* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5.1 The Cell Cycle
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
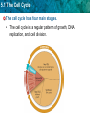
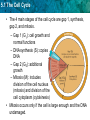
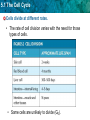
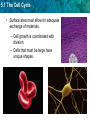
5.1 The Cell Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 5.1 The Cell Cycle • I can describe the stages of the cell cycle. • I can compare rates of division in different cell types. • I can identify factors that limit cell size. 5.1 The Cell Cycle The cell cycle has four main stages. • The cell cycle is a regular pattern of growth, DNA replication, and cell division. 5.1 The Cell Cycle • The 4 main stages of the cell cycle are gap 1, synthesis, gap 2, and mitosis. – Gap 1 (G1): cell growth and normal functions – DNA synthesis (S): copies DNA – Gap 2 (G2): additional growth – Mitosis (M): includes division of the cell nucleus (mitosis) and division of the cell cytoplasm (cytokinesis) • Mitosis occurs only if the cell is large enough and the DNA undamaged. 5.1 The Cell Cycle Cells divide at different rates. • The rate of cell division varies with the need for those types of cells. • Some cells are unlikely to divide (G0). 5.1 The Cell Cycle Cell size is limited. • Volume increases faster than surface area. 5.1 The Cell Cycle • Surface area must allow for adequate exchange of materials. – Cell growth is coordinated with division. – Cells that must be large have unique shapes. 5.1 The Cell Cycle In which stage of the cell cycle do the nucleus and its contents divide? • A. synthesis • B. gap 1 • C. mitosis • D. gap 2 5.1 The Cell Cycle 5.1 The Cell Cycle During the gap 1 stage of the cell cycle, a cell • a. splits into two new cells. • b. carries out its normal functions. • c. duplicates its DNA. • d. divides its cytoplasm. 5.1 The Cell Cycle Which of the following phrases best describes cytokinesis? • a. division of the cytoplasm • b. division of the nucleus • c. division of DNA • d. division of surface area 5.1 The Cell Cycle Which statement is true about the rates of cell division in eukaryotes? • A. They remain the same for the life of the organism. • b. They are faster than that of prokaryotes. • c. They increase with the age of the organism. • d. They vary greatly within an organism. 5.1 The Cell Cycle Which of the following limits the maximum size of a cell? • a. the stage of the cell cycle • b. the ratio of cell surface area to volume • c. the number of mitochondria in the cell • d. the size of the organism