Diphenylsilene - American Chemical Society
... enolizable hydrogens, and formal [2 + 21- or [4 + 21-cycloaddition products when it does not.2 These reactions are thought to involve the carbonyl n-orbital and proceed by a nonpericyclic mechanism, but it is not known whether the reaction is concerted or stepwise. The relative rates of reaction of ...
... enolizable hydrogens, and formal [2 + 21- or [4 + 21-cycloaddition products when it does not.2 These reactions are thought to involve the carbonyl n-orbital and proceed by a nonpericyclic mechanism, but it is not known whether the reaction is concerted or stepwise. The relative rates of reaction of ...
8. Alkynes: An Introduction to Organic Synthesis
... the movement of a proton and are called tautomers Enols rearrange to the isomeric ketone by the rapid transfer of a proton from the hydroxyl to the alkene carbon The keto form is usually so stable compared to the enol that only the keto form can be observed ...
... the movement of a proton and are called tautomers Enols rearrange to the isomeric ketone by the rapid transfer of a proton from the hydroxyl to the alkene carbon The keto form is usually so stable compared to the enol that only the keto form can be observed ...
Reductions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives - IDC
... reduction of alkynes to alkenes. This reduction stops at the aldehyde stage, providing us with a useful two-step procedure for converting carboxylic acids to aldehydes, as reaction #1 below demonstrates. Equivalent reductions of anhydrides have not been reported, but we might speculate that they wou ...
... reduction of alkynes to alkenes. This reduction stops at the aldehyde stage, providing us with a useful two-step procedure for converting carboxylic acids to aldehydes, as reaction #1 below demonstrates. Equivalent reductions of anhydrides have not been reported, but we might speculate that they wou ...
O R` R
... • The phosphorus ylides are easily prepared from triphenylphoshine (an excellent nucleophile and weak base) with 1º and 2 º alkyl halides via an SN2 mechanism. • A strong base (usually an alkyllithium or phenyllithium) is required to remove a proton from the intermediate ...
... • The phosphorus ylides are easily prepared from triphenylphoshine (an excellent nucleophile and weak base) with 1º and 2 º alkyl halides via an SN2 mechanism. • A strong base (usually an alkyllithium or phenyllithium) is required to remove a proton from the intermediate ...
ppt
... The sulfur atom of sulfides is much more nucleophilic than the oxygen atom of ethers, and will react with alkyl halides to give stable sulfonium salts. H3C ...
... The sulfur atom of sulfides is much more nucleophilic than the oxygen atom of ethers, and will react with alkyl halides to give stable sulfonium salts. H3C ...
16.2: Structure and Bonding in Ethers and Epoxides
... The sulfur atom of sulfides is much more nucleophilic than the oxygen atom of ethers, and will react with alkyl halides to give stable sulfonium salts. ...
... The sulfur atom of sulfides is much more nucleophilic than the oxygen atom of ethers, and will react with alkyl halides to give stable sulfonium salts. ...
Ketones and Aldehydes Reading: Wade chapter 18, sections 18
... Dipole-dipole interactions are the main intermolecular force holding ketones and aldehydes in the liquid phase. The dipole-dipole interaction is strong because of the high dipole moment attributable to the carbonyl group, giving ketones and aldehydes higher boiling points than hydrocarbons. However, ...
... Dipole-dipole interactions are the main intermolecular force holding ketones and aldehydes in the liquid phase. The dipole-dipole interaction is strong because of the high dipole moment attributable to the carbonyl group, giving ketones and aldehydes higher boiling points than hydrocarbons. However, ...
reactions.html Reaction 1. Electrophilic addition of
... http://courses.chem.psu.edu/chem38/reactions/reactions.html Reaction 1. Electrophilic addition of hydrogen halides (HX) to alkenes. ...
... http://courses.chem.psu.edu/chem38/reactions/reactions.html Reaction 1. Electrophilic addition of hydrogen halides (HX) to alkenes. ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... Naming Aldehydes IUPAC Replace the -e in the alkane name with –al Common Add aldehyde to the prefixes form (1C), acet (2C), propion(3), and butry(4C) O ...
... Naming Aldehydes IUPAC Replace the -e in the alkane name with –al Common Add aldehyde to the prefixes form (1C), acet (2C), propion(3), and butry(4C) O ...
Chapter 1 Chemical Bonding and Chemical Structure
... 2) If the alkyl chain has more than 6 carbons, then the benzene ring is the substituent and is called a “phenyl” group ...
... 2) If the alkyl chain has more than 6 carbons, then the benzene ring is the substituent and is called a “phenyl” group ...
More reactions of alkenes Objective
... 3) You get a positiviely charged carbocation intermediate. The Br- now zooms over…… ...
... 3) You get a positiviely charged carbocation intermediate. The Br- now zooms over…… ...
Summer Scholar Report
... A method for synthesis of allylic tosylates from allylic alcohols was developed that does not require metal catalysis or harsh conditions. The method was also utilized to produce secondary tosylates from their parent alcohols. Sodium hydride was used to generate the alkoxide, which can then be trea ...
... A method for synthesis of allylic tosylates from allylic alcohols was developed that does not require metal catalysis or harsh conditions. The method was also utilized to produce secondary tosylates from their parent alcohols. Sodium hydride was used to generate the alkoxide, which can then be trea ...
ETHER
... Has a pair of alkyl or atomic groups attached to a linking oxygen atom. Functional group is ROR Have primary, secondary, and tertiary structures ...
... Has a pair of alkyl or atomic groups attached to a linking oxygen atom. Functional group is ROR Have primary, secondary, and tertiary structures ...
Regiospecificity according to Markovnikov
... • If the alkyl groups at either end of the C-C triple bond are not the same, both products can form and this is not normally useful • If the triple bond is at the first carbon of the chain (then H is what is attached to one side) this is called a terminal alkyne • Hydration of a terminal always give ...
... • If the alkyl groups at either end of the C-C triple bond are not the same, both products can form and this is not normally useful • If the triple bond is at the first carbon of the chain (then H is what is attached to one side) this is called a terminal alkyne • Hydration of a terminal always give ...
Alcohols I Reading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10
... electron-withdrawing effect of the local halogens enhances the acidity of the parent alcohols; this effect is additive, with trichloroethanol being more acidic than chloroethanol and ethanol. Phenol (an aromatic ring with an alcohol attached) is a relatively acidic alcohol because the corresponding ...
... electron-withdrawing effect of the local halogens enhances the acidity of the parent alcohols; this effect is additive, with trichloroethanol being more acidic than chloroethanol and ethanol. Phenol (an aromatic ring with an alcohol attached) is a relatively acidic alcohol because the corresponding ...
Conjugate addition_Clayden
... Conjugate addition of alcohols can be catalysed by acid or base Alcohols undergo conjugate addition only very slowly in the absence of a catalyst: they are not such good nucleophiles as amines for the very reason we have just mentioned in connection with the reactivity of hydroxylamine—oxygen is mor ...
... Conjugate addition of alcohols can be catalysed by acid or base Alcohols undergo conjugate addition only very slowly in the absence of a catalyst: they are not such good nucleophiles as amines for the very reason we have just mentioned in connection with the reactivity of hydroxylamine—oxygen is mor ...
ALKANE ALKYL HALIDE Halogenation of Alkanes
... reagent is a peroxy acid and may be abbreviated PhCO3H not subject to rearrangements oxygen is added to the same side of the C=C (syn addition; "cis stays cis & trans stays trans") ...
... reagent is a peroxy acid and may be abbreviated PhCO3H not subject to rearrangements oxygen is added to the same side of the C=C (syn addition; "cis stays cis & trans stays trans") ...
Document
... The carbon atom is approximately sp² hybridized and forms o bonds to two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen. The molecule is planar and the Н-С-O and Н-С-Н bond angles are close to 1200, the idealized sp² angles. The remaining carbon p orbital overlaps with the oxygen р, orbital, giving rise to а -bond ...
... The carbon atom is approximately sp² hybridized and forms o bonds to two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen. The molecule is planar and the Н-С-O and Н-С-Н bond angles are close to 1200, the idealized sp² angles. The remaining carbon p orbital overlaps with the oxygen р, orbital, giving rise to а -bond ...
RULE
... Reaction of alkenes with HBr: Step 1 - Slow addition of electrophilic proton to nucleophilic alkene (shown via “attack” by Nu: electrons) forms a carbocation intermediate Step 2 - rapid reaction of positively charged carbocation intermediate (E+) with negatively charged bromide ion (Nu:) generates ...
... Reaction of alkenes with HBr: Step 1 - Slow addition of electrophilic proton to nucleophilic alkene (shown via “attack” by Nu: electrons) forms a carbocation intermediate Step 2 - rapid reaction of positively charged carbocation intermediate (E+) with negatively charged bromide ion (Nu:) generates ...
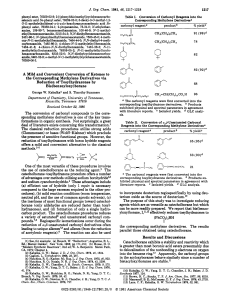
A Mild and Convenient Conversion of Ketones to the Corresponding
... to incorporate deuterium regiospecifically by using deuterium oxide as the source of deuterium.’O The purpose of this study was to investigate reducing agents which are as versatile as catecholborane but which can be more readily prepared. We report that bis(benzoyloxy)borane, I,l1J2effectively redu ...
... to incorporate deuterium regiospecifically by using deuterium oxide as the source of deuterium.’O The purpose of this study was to investigate reducing agents which are as versatile as catecholborane but which can be more readily prepared. We report that bis(benzoyloxy)borane, I,l1J2effectively redu ...
cycloadditions with singlet oxygen
... electron-rich olefin was farther from the directing hydroxyl group and a decreased selectivity was observed. When the methoxy group was placed in the ortho position, the selectivity was increased because singlet oxygen bonded to the electron-rich olefin first and was closer to the directing hydroxyl ...
... electron-rich olefin was farther from the directing hydroxyl group and a decreased selectivity was observed. When the methoxy group was placed in the ortho position, the selectivity was increased because singlet oxygen bonded to the electron-rich olefin first and was closer to the directing hydroxyl ...
Contents - Personal WWW Pages
... As can be seen, these reactions all result in changes of -2, 0 or +2 valence electrons, supporting the assertion in Tolman’s rules that the component steps in catalytic reactions should proceed via intermediates with either 16 or 18 valence electrons. When we consider catalytic reactions, they can b ...
... As can be seen, these reactions all result in changes of -2, 0 or +2 valence electrons, supporting the assertion in Tolman’s rules that the component steps in catalytic reactions should proceed via intermediates with either 16 or 18 valence electrons. When we consider catalytic reactions, they can b ...