* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Formation of Amino Acids
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
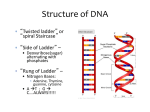
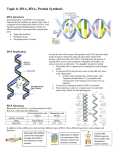
Journal 10/13/16 What do you remember about DNA? Make a list. Objective To learn how cells process information Tonight’s Homework p 91: 1, 2, 8 p 100: 2 Bring in your active transport device tomorrow! Notes on Cellular Metabolism What is metabolism? Metabolism is the process of a cell carrying out life functions. Growth, respiration, movement, and everything else. For a long time, scientists didn’t know how the cell knew when to do each of these kinds of things. We now know it comes down to two things: - Proteins - DNA Notes on Cellular Metabolism Protein Synthesis The biggest way for a cell to send out instructions is through proteins. Proteins have the proper shape to “plug in” to different things in organelles, telling them what to do. Proteins are made of thousands of little molecules called amino acids. Each amino acid twists the chain with a new bend. After thousands of amino acids, you get a very specific and twisty shape. Notes on Cellular Metabolism There are thousands of different types of proteins, each one serving a specific function. So what we really want to know is… how does a cell make proteins? Notes on Cellular Metabolism DNA Codes Remember DNA? How it has 4 different kinds of chemicals? We can read a string of DNA like words on a page. The order of the chemicals – the base pairs - tells the cell what to make. Notes on Cellular Metabolism DNA Codes Remember DNA? How it has 4 different kinds of chemicals? We can read a string of DNA like words on a page. The order of the chemicals – the base pairs - tells the cell what to make. This is: G T C G T C C T G T Notes on Cellular Metabolism Each “word” is just 3 “letters” long. We call each of these “words” a “codon”. Most codons make either a single amino acid or have a special code to start and stop the cell from reading DNA. Total, there are about 20 different amino acids. Notes on Cellular Metabolism Each “word” is just 3 “letters” long. We call each of these “words” a “codon”. Most codons make either a single amino acid or have a special code to start and stop the cell from reading DNA. Total, there are about 20 different amino acids. Examples: AUG – Code to start reading DNA UAA – Code to stop reading DNA GAC – Amino acid “aspartate” GUU – Amino acid “valine” There is a table in your book on page 103! Notes on Cellular Metabolism Types of RNA So how does a cell “read” this DNA? For that, we have to have 3 kinds of RNA. RNA is just like DNA, but instead of two strands twisting, it’s just one. There are 3 kinds of RNA that help a cell read DNA. - Messenger RNA - Transfer RNA - Ribosomal RNA Notes on Cellular Metabolism Messenger RNA This is RNA copied from the DNA in the nucleus of the cell. This copy leaves the nucleus and finds a ribosome so it can be read. The ribosome then reads the mRNA and makes the amino acid. Notes on Cellular Metabolism Transfer RNA This type of RNA attaches to the end of the mRNA and helps it “plug in” to the ribosome. Think of this like a zipper. You can’t attach the two ends without the thing you pull. Just like you can’t attach mRNA to a ribosome without tRNA. Notes on Cellular Metabolism Ribosomal RNA Our ribosomes can’t read RNA without an “instruction book”. Ribosomal RNA is a small bit of RNA inside the ribosome that tells it how to do this. Notes on Cellular Metabolism Formation of Amino Acids Let’s look at what happens inside the ribosome in more detail. 1) The mRNA lines up with a ribosome Notes on Cellular Metabolism Formation of Amino Acids Let’s look at what happens inside the ribosome in more detail. 1) The mRNA lines up with a ribosome 2) The ribosome looks for a “start” codon to know where to begin. Notes on Cellular Metabolism Formation of Amino Acids Let’s look at what happens inside the ribosome in more detail. 1) The mRNA lines up with a ribosome 2) The ribosome looks for a “start” codon to know where to begin. 3) The RNA starts going through the ribosome one codon at a time. As it goes, the ribosome starts putting together amino acids into a twisty shape. Notes on Cellular Metabolism Formation of Amino Acids Let’s look at what happens inside the ribosome in more detail. 1) The mRNA lines up with a ribosome 2) The ribosome looks for a “start” codon to know where to begin. 3) The RNA starts going through the ribosome one codon at a time. As it goes, the ribosome starts putting together amino acids into a twisty shape. 4) This keeps going until the ribosome finds the “stop” codon. Then it lets the new protein go. Notes on Cellular Metabolism Notes on Cellular Metabolism Homeostasis One last major idea here. If all the previous stuff works properly, our cell has a good, stable metabolism. We call this homeostasis. Notes on Cellular Metabolism Homeostasis One last major idea here. If all the previous stuff works properly, our cell has a good, stable metabolism. We call this homeostasis. To keep homeostasis, some organisms have to process energy and metabolize faster. We say they have a higher metabolic rate. Others process slower. We say they have a lower metabolic rate. Notes on Cellular Metabolism Homeostasis One last major idea here. If all the previous stuff works properly, our cell has a good, stable metabolism. We call this homeostasis. To keep homeostasis, some organisms have to process energy and metabolize faster. We say they have a higher metabolic rate. Others process slower. We say they have a lower metabolic rate. When creatures build up material and store energy, we call it anabolism. When they break things down, we call it catabolism. Exit Question What is a codon? a) RNA b) A group of 3 “letters” from DNA. c) The organelle that process RNA d) The DNA in the middle of a cell. e) A secret code used in World War II f) None of the above