* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
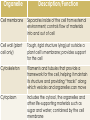
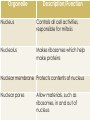
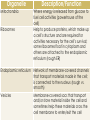
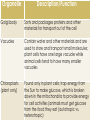
Cells Microscope Lab Cell division (mitosis and the cell cycle) Plants Animal tissues Animal body systems Frog dissection Biology Exhibit Test Periodic formative quizzes (some are embedded into the PPTs) Summative Assessments: Biology Exhibit Microscope Lab Report A couple of quizzes Unit Test ALIVE! NOT ALIVE! ALIVE! ALIVE! Depends on what you classify as alive… Basic units of life First described in 1665 Study of cells related to the development of the microscope Humans are composed of trillions of cells All living organisms are made of one or more cells The cell is the basic organizational unit of life All cells come from pre-existing cells Organelle Description/Function Cell membrane Separates inside of the cell from external environment; controls flow of materials into and out of cell Cell wall (plant cell only) Tough, rigid structure lying just outside a plant cell’s membrane; provides support for the cell Cytoskeleton Filaments and tubules that provide a framework for the cell, helping it maintain its structure and providing “tracks” along which vesicles and organelles can move Cytoplasm Includes the cytosol, the organelles and other life-supporting materials such as sugar and water; contained by the cell membrane Organelle Description/Function Nucleus Controls all cell activities, responsible for mitosis Nucleolus Makes ribosomes which help make proteins Nuclear membrane Protects contents of nucleus Nuclear pores Allow materials, such as ribosomes, in and out of nucleus Organelle Mitochondria Ribosomes Endoplasmic reticulum Vesicles Description/Function Where energy is released from glucose to fuel cell activities (powerhouse of the cell) Help to produce proteins, which make up a cell’s structure and are required for activities necessary for the cell’s survival; some ribosomes float in cytoplasm and others are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER) Network of membrane-covered channels that transport materials made in the cell; is connected to the nucleus (rough vs. smooth) Membrane-covered sacs that transport and/or store material inside the cell and sometimes help these materials cross the cell membrane to enter/exit the cell Organelle Description/Function Golgi body Sorts and packages proteins and other materials for transport out of the cell Vacuoles Contain water and other materials and are used to store and transport small molecules; plant cells have one large vacuole while animal cells tend to have many smaller vacuoles Chloroplasts (plant only) Found only in plant cells; trap energy from the Sun to make glucose, which is broken down in the mitochondria to provide energy for cell activities (animals must get glucose from the food they eat (autotropic vs. heterotropic) CELLS TISSUES ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEMS ORGANISM READ pages 7-14 Make sure you have completed the work assigned from the textbook (on the drive under Day 45)