* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reactions of Alkenes Organic Chemistry
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Aromatization wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
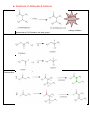
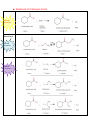
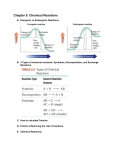
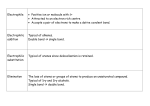
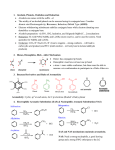
Organic Chemistry REACTIONS OVERVIEW Note: These examples were adapted and revised from General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry textbook (with author: Janice Gorzynski Smith) Reactions of Alkenes Addition Hydrogenation ( addition of hydrogen) Alkane Formation Halogenation (addition of halogens such as chlorine, bromine, etc.) Hydrohalogenation (addition of a halogen such as HCl, HBr) Markovnikov’s Rule Hydration (addition of water in presence of a strong acid, H2SO4) Alcohol Formation Markovnikov’s Rule ** catalyst a reactant that speeds up the reaction but it is not used up ** Markovnikov’s Rule states that if the alkene is unsymmetrical, the Hydrogen atoms will be attached to the carbon atom with most hydrogen atoms. Reactions of Aromatic compounds Substitution Chlorination ( addition of Chlorine) Sulfonation (addition of SO3H) Nitration ( addition of NO2) FriedelCrafts Acylation Ketone Formation Reactions of Alcohols Elimination Dehydration loss of water Alkene Formation Oxidation C—OH bond becomes C=O Oxidation is notated by [O]. Commonly, KMnO 4 is used for oxidation. Primary alcohols Aldehyde Formation Secondary alcohols Ketone Formation Tertiary alcohols THIOLS AND DISULFIDES If an alcohol has its O—H bond converted to S—H, the alcohol is said to be a thiol. Oxidation of Thiols makes a disulfide (S—S bond) Reduction Reduction (notated by [H]) of sulfides to make thiols the process during which C—O or C—S bond break. Also refers to breakdown of S—S bond. Reactions of Aldehydes & Ketones Oxidation Carboxylic Acid Formation Reduction **note H of the aldehyde was converted into an OH, thus a ketone will not undergo oxidation because has a C=O bonded to two alkyl groups. Ketones Aldehydes Aldol Condensation Two ketones come together: Two aldehydes come together: Reactions of Carboxylic Acids Neutralization WATER formation Fisher Esterification ESTER formation AMIDE formation Reactions of Esters & Amides Hydrolysis Esters Carboxylic Acid Formation Amides Carboxylic Acid Formation Alcohol Formation