Ethers and Epoxides - faculty at Chemeketa
... organic substituents and adding the word ether If other functional groups are present, the ether part is considered an alkoxy substituent R–O–R ~ tetrahedral bond angle (112° in dimethyl ether) Oxygen is sp3-hybridized Oxygen atom gives ethers a slight dipole moment ...
... organic substituents and adding the word ether If other functional groups are present, the ether part is considered an alkoxy substituent R–O–R ~ tetrahedral bond angle (112° in dimethyl ether) Oxygen is sp3-hybridized Oxygen atom gives ethers a slight dipole moment ...
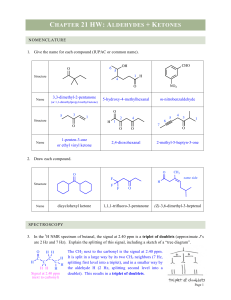
Chapter Sixteen Aldehydes and Ketones
... C atom form a planar triangle. ► The simplest aldehydes and ketones are known by common names. Aldehydes are named systematically by replacing the final -e in an alkane name with -al. ► Ketones are named systematically by replacing the final -e in an alkane name with -one and numbering starting with ...
... C atom form a planar triangle. ► The simplest aldehydes and ketones are known by common names. Aldehydes are named systematically by replacing the final -e in an alkane name with -al. ► Ketones are named systematically by replacing the final -e in an alkane name with -one and numbering starting with ...
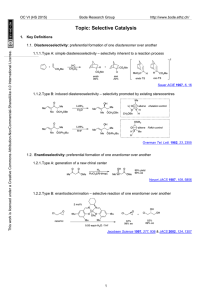
Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation by Reductive Coupling with
... Hydrocarbons: Although titanium (II) chlo ride in the form of complexes 1, 2 and 3 and ad mixed with a six to eight-fold excess of M e2AlCl is able to catalyze the polymerization of ethylene and other alpha-olefins [4], complex 1 in TH F or unsolvated TiCl2 suspended in toluene [6] caused neither ...
... Hydrocarbons: Although titanium (II) chlo ride in the form of complexes 1, 2 and 3 and ad mixed with a six to eight-fold excess of M e2AlCl is able to catalyze the polymerization of ethylene and other alpha-olefins [4], complex 1 in TH F or unsolvated TiCl2 suspended in toluene [6] caused neither ...
Learning Guide for Chapter 16
... Synthesize the following ethers by either the Williamsen ether synthesis or alkoxymercuration-reduction. Explain why the other won't work! ...
... Synthesize the following ethers by either the Williamsen ether synthesis or alkoxymercuration-reduction. Explain why the other won't work! ...
Synthesis of [RuCl2(NO)2(THF)] and its Double CN BondForming
... investigation, methods for controlling the reactivity of nitric oxide at transition-metal centers have received considerably less attention.[1–3] For example, the migratory insertion of NO into metal–alkyl or metal–aryl bonds has been observed in only a handful of metal complexes,[3] despite the ana ...
... investigation, methods for controlling the reactivity of nitric oxide at transition-metal centers have received considerably less attention.[1–3] For example, the migratory insertion of NO into metal–alkyl or metal–aryl bonds has been observed in only a handful of metal complexes,[3] despite the ana ...
Ethers and Epoxides
... organic substituents and adding the word ether If other functional groups are present, the ether part is considered an alkoxy substituent R–O–R ~ tetrahedral bond angle (112° in dimethyl ether) Oxygen is sp3-hybridized Oxygen atom gives ethers a slight dipole moment ...
... organic substituents and adding the word ether If other functional groups are present, the ether part is considered an alkoxy substituent R–O–R ~ tetrahedral bond angle (112° in dimethyl ether) Oxygen is sp3-hybridized Oxygen atom gives ethers a slight dipole moment ...
Chapter 18: Ethers and Epoxides
... organic substituents and adding the word ether If other functional groups are present, the ether part is considered an alkoxy substituent R–O–R ~ tetrahedral bond angle (112° in dimethyl ether) Oxygen is sp3-hybridized Oxygen atom gives ethers a slight dipole moment ...
... organic substituents and adding the word ether If other functional groups are present, the ether part is considered an alkoxy substituent R–O–R ~ tetrahedral bond angle (112° in dimethyl ether) Oxygen is sp3-hybridized Oxygen atom gives ethers a slight dipole moment ...
6. Low valent of Vanadium catalyst in organic synthesis
... *the coordination of the phosphorus raises the reduction capability and selectivity. *the bulky reductant is liable to approach the bromide from the less hindered side Toshikazu Hirao,J. Org. Chem., 1993, 58 (23), 6529-6530 ...
... *the coordination of the phosphorus raises the reduction capability and selectivity. *the bulky reductant is liable to approach the bromide from the less hindered side Toshikazu Hirao,J. Org. Chem., 1993, 58 (23), 6529-6530 ...
Chemistry 0310 - Organic Chemistry 1 Chapter 12. Reactions of
... - Syn-Hydroxylations of alkenes are most conveniently performed with catalytic OsO4 and NMO (N-methylmorpholine N-oxide) as co-oxidant. Attack occurs from the less-hindered face of the alkene, and a vicinal syn-diol is isolated after reductive workup. - Oxidative cleavage of 1,2-disubstituted alken ...
... - Syn-Hydroxylations of alkenes are most conveniently performed with catalytic OsO4 and NMO (N-methylmorpholine N-oxide) as co-oxidant. Attack occurs from the less-hindered face of the alkene, and a vicinal syn-diol is isolated after reductive workup. - Oxidative cleavage of 1,2-disubstituted alken ...
File
... 6. Cyclohexanone has a strong signal in its IR spectrum at 1718 cm-1, while 2-cyclohexenone has a strong signal at 1691 cm-1. Both signals represent vibration of the same kind of bond. Explain why the absorption in 2-cyclohexenone is at a lower wavenumber, including resonance structures. Both signa ...
... 6. Cyclohexanone has a strong signal in its IR spectrum at 1718 cm-1, while 2-cyclohexenone has a strong signal at 1691 cm-1. Both signals represent vibration of the same kind of bond. Explain why the absorption in 2-cyclohexenone is at a lower wavenumber, including resonance structures. Both signa ...
Aldehydes and ketones
... with other molecules like themselves. Consequently, boiling points for aldehydes and ketones are lower than for alcohols of similar molar mass. • The C-O double bond in these molecules is polar, so dipoledipole forces do exist. As a result, their boiling points tend to be higher than for alkanes of ...
... with other molecules like themselves. Consequently, boiling points for aldehydes and ketones are lower than for alcohols of similar molar mass. • The C-O double bond in these molecules is polar, so dipoledipole forces do exist. As a result, their boiling points tend to be higher than for alkanes of ...
Aldehydes can react with alcohols to form hemiacetals
... belonged to the carbonyl group will be lost. Usually, this is of no consequence, but it can be useful. For example, in 1968 some chemists studying the reactions that take place inside mass spectrometers needed to label the carbonyl oxygen atom of this ketone with the isotope 18O. By stirring the ‘no ...
... belonged to the carbonyl group will be lost. Usually, this is of no consequence, but it can be useful. For example, in 1968 some chemists studying the reactions that take place inside mass spectrometers needed to label the carbonyl oxygen atom of this ketone with the isotope 18O. By stirring the ‘no ...
Changing counterion can switch the preference for selective 1,2
... functional groups. For example, the hypothetical green carbonyl attack shown below would lead to a regioisomeric product, but this product is not formed due to the inversion of polarity this would require. ...
... functional groups. For example, the hypothetical green carbonyl attack shown below would lead to a regioisomeric product, but this product is not formed due to the inversion of polarity this would require. ...
無投影片標題 - SKHSBS
... are only loosely held by the carbon atoms and are exposed, the carboncarbon double bond is susceptible to electron-loving reagents (i.e. electrophiles) ...
... are only loosely held by the carbon atoms and are exposed, the carboncarbon double bond is susceptible to electron-loving reagents (i.e. electrophiles) ...
Compounds Containing a C=O (Carbonyl) Group
... Naming Aldehydes, Naming Ketones, Physical Properties, Interesting Aldehydes and Ketones, Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones, Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones (Addition of 1° Amines, Addition of 2° Amines, Addition of H2O—Hydration, Addition of Alcohols—Acetal Formation, Acetals as Protecting Gr ...
... Naming Aldehydes, Naming Ketones, Physical Properties, Interesting Aldehydes and Ketones, Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones, Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones (Addition of 1° Amines, Addition of 2° Amines, Addition of H2O—Hydration, Addition of Alcohols—Acetal Formation, Acetals as Protecting Gr ...
Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones
... C=O Proton is lost from N and adds to O to yield a neutral amino alcohol (carbinolamine) Protonation of OH converts into water as the leaving group Result is iminium ion, which loses proton Acid is required for loss of OH – too much acid blocks RNH2 ...
... C=O Proton is lost from N and adds to O to yield a neutral amino alcohol (carbinolamine) Protonation of OH converts into water as the leaving group Result is iminium ion, which loses proton Acid is required for loss of OH – too much acid blocks RNH2 ...
TOPIC 7. ELIMINATION REACTIONS (chapter 7 and parts of
... SYNTHETIC STRATEGIES: TWO (OR MORE) STEP SYNTHESES ...
... SYNTHETIC STRATEGIES: TWO (OR MORE) STEP SYNTHESES ...
physicochemical properties of organic medicinal agents
... Like alkenes, alkynyl groups can facilitate nucleophilic substitution reactions at adjacent or "allylic" carbon atoms as discussed in more detail in the Resonance and Induction Tutorial and in the Alkene Tutorial. In such cases the allylic alkynyl group enhances the displacement reaction by resonanc ...
... Like alkenes, alkynyl groups can facilitate nucleophilic substitution reactions at adjacent or "allylic" carbon atoms as discussed in more detail in the Resonance and Induction Tutorial and in the Alkene Tutorial. In such cases the allylic alkynyl group enhances the displacement reaction by resonanc ...







![Synthesis of [RuCl2(NO)2(THF)] and its Double CN BondForming](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001773792_1-763ad0089529123821e01ed17077bbf2-300x300.png)