* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
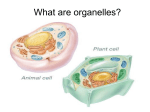
Download Animal and plant cells have a nucleus, cytoplasm, and a cell
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
7th Grade Science Final Review CELLS, PROCESSES, AND THE MICROSCOPE On loose leaf, write the answers to the following checklist of topics. You can write in words and draw labeled pictures. For the numbered questions, write the answers in the spaces provided. Students will be able to: Cells _____ State the differences and similarities between plant and animal cells. Animal and plant cells have a nucleus, cytoplasm, and a cell membrane. Only plant cells have chloroplasts and a cell wall. _____ Identify the following parts of cells (plant and animal) and state their functions: cell membrane – regulates what goes into and out of a cell cytoplasm – allows the organelles to circulate inside the cell chloroplasts – where food is produced in a plant cell vacuoles – store water and food nucleus – directs all the activities of the cell cell wall – protects and supports a plant cell chromosomes (genetic material) – contains the code to make proteins _____ List and describe the features of living things: movement – the organism moves on its own respiration – energy releasing process sensitivity (response to stimuli) – organisms react to changes in the environment nutrition – organisms take in food and digest it into usable nutrients excretion – getting rid of liquid and gas wastes reproduction – making offspring growth – getting larger by cell division _____ Describe the difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms unicellular – organism has only one cell multicellular – organism is made of more than one cell Cell Processes _____ Compare and contrast photosynthesis and respiration photosynthesis – a food making process in which plants use sunlight to make food respiration – an energy releasing process in which food and oxygen combine to release energy _____ Describe the following cell processes: diffusion – a substance moves from a higher concentration to a lower concentration osmosis – water diffuses across a cell membrane active transport – energy is required to move a substance across the cell membrane respiration – oxygen and glucose combine to release energy _____ Explain how the cell membrane is selectively permeable Cell membrane allows only some substances to pass in and out of the cell. _____ Explain how an organism’s body plan helps it maintain a balanced state (homeostasis) You feel thirsty when you are dehydrated. In times of stress, your body breathes quicker and your heart beats faster to get oxygen to body cells. Microscope _____ Identify the parts of a microscope and their functions objectives – magnify the specimen course adjustment knob – focuses quickly fine adjustment knob – focuses slowly and is used to see depth in a specimen diaphragm – regulates the amount of light passing through a specimen revolving nosepiece – switch to a higher power objective to see more detail _____ Estimate the size of a specimen by comparing it to the diameter of the field of view Compare the size of the specimen to the diameter of the field of view. 7 mm _____ Describe how specimens appear to move when viewed through a compound microscope The specimen appears to move in the opposite direction than it is actually moving. _____ Calculate total magnification using eyepiece magnification and objective lens magnification Total magnification = eyepiece x objective total magnification 10x eyepiece 10x objective 1. In the space below draw a diagram of a plant and animal cell and label the following structures: nucleus, cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm, chromosomes and vacuole. chromosome vacuole 2. Give 3 differences between animal and plant cells. no cell wall has a cell wall no chloroplasts has chloroplasts small vacuoles one large vacuole 3. Describe how a plant cell is different from a paramecium. A plant cell has a cell wall, has chloroplasts, has one large vacuole, and is autotrophic, it can make its own food through photosynthesis. A paramecium is an animal-like protist so it does not have a cell wall, does not have chloroplasts, has many small vacuoles, and is heterotrophic, it does locomotion to find its food. 4. Give the functions of the following microscope parts: eyepiece – magnifies the specimen (lens closest to the eye) objective lens – magnifies diaphragm – adjusts the brightness of the field of view coarse adjustment – moves stage – the specimen (lens closest to the specimen the stage quickly holds the specimen slide 5. Describe the relationship between how you move a microscope slide and how the specimen appears in the field of view. When you move the microscope slide, the specimen move in the opposite direction in the field of view. 6. How do you estimate the size of a specimen that you are viewing under the microscope. Compare the size of the specimen drawing to a drawing of the grid slide. 7. What is homeostasis? Give an example. homeostasis - maintaining stable internal conditions despite changing conditions in the environment For example, when a person gets hot in summer, they sweat to release heat and cool down. 8. Match the life function to its description: A. Sensitivity F the ability to produce more of its own kind ___ B. Excretion E the ability to move all or part of the organism ___ C. Ingestion D a cell changes oxygen and food into usable energy ___ D. Respiration A the ability of an organism to respond to a stimulus ___ E. Locomotion B getting rid of wastes ___ F. Reproduction G the increase in size and complexity of an organism ___ G. Growth & Development ___ C the ability to take in food or raw materials 9. Identify the following as diffusion or osmosis: Osmosis 8 CO2 6 H2O 10 H2O Diffusion 2 CO2 10. Give an example of how the cell membrane is “selectively permeable.” The cell membrane lets in small molecules such as oxygen and carbon dioxide. Large molecules such as starch cannot enter the cell. 11. Use checkmarks to compare and contrast photosynthesis and respiration. Photosynthesis Respiration X X X X Occurs in plants Occurs in animals Happens in mitochondria Happens in chloroplasts X X Needs glucose + oxygen Makes glucose + oxygen X X Makes water + carbon dioxide Needs water + carbon dioxide X X Produces energy Requires energy (sunlight) Occurs during the day X X Occurs during the night X X Circle the best choice: 1. Photosynthesis takes place in [only animal, only plant, both animal and plant] cells. 2. Photosynthesis takes place in the [cytoplasm, chromosome, chloroplast, mitochondria]. 3. Circle the chemical reaction for photosynthesis: glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + energy water + carbon dioxide + light glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + oxygen + glucose energy + water glucose + water + light carbon dioxide + water 4. Respiration takes place in [only animal, only plant, both animal and plant] cells. 5. Respiration takes place in the [ribosome, mitochondria, chloroplast, nucleus]. 6. Circle the chemical reaction for respiration: glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + energy water + carbon dioxide + light glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + oxygen + glucose energy + water glucose + water + light carbon dioxide + water