* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Structure
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
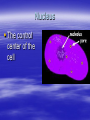
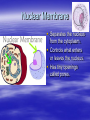
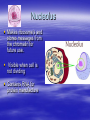
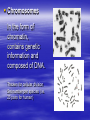
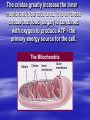
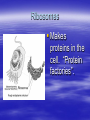
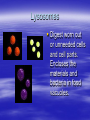
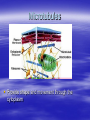
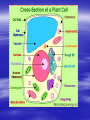
Cellular Structure Nucleus The control center of the cell Nuclear Membrane Separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm. Controls what enters or leaves the nucleus. Has tiny openings called pores. Nucleolus Makes ribosome's and stores messages from the chromatin for future use. Visible when cell is not dividing Contains RNA for protein manufacture Chromatin Determines cell activities and carries on the hereditary traits of the cell. Chromosomes In the form of chromatin, contains genetic information and composed of DNA. Thicken for cellular division Set number per species (i.e. 23 pairs for human) Cytoplasm The watery fluid which contains the materials which enter the cell. Organelles Little, tiny structures in the cell performing specific activities. Mitochondria The “powerhouse” of the cell. They create food to obtain energy for cell activities. The cristae greatly increase the inner membrane's surface area. It is on these cristae that food (sugar) is combined with oxygen to produce ATP - the primary energy source for the cell. Ribosomes Makes proteins in the cell. “Protein factories”. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) A system of canals which transport substances to the inside of the cell. It is also a chemical producer. Golgi Apparatus Package proteins for storage and secretion from the cell. Creates lysosomes Lysosomes Digest worn out or unneeded cells and cell parts. Encloses the materials and bacteria in food vacuoles. Centrioles Paired structures in animal cells which help in cell division. Only visible in animal cells, still in plant cells, but you can’t see them. Vacuole Stores food, water, and wastes. Much bigger in plant cells. Chloroplasts Found only in plant cells. Absorbs sunlight in the process of photosynthesis. Microtubules Provide shape and movement through the cytoplasm Cell Membrane Controls what enters and leaves the cell. It contains the cell contents and protects the cell. composed of lipids hydrophobic lipid ends facing inward and the hydrophilic phosphate ends facing outward. Also called lipid bilayer. Cell Wall Thick, outer wall surrounding plant cells. Helps support and protect the plant cell. Specialized Structures Cilia and flagella are often present on cells. They help provide locomotion. Specialized Organelles found in Plants Plastid: Found in plants Stores food or pigments Cell Wall: Found in plants o Supports and protects the cell Vacuole: Much larger in plant cells. Stores enzymes and waste products Specialized Organelles only found in animal or protist (unicellular organisms –fungi) cells Centriole: Found in animal cells and some protists. Protein fibers that aid in cell division Cilia: Hair-like microtubules attached to the plasma membrane that often help in movement