* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download form follows function in organelles
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
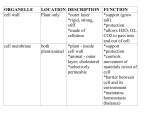
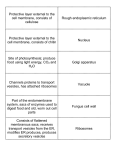
organelle function form How form follows function Nucleus Contains DNA DNA has code Easy to copy code when (genetic blue-‐ that’s easy to sending instructions to print), directs copy, packaged cell, chromosomes make cell activities in chromosomes cell replication easier Chloroplasts Capture energy Full of sacs with Lots of surface area on of sunlight to chlorophyll sacs for capturing light make food (which captures light energy) Mitochondria “burning” food Inner membrane Folds provide lots of to release has many folds surface area for reaction energy that releases energy ribosomes Make proteins Made up of 2 Protein-‐making (free or in pieces instructions fit between rough ER) 2 pieces to be “read” Golgi Puts finishing Pancake-‐shaped membranes break off as apparatus touches on stack of “bubbles” for delivery protein membranes products, then wraps & tags them for deli-‐ very elsewhere Lysosomes Recycle old cell parts, digest invaders Vacuoles/ Storage, vesicles digestion, osmotic pressure, product delivery Cytoskeleton Provides cell with structure, cilia & flagella on outside can move cell cytoplasm Thick fluid, fills cell, chemical reactions take place here, organelles “float” in it Cell wall Provides rigid structure to cell and plant, makes osmotic pressure possible Cell See notes membrane Sacs filled with digestive enzymes Sacs of various sizes enclosed by membrane Keep digestive enzymes away from rest of cell Different sizes, strong Strength gives support to cell, flagella and cilia right shape to be “paddles” (flagella and cilia) Is water-‐based so reactants dissolve, thick enough that molecules and organelles don’t move too quickly Jelly-‐like Made of tough, but permeable cellulose See notes Membrane controls what goes in and out; in plants, big enough to fill with water and provide osmotic pressure Permeable so doesn’t interfere with membrane, tough so defines cell shape and can stand up under osmotic pressure See notes