* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt - University of Kentucky
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
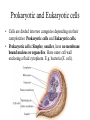
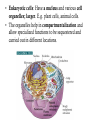
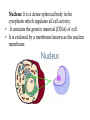
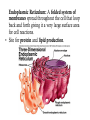
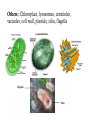
The Cell Basics of cell biology [Presentation for t.A. screen test] Mohati Desai Dept of biology University of kentucky The Cell • Cell- basic structural, functional unit of all living organisms • All living organisms are made up of cells • Cells perform the various functions needed by the organism to survive Unicellular and Multicellular Organisms • Unicellular organisms: only a single cell that performs all the functions E.g. Bacteria • Multicellular organisms: more than one cell and in many cases more than one type of cells; collectively perform all the functions of the organism. E.g. Higher plants and animals Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells • Cells are divded into two categories depending on their complexities: Prokaryotic cells and Eukaryotic cells. • Prokaryotic cells: Simpler, smaller, have no membrane bound nucleus or organelles. Have outer cell wall enclosing a fluid cytoplasm. E.g. bacteria (E. coli). • Eukaryotic cells: Have a nucleus and various cell organelles; larger. E.g. plant cells, animal cells. • The organelles help in compartmentalization and allow specialized functions to be sequestered and carried out in different locations. Components and Organelles of Cells Cell membrane/ Plasma membrane: Outermost covering that confers structure, shape and protection. • It is made up of lipids embedded with proteins. Cytoplasm: Everything between the cell membrane and the nucleus. • Primarily composed of water and includes salts, dissolved gases, enzymes, nutrients, proteins and all the cell organelles except the nucleus. Nucleus: It is a dense spherical body in the cytoplasm which regulates all cell activity. • It contains the genetic material (DNA) of cell. • It is enclosed by a membrane known as the nuclear membrane. Mitochondria: Known as the power house of the cell • Site of aerobic respiration and energy production. Endoplasmic Reticulum: A folded system of membranes spread throughout the cell that loop back and forth giving it a very large surface area for cell reactions. • Site for protein and lipid production. Ribosomes: Small organelles found either attached to the surface of the ER or free in the cytoplasm. • Involved in protein synthesis Golgi Bodies: Structure similar to the ER though not so large and wide spread. • Responsible for processing and packaging proteins for the cell. • Proteins are squeezed off into the little blebs which drift off into the cytoplasm Others: Chloroplast, lysosomes, centrioles, vacuoles, cell wall, plastids, cilia, flagella Flagella Cilia