* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Addition/elimination under acidic conditions
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Diels–Alder reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition wikipedia , lookup
Vinylcyclopropane rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Aldol reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
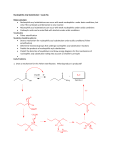
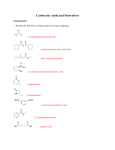
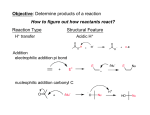
Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution—weak Nu Major concepts Nucleophilic acyl substitutions can occur with weak nucleophiles under basic conditions, but only if the carboxylic acid derivative is very reactive Nulceophilic acyl substitutions can occur with weak nucleophiles under acidic conditions Carboxylic acids can be esterified with alcohols under acidic conditions Vocabulary Fisher esterification Students should be able to: Draw a mechanism for nucleophilic acyl substitution under acidic conditions (Fisher esterification) Determine functional groups that undergo nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions Predict the products of nucleophilic acyl substitutions Predict the direction of equilibrium and draw energy diagrams for the mechanisms of nucleophilic acyl substitution taking into account Le Chatlier’s principle Daily Problems 1. Draw a mechanism for this Fisher esterification. What byproduct is produced? 2. Although the stability of the starting materials and products are about the same in the reaction above, the equilibrium lies far to the right. Explain how this is possible. How could this reaction be forced back to the left? (Hint: What is the byproduct of the reaction?) 3. These reactive carboxylic acid derivatives will react with these weak nucleophiles. Predict the product, and explain what the purpose of the triethylamine (TEA) and pyridine (pyr) is in each reaction. 4. Predict the products of these nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions. Cumulative problems: 5. Label each reaction as a nucleophilic substitution, a nucleophilic addition, or a nucleophilic acyl substitution. Then predict the product.