* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cell wall - WordPress.com
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
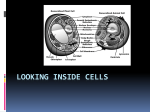
Name ___________________________________Hour ___ Cells & Heredity Chapter 1 Lesson 2 Directed Reading Please read pages 12-21 answering the following questions as you go. (p 12) 1. Why do scientists use stain when studying cells under the microscope? Stains make cells and cell structures easier to see. (p 13) 2. How do the parts of a Cell Work? Each kind of cell structure has a different function within a cell. 3. The cell wall is a rigid layer that surrounds the cells of plants and other organisms. 4. A plant’s cell wall helps to protect and support the cell. 5. What is the cell wall of a plant made of? cellulose 6. List 2 examples of materials that move easily through the cell wall. Water & oxygen 7. The job of the cell membrane is compared to which common item? Why? window screen: allows some materials to enter & not others 8. Everything a cell needs such as Food, water, and oxygen enters through the cell membrane. 9. Waste products move the same way. 10. The cell membrane keeps harmful materials out. T or F 11.Only plant cells have cell membranes. T or F (p 14) 12. Which organelle acts as the control center of the cell? nucleus 13.What does the nuclear envelope do? controls what enters and leaves the nucleus 14. How does the nucleus direct the activities of the cell? The nucleus contains chromatin. Chromatin (DNA) contains the information for directing a cells functions. 15. What is the function of the ribosomes? makes proteins 16. Where are ribosomes made? in the nucleolus (p 15) 17.Where are ribosomes found in the cell? on the ER or floating in the cytoplasm. 18. The space between the cell membrane and the nucleus is filled with a fluid called cytoplasm. 19. What is the job of the mitochondria? Convert energy stored in food to energy the cell can use (ATP) to live and funtion 20. The endoplasmic reticulum is often called simply the ER. 21. One job of the ER is to help the ribosomes when they produce… a. Proteins b. Nucleic acids c. Carbohydrates (p 16-17) 22. Which organelles are found in both plant and animal cells? Cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, ER, vacuoles, golgi apparatus, lysosomes 23. Which organelles are found only in plant cells? cell wall, chloroplasts, LARGE vacuoles, and fewer lysosomes (p 18) 24. The Golgi apparatus (also called the Golgi body and Golgi Complex) receives proteins and other materials from the ER, packages them, and transports them to other parts of the cell or outside of the cell. (Kind of like Fedex or UPS) 25. What is the water storage organelle that is unique to plants? Vacuole (generally large) 26. What does this organelle store besides water? Food, enzymes, waste and other materials (p 19) 27. A typical plant cell contains green structures, called chloroplasts in the cytoplasm. 27.What is the job of the chloroplasts? Capture energy from the sun and change it to food energy 29. Animal cells DON’T have chloroplasts. 30. Saclike organelles called lysosomes contain substances that break down large food particles into smaller ones. They also break down old cell parts and release substances so they can be used again. 31. Think of lysosomes as the cell’s recycling centers. (Summarize) 32. Summarize the differences between a plant cell and animal cell. cell wall and chloroplasts – plant cells only Large vacuoles – plant cells only More lysosomes – animal cells 33. How are the functions of the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus related? Proteins and other substances made in the ER are stored, packaged, and distributed by the Golgi complex 34. A solar panel collects sunlight and converts it to heat or electrical energy. How is a solar panel similar to chloroplasts? Chloroplasts collect sunlight and convert it to food energy 35. What are cells made of? Cell membrane, cytoplasm, DNA (genetic material), and other organelles (p 20) 36. Plants and animals (including you) are multicellular, which means “made of many cells”. Single-celled organisms are called unicellular. 37. Cells in a multicellular organism may be specialized, which means they perform specific functions that benefit the entire organism. 38. What does “division of labor” mean when talking about multicellular organisms? The overall job of maintaining the life of the organism is divided up among the cells - One type of cell does one kind of job, while other types of cells do other jobs and together they keep the organism living 39. How do cells work together in an organism?(key question) In multicellular organisms, cells are the basic unit of structure and function. Similar cells are organized into tissues. Different tissues working together to perform a specific job form organs. Groups of organs working together form organ systems. Organ systems work together to form an organism which is anything that can live on it’s own. 40. Define and give an example of: tissue: group of similar cells working together: connective tissue or muscle tissue organ: different tissues working together: heart, liver, skin organ system: groups of organs working together to perform a specific function: respiratory system, cardiovascular system, skeletal system 41. Living things are organized in levels of increasing complexity 42. Would a tissue or an organ have more kinds of specialized cells? Explain your answer. An organ would have more kinds of specialized cells, because it is made of different types of tissues which are made of specialized cells. 43. Draw a picture of, and label the “organization of your body”. See figure above or illustration in book – Pg. 21 figure 7