ...