Reaction of Organometallic Reagents with Aldehydes and Ketones.
... epoxide rings with other negatively charged nucleophiles—that is, nucleophilic attack from the back side of the epoxide, followed by protonation of the resulting alkoxide. • In unsymmetrical epoxides, nucleophilic attack occurs at the less substituted carbon atom. ...
... epoxide rings with other negatively charged nucleophiles—that is, nucleophilic attack from the back side of the epoxide, followed by protonation of the resulting alkoxide. • In unsymmetrical epoxides, nucleophilic attack occurs at the less substituted carbon atom. ...
An Overview of Carbonyl Compound Chemistry
... carbon cation character. Like a typical carbon cation, two possible reactions can occur around the carbonyl carbon. The first is simply an addition reaction in which a nucleophile is added to the carbonyl to form a new covalent bond (termed AdN , addition nucleophilic). The second is a β-elimination ...
... carbon cation character. Like a typical carbon cation, two possible reactions can occur around the carbonyl carbon. The first is simply an addition reaction in which a nucleophile is added to the carbonyl to form a new covalent bond (termed AdN , addition nucleophilic). The second is a β-elimination ...
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS - NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION
... This Powerpoint show is one of several produced to help students understand selected topics at AS and A2 level Chemistry. It is based on the requirements of the AQA and OCR specifications but is suitable for other examination boards. Individual students may use the material at home for revision purp ...
... This Powerpoint show is one of several produced to help students understand selected topics at AS and A2 level Chemistry. It is based on the requirements of the AQA and OCR specifications but is suitable for other examination boards. Individual students may use the material at home for revision purp ...
oxidation and reduction
... Singlet oxygen is a reactive intermediate which does many pericyclic reactions. For example, with cyclopentadiene at -78oC, a Diels-Alder reaction gives a strained endoperoxide which, as it warms to room temperature, fragments the weak O-O bond. ...
... Singlet oxygen is a reactive intermediate which does many pericyclic reactions. For example, with cyclopentadiene at -78oC, a Diels-Alder reaction gives a strained endoperoxide which, as it warms to room temperature, fragments the weak O-O bond. ...
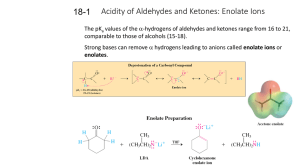
18-1 Enolates (PPT)
... For ordinary aldehydes and ketones, only traces of the enol form are present. The enol form is less stable by 8-12 kcal mol-1. However, for acetaldehyde, the enol form is about 100-times more stable than that of acetone because the less substituted aldehyde carbonyl is more stable than the more subs ...
... For ordinary aldehydes and ketones, only traces of the enol form are present. The enol form is less stable by 8-12 kcal mol-1. However, for acetaldehyde, the enol form is about 100-times more stable than that of acetone because the less substituted aldehyde carbonyl is more stable than the more subs ...
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the
... A hemiacetal has a hydroxyl and alkoxyl group on the same carbon Acylic hemiacetals are generally not stable, however, cyclic five- and sixmembered ring hemiacetals are ...
... A hemiacetal has a hydroxyl and alkoxyl group on the same carbon Acylic hemiacetals are generally not stable, however, cyclic five- and sixmembered ring hemiacetals are ...
Identification of Ketones and Aldehydes
... Aldehydes and ketones share the carbonyl functional group which features carbon doubly bonded to oxygen. In the case of ketones there are two carbon atoms bonded to the carbonyl carbon and no hydrogens. In the case of aldehydes there is at least one hydrogen bonded to the carbonyl carbon, the other ...
... Aldehydes and ketones share the carbonyl functional group which features carbon doubly bonded to oxygen. In the case of ketones there are two carbon atoms bonded to the carbonyl carbon and no hydrogens. In the case of aldehydes there is at least one hydrogen bonded to the carbonyl carbon, the other ...
alkene structure, naming, stereochemistry & preparation
... Reagent: very strong, bulky base Reaction flow: concerted Transition state: concerted reaction Stereochemistry: anti- and syn-periplanar ...
... Reagent: very strong, bulky base Reaction flow: concerted Transition state: concerted reaction Stereochemistry: anti- and syn-periplanar ...
PP Aldehyde and ketone
... ammoniacal silver nitrate mild oxidising agent which will oxidise aldehydes but not ketones contains the diammine silver(I) ion - [Ag(NH3)2 ]+ the silver(I) ion is reduced to silver Ag+(aq) + e¯ ——> Ag(s) the test is known as THE SILVER MIRROR TEST ...
... ammoniacal silver nitrate mild oxidising agent which will oxidise aldehydes but not ketones contains the diammine silver(I) ion - [Ag(NH3)2 ]+ the silver(I) ion is reduced to silver Ag+(aq) + e¯ ——> Ag(s) the test is known as THE SILVER MIRROR TEST ...
a,b
... Decarboxylation is unique to carboxylic acids with a second carbonyl group located at the b position Decarboxylation occurs via a cyclic mechanism • Involves initial formation of an enol ...
... Decarboxylation is unique to carboxylic acids with a second carbonyl group located at the b position Decarboxylation occurs via a cyclic mechanism • Involves initial formation of an enol ...
Chapter 14 Selenium reagents
... reactio with electrophiles. Hydrogenolysis of carbon-selenium bonds is achievable using catalytic methods, dissolving metals, triaryltin hydrides and ‘nickel boride’. 1,2,3-Selenadiazole undergo elimination, giving alkynes, either on heating or treatment with organolithium reagents. Highly react ...
... reactio with electrophiles. Hydrogenolysis of carbon-selenium bonds is achievable using catalytic methods, dissolving metals, triaryltin hydrides and ‘nickel boride’. 1,2,3-Selenadiazole undergo elimination, giving alkynes, either on heating or treatment with organolithium reagents. Highly react ...
THE CARBON-CARBON DOUBLE BOND
... Subsequent hydrolysis of amide (RCONH2) to the corresponding carboxylic acid (RCO2H) is generally rapid under acidic conditions. (These - and similar - reactions of carbonyl compounds will be studied ...
... Subsequent hydrolysis of amide (RCONH2) to the corresponding carboxylic acid (RCO2H) is generally rapid under acidic conditions. (These - and similar - reactions of carbonyl compounds will be studied ...
Synthesis of Cyclobutanes by Lewis Acid-Promoted Ketene
... significant hazards are associated with the chemicals involved in that procedure. Prior to performing a reaction, a thorough risk assessment should be carried out that includes a review of the potential hazards associated with each chemical and experimental operation on the scale that is planned for ...
... significant hazards are associated with the chemicals involved in that procedure. Prior to performing a reaction, a thorough risk assessment should be carried out that includes a review of the potential hazards associated with each chemical and experimental operation on the scale that is planned for ...
1072. A General Synthesis of Ethers.
... solution, hydrogenation of a ketal gives the same results as that of the carbonyl compound. Enolethers such as 1-methoxycyclopentene also give a mixture of alkane and saturated ether, but in a ratio different from that found for direct hydrogenation of cyclopentanone in acid methanol. This could be ...
... solution, hydrogenation of a ketal gives the same results as that of the carbonyl compound. Enolethers such as 1-methoxycyclopentene also give a mixture of alkane and saturated ether, but in a ratio different from that found for direct hydrogenation of cyclopentanone in acid methanol. This could be ...
Study Guide for Exam 2-‐ Aldehydes and Ketones
... forming an oxaphosphetane intermediate. Thus, the electrophile is not H+ as in the previous examples but the phosphonium center. The intermediate undergoes a reverse 2+2 process to ...
... forming an oxaphosphetane intermediate. Thus, the electrophile is not H+ as in the previous examples but the phosphonium center. The intermediate undergoes a reverse 2+2 process to ...
m4 carbonyl
... ammoniacal silver nitrate mild oxidising agent which will oxidise aldehydes but not ketones contains the diammine silver(I) ion - [Ag(NH3)2 ]+ the silver(I) ion is reduced to silver Ag+(aq) + e¯ ——> Ag(s) the test is known as THE SILVER MIRROR TEST ...
... ammoniacal silver nitrate mild oxidising agent which will oxidise aldehydes but not ketones contains the diammine silver(I) ion - [Ag(NH3)2 ]+ the silver(I) ion is reduced to silver Ag+(aq) + e¯ ——> Ag(s) the test is known as THE SILVER MIRROR TEST ...
Chapter 7: Dienes
... Reactions of Dienes: Two Key Types of Reaction I. Reaction Type: Reactivity: ...
... Reactions of Dienes: Two Key Types of Reaction I. Reaction Type: Reactivity: ...
CrO3/Al2O3: Rapid oxidation of alcohols to carbonyl compounds in
... the ratio 10:1 (w/w) in an agate mortar. In this simple and efficient method the alcohols were oxidized to the corresponding carbonyl compounds when the former was ground in a mortar with a pestle in the presence of supported CrO3 on Al2O3 and a few drops of tBuOH (Scheme I). The feasibility of the ...
... the ratio 10:1 (w/w) in an agate mortar. In this simple and efficient method the alcohols were oxidized to the corresponding carbonyl compounds when the former was ground in a mortar with a pestle in the presence of supported CrO3 on Al2O3 and a few drops of tBuOH (Scheme I). The feasibility of the ...