* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Oxidation and Reduction - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Reaction progress kinetic analysis wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Industrial catalysts wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
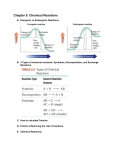
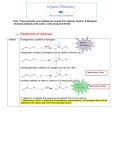
Oxidation and Reduction Reduction Reaction: A reduction is a chemical reaction that involves one atom gaining electrons. Reduction Reaction (w/out electron gain): A reduction reaction is an increase in the number of bonds between a carbon and atoms that are less electronegative than carbon (often hydrogen). *Since this reaction does not simply “gain electrons” one must look at other factors of the reaction. The product results in a new bond with a hydrogen, and as Carbon electronegativity is 2.5, and Hydrogen electronegativity is 2.1, it is a reduction. Oxidation Reaction: An oxidation is a chemical reaction that occurs when electrons from one atom are lost. Oxidation Reaction(w/out loss of electrons): An oxidation occurs when there is an increase in the number of bonds between a carbon and atoms that are more electronegative than the carbon (often oxygen). ❖ Useful tip for remembering the functions of reduction and oxidation is: OIL RIG Oxidation Is Lost Reduction Is Gained Oxidation and reduction reactions are important to know as they can be used to interconvert carbonyl groups and alcohols. Alcohols can be oxidized into aldehydes, and aldehydes can be reduced into alcohols. Works Cited Hardinger, Steven. “Chemistry 14D Lecture Supplement” 4th Ed. Hayden McNeil. 2016. Print.