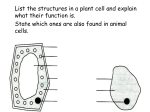
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Investigating Cells
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
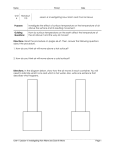
Investigating Cells Interactive Summaries This is an interactive exercise were you can fill in the correct blanks as you go! The Investigating Cells unit is divided into 4 sub-units: o o o o Investigating Living Cells Investigating Diffusion Investigating Enzymes Investigating Cell Division The first sets of summaries in each sub-unit are all at CREDIT LEVEL! To select an answer for each blank simply click on the grey box and choose your answer. You can check your answer by using the F1 key. Investigating Living Cells The summaries for this section are all at General level! Investigating Diffusion The Importance of Diffusion in Living Things o In a multicellular animal like a human being, diffusion plays a very important role. o For example, blood returning to the lungs from the cells contains a higher concentration of and lower concentration of than in the air sac. Carbon dioxide therefore diffuses out of the blood and oxygen diffuses in. Air sa o In living cells oxygen and is constantly being used up during respiration. Therefore the oxygen and glucose concentration inside the cell will be than in the surrounding blood. o Oxygen and glucose will therefore diffuse into the cell from a concentration to a concentration. oxygen oxygen o At the same time carbon dioxide is constantly being during respiration and will build up in the cell. o Therefore there will be a concentration inside the cell and a concentration in the surrounding blood. Therefore carbon dioxide will diffuse the cell. Carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide o Diffusion is important so that substances can diffuse into cells and products and can diffuse out of cells during respiration. Diffusion in Cells o The difference in concentration that exists between two regions before diffusion is known as the . o During diffusion molecules always move along a concentration gradient from to concentration. Cell membrane High concentration Osmosis in Plant Cells o If a plant cell was placed in pure water, water would the cell by osmosis. This is because the pure water has a water concentration than the contents of a normal plant cell. o The vacuole against the o The cell . wall . stretches o The cell is said to be and pushes the cytoplasm slightly but does not . o If a plant cell is placed in concentrated sugar solution water will the cell by osmosis. This is because there is a water concentration inside the cell compared to the surrounding solution. o The rigid. vacuole and the cytoplasm from the cell wall which is still fairly o The cells is said to be flaccid. or has become o Dilute sucrose solution would have the same water concentration as the contents of a normal cell so net movement of water would occur. Osmosis in Animal Cells o If red blood cells are placed in pure water, water will by osmosis until the cell bursts. This is because there is a water concentration outside the cell compared to inside the cell. o The cell bursts because animal cells do not have a . o If red blood cells are placed in , water will exit the cell by osmosis. This is because there is a higher water concentration inside the cell compared to outside the cell. This will cause the cell to . o As 0.85% salt solution has the same water concentration as the red blood cell contents, there is no net flow of water into or out of the cell by osmosis. Investigating Enzymes Specificity of an Enzyme o Each enzyme only acts on one type of . o Catalase, for example, will only breakdown and no other substrate. o Each enzyme is said to be substrate. to its o The shape of a molecule of enzyme exactly matches the shape of a molecule of its substrate. This is known as the theory. This allows the two molecules to combine briefly bringing about the reaction. o Each enzyme will also work best at a specific pH and temperature. o The particular condition at which an enzyme works best is called the condition. Mitosis o Stage (a): the nucleus containing long uncoiled chromosomes each double to form two identical o Stage (b): Short coiled up visible. are o Stage (c): Chromosomes become attached at the equator. A forms and each chromosome becoames attached by its . o Stage (d): Pairs of identical are separated and move to opposite ‘poles’ of the cell. o Stage (e) –(f): The nuclear membrane and divides. Separated chromatids are now called chromosomes. Two cells are formed each containing the same number of chromosomes as the original cell. Maintaining Chromosome Number o Chromosomes contain the main source of genetic information typical of a particular species. o It is essential that each cell formed as a result mitosis recieves a complement of chromosomes so that during the cells of multicellular organism will beable to provide the species with all of its characteristics. This is the end of the Credit section. Well done!! Take note of sections you found difficult and remember to ask your Biology teacher for help