* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Operant Conditioning
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Bullying and emotional intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Attitude change wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Prosocial behavior wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Residential treatment center wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Parent management training wikipedia , lookup
Counterproductive work behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
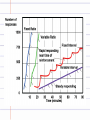
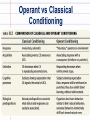
Learning Theories Goal How do we acquire behaviors through operant conditioning? Edward Thorndike’s Law of Effect • Cats placed in “puzzle boxes” • Use trial-and-error to “escape” • Continue behaviors w/good result • Discontinue behaviors w/bad result B.F. Skinner “Skinner Boxes” Reinforcement Positive Reinforcement • Increases response by presenting positive stimulus Negative Reinforcement • Increases response by removing negative stimulus Punishment Positive Punishment Negative Punishment • Decrease behavior by presenting bad stimulus • Decrease behavior by removing good stimulus Punishment • Suppresses behavior (not forgotten) • Teaches discrimination • Teaches fear • May increase aggressiveness Reinforcers Primary Reinforcer • Unlearned Conditioned (Secondary) Reinforcer • Learned through association Immediate v. Delayed Reinforcers Continuous v. Partial (Intermittent) Reinforcement Shaping • Reinforce each step (successive approximation) toward desired behavior • Chaining – linking behaviors together into a routine (ex: putting reinforced dance moves into a choreographed performance) Schedules of Partial Reinforcement • Fixed-ratio – reinforcement after a set or fixed number of behaviors occur • Variable-ratio – reinforcement after different numbers of behaviors Schedules of Partial Reinforcement • Fixed-interval – reinforcement after a set or fixed amount of time • Variable-interval – reinforcement after different amounts of time Extending Operant Conditioning Cognitive Influences • Cognitive map – mental representation of environment • Latent Learning – learning not known until there is motivation to demonstrate it Operant Conditioning & Motivation • Intrinsic & extrinsic motivation (we will discuss these more in our motivation unit) – Intrinsic = internal desire to perform behavior, “for its own sake” – Extrinsic = need external reward or avoidance of punishment to perform behavior Biology & Operant Conditioning • Biological constraints predispose organisms to learn associations that are naturally adaptive – Pigeons naturally peck • Easy to teach pigeons to peck to receive food – Pigeons naturaly flap wings • Teach pigeons to flap wings to avoid shock – However, difficult to teach pigeon to flap wings to get food, or peck to avoid shock Premack Principle • Use preferred behaviors to reinforced nonpreferred behaviors – Parents make children eat vegetables in order to get dessert Applications of Operant Conditioning • • • • • School – token economy Sports Work – schedules of reinforcement Home Self-improvement - Biofeedback Operant vs Classical Conditioning