* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Division by Mitosis
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
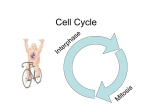
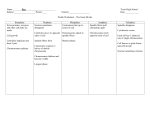
Cell Division by Mitosis Label each phase of cell division below. Then and match each statement with each phase _____________ _____________ _____________ _____________ _____________ In animal cells a ring of actin filaments forms In animal cells a ring of actin filaments forms round the equator of the cell, and then round the equator of the cell, and then tightens to form a cleavage furrow, which tightens to form a cleavage furrow, which splits the cell in two. splits the cell in two. chromosomes condensed and visible chromosomes condensed and visible centrioles at opposite poles of cell centrioles at opposite poles of cell nucleolus disappears nucleolus disappears phase ends with the breakdown of the phase ends with the breakdown of the nuclear membrane chromosomes align along equator of cell nuclear membrane chromosomes align along equator of cell spindle fibres (microtubules) connect centrioles spindle fibres (microtubules) connect centrioles to chromosomes to chromosomes spindle fibres disperse spindle fibres disperse nuclear membraness from nuclear membraness from nucleoli form nucleoli form chromatin not visible chromatin not visible DNA, histones and centrioles all replicated DNA, histones and centrioles all replicated In plant cells vesicles move to the equator, In plant cells vesicles move to the equator, line up and fuse to form two membranes line up and fuse to form two membranes called the cell plate. A new cell wall is laid called the cell plate. A new cell wall is laid down between the membranes, which fuses down between the membranes, which fuses with the existing cell wall. with the existing cell wall. centromeres split, allowing chromatids to separate chromatids move towards poles, centromeres split, allowing chromatids to separate chromatids move towards poles, centromeres first, pulled by kinesin (motor) centromeres first, pulled by kinesin (motor) proteins walking along microtubules (the proteins walking along microtubules (the track) track) Cell Division by Mitosis Interphase Prophase chromatin not visible DNA, histones and centrioles all replicated chromosomes condensed and visible centrioles at opposite poles of cell nucleolus disappears phase ends with the breakdown of the nuclear membrane Metaphase chromosomes align along equator of cell spindle fibres (microtubules) connect centrioles to chromosomes Anaphase centromeres split, allowing chromatids to separate chromatids move towards poles, centromeres first, pulled by kinesin (motor) proteins walking along microtubules (the track) Telophase Cytokinesis spindle fibres disperse nuclear membraness from nucleoli form In animal cells a ring of actin filaments forms round the equator of the cell, and then tightens to form a cleavage furrow, which splits the cell in two. In plant cells vesicles move to the equator, line up and fuse to form two membranes called the cell plate. A new cell wall is laid down between the membranes, which fuses with the existing cell wall.