Metal-catalysed approaches to amide bond formation
... The amide bond is one of the most important functional groups in contemporary chemistry. It is essential to sustain life, making up the peptide bonds in proteins such as enzymes. It is found in numerous natural products and it is also one of the most prolific moieties in modern pharmaceutical molecul ...
... The amide bond is one of the most important functional groups in contemporary chemistry. It is essential to sustain life, making up the peptide bonds in proteins such as enzymes. It is found in numerous natural products and it is also one of the most prolific moieties in modern pharmaceutical molecul ...
13_lecture_ppt
... Preparation of aldehydes and ketones • Principal means of preparation is oxidation of the corresponding alcohol – Primary alcohol produces an aldehyde – Secondary alcohol produces a ketone – Tertiary alcohol does not oxidize ...
... Preparation of aldehydes and ketones • Principal means of preparation is oxidation of the corresponding alcohol – Primary alcohol produces an aldehyde – Secondary alcohol produces a ketone – Tertiary alcohol does not oxidize ...
Chapter 14 Notes
... • Using the root alkane name, drop the –e ending and change to –one. • Number the longest carbon chain so the C=O group has the lowest number. • Name and number other substituents as before. Examples: ...
... • Using the root alkane name, drop the –e ending and change to –one. • Number the longest carbon chain so the C=O group has the lowest number. • Name and number other substituents as before. Examples: ...
RheniumCatalyzed Deoxydehydration of Diols and Polyols
... previous results was explained by a Hammett study that revealed that two different mechanisms were in competition, thus indicating a highly flexible transition state structure. Interestingly, the suggestion of a highly asynchronous but concerted pathway was also the results of the intense investigat ...
... previous results was explained by a Hammett study that revealed that two different mechanisms were in competition, thus indicating a highly flexible transition state structure. Interestingly, the suggestion of a highly asynchronous but concerted pathway was also the results of the intense investigat ...
Molecular orbital approach to substituent effects in amine
... have been studied. Such substituted amino species have important applications in industrially relevant gas-separation processes. Qualitative molecular orbital arguments, along with detailed calculations at the MNDO level of theory, show that upon methyl substitution at the a-carbon atom the interact ...
... have been studied. Such substituted amino species have important applications in industrially relevant gas-separation processes. Qualitative molecular orbital arguments, along with detailed calculations at the MNDO level of theory, show that upon methyl substitution at the a-carbon atom the interact ...
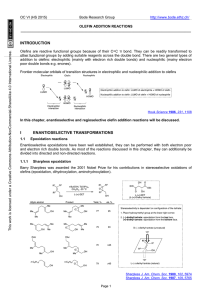
Lecture 1: Key Concepts in Stereoselective Synthesis
... INTRODUCTION Olefins are reactive functional groups because of their C=C π bond. They can be readily transformed to other functional groups by adding suitable reagents across the double bond. There are two general types of addition to olefins: electrophilic (mainly with electron rich double bonds) a ...
... INTRODUCTION Olefins are reactive functional groups because of their C=C π bond. They can be readily transformed to other functional groups by adding suitable reagents across the double bond. There are two general types of addition to olefins: electrophilic (mainly with electron rich double bonds) a ...
Nucleophilic Substitution on the Carbonyl Group
... transfer reaction works well with an acyl halide because the halide ion is a weak base. Thus, an acyl halide has a very good leaving group. Conversely, acyl transfer reactions do not occur with aldehydes and ketones because the leaving group, either a hydride or a carbanion, is generally too strong ...
... transfer reaction works well with an acyl halide because the halide ion is a weak base. Thus, an acyl halide has a very good leaving group. Conversely, acyl transfer reactions do not occur with aldehydes and ketones because the leaving group, either a hydride or a carbanion, is generally too strong ...
File - Rasapalli Research Group
... Protection of alcohols is required in order to mask them participating in unwanted reactions. ...
... Protection of alcohols is required in order to mask them participating in unwanted reactions. ...
23.3 Carbonyl Compounds
... Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones • Aldehydes and ketones can form weak hydrogen bonds between the carbonyl oxygen and the hydrogen atoms of water. – The lower members of the series—up to three carbons—are soluble in water in all proportions. – As the length of the hydrocarbon chain increases abov ...
... Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones • Aldehydes and ketones can form weak hydrogen bonds between the carbonyl oxygen and the hydrogen atoms of water. – The lower members of the series—up to three carbons—are soluble in water in all proportions. – As the length of the hydrocarbon chain increases abov ...
lecture 11 catalysis_hydrogenation of alkenes
... second step, a reaction that does not require a vacant site at the metal, but does require the resulting organic radical to be moderately stable—hence the fact that the Iguchi catalyst will reduce only activated alkenes, such as cinnamate ion, in which the radical is benzylic and therefore stabilize ...
... second step, a reaction that does not require a vacant site at the metal, but does require the resulting organic radical to be moderately stable—hence the fact that the Iguchi catalyst will reduce only activated alkenes, such as cinnamate ion, in which the radical is benzylic and therefore stabilize ...
Module 5 Reactions with Miscellaneous Reagents
... Alkenes react with NBS in dry CCl4 under reflux conditions to give allyl bromide. The reaction is initiated by light or peroxide. Although a number of reagents are available for bromination of allylic C-H bond of alkenes, NBS is most commonly used. The reaction is called Wohl-Zigler bromination. For ...
... Alkenes react with NBS in dry CCl4 under reflux conditions to give allyl bromide. The reaction is initiated by light or peroxide. Although a number of reagents are available for bromination of allylic C-H bond of alkenes, NBS is most commonly used. The reaction is called Wohl-Zigler bromination. For ...
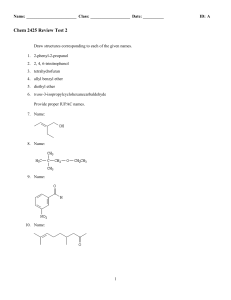
Aldehydes and Ketones - Belle Vernon Area School District
... IUPAC - # chain from the end closest to the carbonyl, give the carbon #, drop –e add –one Name the groups on either side of the carbonyl and follow with ketone list groups by order of sixe of molar mass (smaller 1st) ...
... IUPAC - # chain from the end closest to the carbonyl, give the carbon #, drop –e add –one Name the groups on either side of the carbonyl and follow with ketone list groups by order of sixe of molar mass (smaller 1st) ...
Carbonyl Compounds
... NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION • The carbonyl groups in aldehydes and ketones are polarised because of the difference in the electronegativity of carbon and oxygen. • The carbon atom carries a partial positive charge while oxygen atom carries a partial negative charge. • Aldehydes and ketones are susceptibl ...
... NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION • The carbonyl groups in aldehydes and ketones are polarised because of the difference in the electronegativity of carbon and oxygen. • The carbon atom carries a partial positive charge while oxygen atom carries a partial negative charge. • Aldehydes and ketones are susceptibl ...
Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones – Nucleophilic Addition
... The negative charge of the enolate anion is distributed on both oxygen and carbon, the ion can combine with a proton at either site. ...
... The negative charge of the enolate anion is distributed on both oxygen and carbon, the ion can combine with a proton at either site. ...
Aldehydes and ketones
... in the presence of an acid, the resulting product is called a hemiacetal. Hemiacetals can further react with alcohols to form acetals: aldehyde or ketone + alcohol ...
... in the presence of an acid, the resulting product is called a hemiacetal. Hemiacetals can further react with alcohols to form acetals: aldehyde or ketone + alcohol ...
98 pts
... • (T) All E1 reactions involve formation of carbocations; • (T) More stable carbocations are generated faster; • (T) Carbocations are electrophiles; • (T) Carbocations are electron deficient; • (T) Free radicals are electron deficient; • (T) Alcohols are Brønsted bases; • (F) The rate-determining st ...
... • (T) All E1 reactions involve formation of carbocations; • (T) More stable carbocations are generated faster; • (T) Carbocations are electrophiles; • (T) Carbocations are electron deficient; • (T) Free radicals are electron deficient; • (T) Alcohols are Brønsted bases; • (F) The rate-determining st ...
- kunleoloruntegbe.com
... It was been widely studied because it is one of the substance made when milk goes sour. The acid is formed by the action of a microorganisms, Bacillus acidi lactici, on sugar. In the early 1900’s large amount of the bacteria were isolated and used to prepare lactic on an industry scale.The acid was ...
... It was been widely studied because it is one of the substance made when milk goes sour. The acid is formed by the action of a microorganisms, Bacillus acidi lactici, on sugar. In the early 1900’s large amount of the bacteria were isolated and used to prepare lactic on an industry scale.The acid was ...
Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones
... C=O Proton is lost from N and adds to O to yield a neutral amino alcohol (carbinolamine) Protonation of OH converts into water as the leaving group Result is iminium ion, which loses proton Acid is required for loss of OH – too much acid blocks RNH2 ...
... C=O Proton is lost from N and adds to O to yield a neutral amino alcohol (carbinolamine) Protonation of OH converts into water as the leaving group Result is iminium ion, which loses proton Acid is required for loss of OH – too much acid blocks RNH2 ...
First palladium- and nickel-catalyzed oxidative
... on the mechanism are currently under investigation [16]. All data points to a sequence of aminometallation followed by a second alkyl-nitrogen bond formation. No radical intermediates are involved in the overall process as selective deuteration at the terminal position of the alkene leads to diaster ...
... on the mechanism are currently under investigation [16]. All data points to a sequence of aminometallation followed by a second alkyl-nitrogen bond formation. No radical intermediates are involved in the overall process as selective deuteration at the terminal position of the alkene leads to diaster ...
Microsoft Word
... Synopsis of the thesis entitled "Synthesis of biologically active compounds from b-hydroxysulfoxide" is divided into five chapters. Chapter-1: Regio- and stereoselective bromohydrin formation from ?-hydroxy sulfoxides This chapter deals with the formation of bromohydrins from acyclic ?hydroxy-?,?-un ...
... Synopsis of the thesis entitled "Synthesis of biologically active compounds from b-hydroxysulfoxide" is divided into five chapters. Chapter-1: Regio- and stereoselective bromohydrin formation from ?-hydroxy sulfoxides This chapter deals with the formation of bromohydrins from acyclic ?hydroxy-?,?-un ...
full size
... group (methanal, the simplest, has two). ¾The group is somewhat more polar than ethers, but like ethers it cannot donate a hydrogen bond to itself. Thus aldehydes are less volatile (higher boiling) than alkanes or ethers but are more volatile than alcohols or carboxylic acids. They are slightly less ...
... group (methanal, the simplest, has two). ¾The group is somewhat more polar than ethers, but like ethers it cannot donate a hydrogen bond to itself. Thus aldehydes are less volatile (higher boiling) than alkanes or ethers but are more volatile than alcohols or carboxylic acids. They are slightly less ...