* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
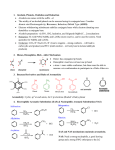
Electrophile Positive ion or molecule with + Attracted to an electron rich centre Accepts a pair of electrons to make a dative covalent bond. Electrophilic addition Typical of alkenes. Double bond single bond. Electrophilic substitution Typical of arenes since delocalisation is retained. Elimination The loss of atoms or groups of atoms to produce an unsaturated compound. Typical of 1ry and 2ry alcohols. Single bond double bond. Nucleophile A negative ion or a molecule with a lone pair of electrons Attracted to a positive/electron deficient centre Donates a pair of electrons to form a dative covalent bond. Nucleophilic addition Typical of aldehydes and ketones. Nucleophilic substitution Typical of halogenoalkanes. Oxidation Typical of 1ry alcohols, 2ry alcohols and aldehydes. Radical substitution Typical of alkanes. Reduction Typical of aldehydes and ketones.