* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 3 | Moving Cellular Material
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
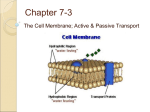
Name ___________ Date __________ Notes: Moving Cellular Material (Pages 61-66) Passive Transport 1. A cell membrane is semipermeable which means that it allows only certain substances to enter or leave a cell. 2. Passive transport is the movement of substances through a cell membrane _without__ using the cell’s energy. 3. Small molecules such as ___oxygen_____ and ___carbon dioxide_____ pass directly through the membrane by passive transport. Diffusion 1. Diffusion is the movement of ANY substances from an area of ___higher_________ concentration to an area of ___lower______ concentration. 2. Usually diffusion continues through a membrane until the substance reaches __equilibrium___. 3. Diffusion does __NOT__ require energy. Osmosis 1. Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules only through a membrane. 2. Since osmosis is diffusion, it does __NOT__ require energy. Facilitated diffusion 1. Facilitated diffusion allows molecules to pass through a cell membrane using __transport_ proteins. a. Carrier proteins carry larger molecules (sugars and salts) through the cell membrane. b. Channel proteins allow ions (sodium and potassium) to pass through the cell membrane. Active Transport 1. Active transport uses the cell’s energy (ATP) to move substances through a cell membrane against the normal direction of diffusion. 2. Active transport moves substances from areas of lower concentration to areas of higher concentration. Endocytosis 1. A cell uses endocytosis to __take in____ a substance by surrounding it with a __vesicle_____ formed by the cell membrane. Exocytosis 1. A cell’s ___vesicle_______ release their contents ___outside_______ the cell during exocytosis.