* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inside the Cell - Riverdale Middle School
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
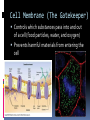
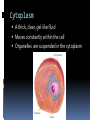
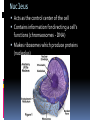
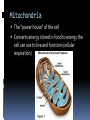
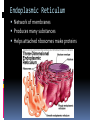
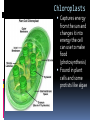
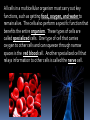
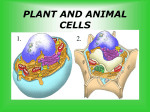
LOOKING INSIDE CELLS How Do the Parts of a Cell Work? The parts of a cell work together. Each kind of cell structure has a different function within a cell. Cell Wall A rigid layer that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms Protects and supports the cell Cell Membrane (The Gatekeeper) Controls which substances pass into and out of a cell (food particles, water, and oxygen) Prevents harmful materials from entering the cell Cytoplasm A thick, clear, gel-like fluid Moves constantly within the cell Organelles are suspended in the cytoplasm Organelles in the Cytoplasm Nucleus Mitochondria Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosomes Golgi Apparatus (Golgi Bodies) Vacuoles Chloroplasts Lysosomes Nucleus Acts as the control center of the cell Contains information for directing a cell’s functions (chromaosomes - DNA) Makes ribosomes which produce proteins (nucleolus) Mitochondria The “power house” of the cell Converts energy stored in food to energy the cell can use to live and function (cellular respiration) Endoplasmic Reticulum Network of membranes Produces many substances Helps attached ribosomes make proteins Ribosomes Small grain-shaped Made in the nucleolus Produce proteins Golgi Apparatus (The Warehouse) Receives proteins and other newly made substances from the ER Packages the materials Distributes the materials to the parts of the cell Vacuole Stores water, food, and other materials needed by the cell Plants have a larger vacuole because they store more water. Chloroplasts Captures energy from the sun and changes it into energy the cell can use to make food (photosynthesis) Found in plant cells and some protists like algae Lysosomes Contains substances that break down large food particles (enzymes) Breaks down old cell parts and recycles them How Do Cells Work Together in an Organism? In a unicellular organism, all of the functions of life are carried out by one cell. Plants and animals are made of many cells. They are multicellular organisms. All cells in a multicellular organism must carry out key functions, such as getting food, oxygen, and water to remain alive. The cells also perform a specific function that benefits the entire organism. These types of cells are called specialized cells. One type of cell that carries oxygen to other cells and can squeeze through narrow spaces is the red blood cell. Another specialized cell that relays information to other cells is called the nerve cell. When specialized cells work together to perform a specific function, it is called a tissue. Muscle cells work together to form muscle tissue. When groups of tissues work together to perform a specific function, it is called an organ. Muscle tissue and other types of tissue work together to form an organ like the stomach. When groups of organs work together to perform a specific function, it is called an organ system. The stomach and other organs like the esophagus work together to form an organ system. When groups of organ systems work together, an organism is formed. The digestive system works together with all organ systems to form an organism.