* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organelles Work in a Cell
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
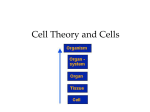
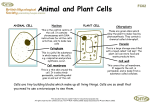
Chapter 7~ VOCABULARY Ch. 7.1 - Vocabulary Definition Picture Definition Picture Cell Cell theory nucleus Eukaryote Prokaryote Ch. 7.2 - Vocabulary organelles cytoplasm Nuclear Envelope Chromatin Chromosome nucleolus ribosome Endoplasmic Recticulum Golgi Apparatus Lysosome Vacuole Mitochondria Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Centriole Ch. 7.3 - Vocabulary Cell membrane Cell wall Definition Picture Lipid bilayer Concentration Diffusion Equilibrium Osmosis Isotonic Hyptertonic Hypotonic Facilitated diffusion Active transport Endocytosis Exocytosis Phagocytosis Pinocytosis Ch. 7.4 - Vocabulary Cell specialization Tissue Organ Definition Picture Life is cellular ~ Ch. 7.1 Discovery of the ___________________ •1665 – Robert _______________________ –Used microscope to look at cork cells ( a plant material) –Saw thousands of tiny ____________________ – called them “______________” •Anton van ________________________ –Observed _______________________ and saw tiny ________________________. Observations leading to cell theory •Numerous observation made it clear that the cell was the basic unit of life. •1838 – Matthias ____________________________ –Stated all ________________________ made of cells •1839 – Theodor ___________________ –Stated all ________________________ made of cells •1855 – Rudolf _______________ –Stated _____________________ only produced from division of existing cells The Cell Theory •States: –_______________________________ are composed of _________________ –Cells are the basic unit of __________________ and _________________ in living things –__________________________ are produced from ____________________________ ________________________ • ________________ than eukaryotes •_______________ complicated •__________ ___________________ –Free floating DNA •Some contain internal membranes •Examples: _________________ Eukaryotes •____________________ than prokaryotes •More ______________________ than prokaryotes •_________________________ -DNA located here •Many internal structures - ___________________ •______________________________________ •Example: Plants, animals, fungi, protists Ch. 7. 2 ~ Eukcaryotic Cell Structures (ORGANELLES) Cell ______________________ and Cell _________________________ Cell Membrane Thin, _____________________ _______________________ around the cell Supports and protects the cell Cell Wall _______________________ _____________________ Supports and protects the cell around the cell membrane Chloroplasts Use energy from _____________________ ______________________________ to make ______________________ Cytoplasm Material _____________________ cell membrane _________________________ organelles _________________________ substance but does not include nucleus Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough ER (#3) Carries the ____________________ Smooth ER (#4) Holds ______________________ that may change _____________________ if needed Golgi Bodies or Golgi Apparatus (#11) Modifies and ________________________ material for movement around cell (RER) Lysosomes ________________________________material to be used by the cell Mitochondria THE MIGHTY MITOCHONDIA!! ________________________ ________________________ from __________________________________________________________ Has _____________________________________ (inner/outer) Nucleus Holds the genetic material (____________) ___________________________ the cells ___________________________ (like the cell’s brain!) Has Pores – called _____________________________ __________________ from nucleus travel through pores to rest of cell Ribosomes (#2) Makes _________________________ Vacuole ________________________ structure __________________________, salt, proteins and ______________________ Provides ______________________ for heavy items such as _______________________, stems Movement __________________________ A ___________________________ structure Located on the ____________________________ of the cell Cilia __________________________ structures Located on the __________________________ of the cell Cells Alive http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm Cell Boundaries ~ Ch. 7.3 Cell Membrane Function: •________________________ what __________________ and leaves a cell •Provides ________________________________ and support What its made of: •_______________________________________ (2) •strong and flexible •_______________________________________ imbedded Regulate what ____________________/____________________ Membrane Types •_____________________________________ _______________________________ substances to pass through easily •Impermeable Does not allow substances to pass at all •Selectively permeable Some substances can pass through membrane Cell Walls __________________________________________________________________________ Only in… •Plants •__________________________________ •Fungi •Many prokaryotes Cell Walls •Function: __________________________________ cell cell __________________________________ what enters and leaves a cell Protects •What it’s made of…. Mostly __________________________________________ •A ________________________________________ The different types of movement across cell boundaries Osmosis Diffusion Facilitated diffusion Active Transport Endocytosis Exocytosis Phagocytosis Pinocytosis Osmosis Diffusion of ______________________________ through a selectively permeable membrane _______________________________ to ______________________________ concentration ____________________________________________________________________________ Osmosis cont… •Isotonic_____________________________ solute concentration on either side of membrane •______________________________________________________________ solute concentration •Hypotonic_______________________________ solute concentration Osmosis cont… •Water will _______________________________ cell until it bursts •How do they overcome this? Cells tend not to contact fresh water Contact is made with isotonic solutions Ex. Blood If they do make contact w/ fresh water, they have rigid ________________________ Ex. Plants and bacteria Diffusion In solution, particles move constantly Move from _________________________ concentration to __________________________ When concentration is equal throughout = ________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Facillitated Diffusion When particles ____________________________ or ______________________________ Go through protein channels Each one allows only one type of molecule through High to Low _________________________________________________ – just a pathway through the membrane ______________________________________________ Transport Moves particles across membrane _________________________________________ Moves against concentration gradient • (_______________________________________________) Endocytosis Take material into cell Needs energy Two types: •___________________________________________ engulf large _________________________________ and take them into the cell •___________________________________________ •engulf ____________________________ into the cell Exocytosis When a cell _________________________________________ large amounts of material __________________________________________________ Vacuole fuses with membrane This is a type ________________________________________ Measuring concentration of solutes in cell Concentration: density = ( mass of solute / volume of solution ) Ex. 12 g. of salt/ 3 L. of water = 4 g/ L Chapter 7.4 The diversity of cellular life Unicellular organisms __________________________ are the basic living units of all organisms _______________________________ – single celled organism _________________________________ Respond to environment Transform ______________________________________ Reproduce ____________________________________________________________________ Multicellular Organisms Multicellular – made up of _____________________ cells Great variety of ________________________________________ organisms All multicellar organisms depend on _______________________________________ and cooperation among __________________________________ cells Cell specialization – cells _______________________________________ to perform specific tasks Multicellular cont… Specialized ______________________ cells Red blood cells – transport O2 Pancreatic cells – make proteins (enzymes) To help digest food Packed with ribosomes (synthesize proteins) Packed with golgi apparatus (for protein export) Packed with storage vacuoles ( for storing enzymes) ____________________ cells Skeletal cells Multicellular cont… Specialized plant cells _________________________________ – where O2, CO2, H20 vapor are released and absorbed Located on underside of ___________________________________ ________________________________________ – surround stomata Help to ____________________________ or close stomata when needed Levels of organization In order from smallest to largest __A_________________________________________________ __C________________________________________________ __T________________________________________________ __O________________________________________________ __O________________________________________________ __O________________________________________________ Tissues Tissues – when ___________________________ _______________________________ grouped into units Perform a particular function 4 main types of tissues _____________________________________ tissue Epithelial tissue _____________________________________ tissue Connective tissue Organs Organs – when many different ___________________________ work together to perform a function Ex. Muscles work because have…. Muscle tissues Nerve tissues Connective tissues Organ Systems Organ system – group of ________________________________ that _____________________________________________ to perform a specific function Makes multicellular life possible Organism Individuals of a species Organelles Work in a Cell (Sung to the tune of “I’ve been working on the Railroad”) Organelles work in a cell, Each with a job to do. The nucleus controls the cell, the Cell membrane lets things through Ribosomes make protein; The ER lets things move. Golgi bodies pack things up So they can go smooth. Mitochondria, mitochondria Mitochondria make energy. Mitochondria, mitochondria Make cell energy. Vacuoles are for storage, Especially for wa-a-a-ter. Lysosomes get rid of wastes, Just like they oughta…. And they all Float in the cytoplasm, Float in the cytoplasm Float in the cytoplasm, While they do the work of the cell. Written by Jan Orndorff Ch. 7.1 Guided Reading 1. The discovery of the cell was possible due to the invention of the _______________________ 2. Who was the first person to see cells? ______________________________ 3. Why did he call them cells? _____________________________________________________ 4. Who was the first person to see tiny organisms living in water? _________________________________________________ 5. List the three components of the CELL THEORY ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 6. High resolution video technology can be used to produce moves of cells as they _________________________________________________________ 7. Transmission electron microscopes can be used to explore cell ______________________ and large _________________molecules 8. Scanning electron microscopes produce [ 2D | 3D | 4D ] images of the cell. (circle) 9. Specimens viewed under electron microscopes must first be [ preserved | stained ]. (circle) 10. Using the timeline, place the following in order of their discovery, from the earliest to the latest ____ All plants are made of cells ____ Cells organelles may have once been free-living organisms ____ The first cells were seen and a book published with drawings ____ All animals are made of cells ____ Observation of organisms living in pond water ____ Cells can only come from other cells 11. What type of microscope is needed to observe single atoms? __________________________ 12. What two things do ALL cells have? ______________________________________________ 13. Define nucleus: ______________________________________________________________ 14. Cells are categorized depending on whether or not they have a ________________________ 15. The greek word “eu” means _____________ whereas “pro” means _____________________ 16. Prokaryote cells have _________________material that is not contained in a _____________ 17. What type of organisms are prokaryotes? _______________________________________ 18. Prokaryotes grow, reproduce and ______________________________________________ 19. What four organisms are classified as eukaryotes? __________________________________ 20. Eukaryotic cells are [ smaller | larger ] than prokaryotes. Ch.7- 2 Guided Reading 1. In some respects, the _________________________________ is like a factory. 2. These structures are known as “little organs.” _____________________________. 3. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell into two major parts the ________________________ and the _____________________________________________. 4. See Figure 7-7. What part of the nucleus (with pointer) contains a small, dense region? ______________________________________________ 5. The nucleus is surrounded by a ____________________________ composed of two membranes. 6. When a cell divides, however; __________________ condenses to form __________________. 7. _________________________ are small particles of RNA and protein found throughout the cytoplasm. 8. The portion of the ___________________ involved in the synthesis of proteins is called ____________ ______________________________ or ________________________________________. 9. See Figure 7-9. What does the Golgi apparatus do to proteins? _______________________________________________________________ 10. The Golgi apparatus is somewhat like a ___________________________, where the finishing touches are put on proteins before they are ready to leave the “factory.” 11. One function of __________________________ is the digestion, or breakdown, of lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins into ________________________________ that can be used by the rest of the cell. 12. What kind of vacuole does the paramecium in Figure 7-10 contain? ____________________________ 13. Most cells get energy in one of two ways ---- from ________________________ or from the ___________. 14. ___________________________ are organelles that convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use. 15. ______________________________ are the biological equivalents of solar power plants. 16. Unlike other organelles that contain no DNA, ________________________ and ____________________ contain their own genetic information in the form of small DNA molecules. 17. Eukaryotic cells have a structure --- the _____________________________ --- that helps support the cell. 18. ___________________________ assembly and disassembly is responsible for the cytoplasmic movements that allow cells, such amoebas, to crawl along surfaces. 19. What plays a critical role in maintaining a cell’s shape? ________________________ 20. _____________________ are located near the nucleus and help to organize cell division. _____________________ are not found in plant cells. Chapter 7-3 Guided Reading 1. 2. 3. 4. Name two functions of the cell membrane: _____________________________________________ The cell membrane contains ____________________molecules that are embedded in the lipid bilayer. Why do scientists call the membrane a “mosaic”? _______________________________________ On the image, label the a. lipid bilayer b. protein channel c. carbohydrate chains 5. What three types of organisms have cell walls? _____________________________ 6. What is the main function of the cell wall? __________________________________________ 7. What are plant cell walls composed of? ___________________ 8. One of the most important functions of the cell membrane is to __________________ the movement of dissolved ________________________ from the liquid on one side of the membrane to the other. 9. A solution is a ________________________ of two or more substances. 10. Define diffusion: ______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 11. When the particles are the same throughout, the system has reached ________________ 12. Diffusion depends on ____________________ particle movements, therefore it [ does | does not ] (circle) require energy. OSMOSIS 13. If a substance is able to diffuse across a membrane, the membrane is said to be _______________ 14. Define osmosis: _________________________________________________________ 15. Isotonic means _____________________________ Hypertonic means ___________________________ Hypotonic means ____________________________ 16. Because cells are hypertonic in relation to fresh water, ___________________________ produces a net movement of water into the cell. If that happens, the cell will become ____________________________ and can even burst. 17. In plant and bacteria cells, what keeps them from bursting due to osmotic pressure? ___________ FACILITATED DIFFUSION 18. Cell membranes have _________________________ that make it easy for certain molecules to cross the membrane. 19. When proteins help molecules move across the membrane, it is called __________________________ ACTIVE TRANSPORT 20. Active transport moves molecules [ with | against ] the concentration gradient. 21. Active transport requires _____________________________ 22. Changes in protein shape seem to play an important role in the ______________ process. 23. Define endocytosis: _______________________________________________________ 24. What are the two types of endocytosis? ________________________________________ 25. How does an amoeba gets it food? ___________________________________ 26. Cells release large amounts of material in a process called _________________________ Plant Cell Coloring Cell Membrane (orange) Cell Wall (dark green) Ribosome (purple) Nucleoplasm (yellow) Nucleolus (brown) Cytoplasm (white) Mitochondria (red) Chloroplasts (light green) Golgi Apparatus (dk blue) Vacuole (lt. Blue) Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (pink) Chromatin (gray) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (pink) D C A D B Questions: E 1. Name two things found in a plant cell that are not found in an animal cell: 2. How does the shape of a plant cell differ from that of an animal cell? 3. What is the function of the chloroplasts? 4. What is the function of the vacuole? Animal Cell Coloring Cell Membrane (brown) Ribosome (red) Cytoplasm (light blue) Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (dark green) Nucleoplasm (pink) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (light green) Nuclear Membrane (dark brown) Mitochondria (orange) Nucleolus (yellow) Lysosome (purple) Golgi Apparatus (dark blue) Microtubules (gray) Flagella (pink) G H D C A B F E Briefly describe the function of the cell parts. 1. Cell membrane _____________________________________________________________ 2. Endoplasmic Reticulum _______________________________________________________ 3. Ribosome _________________________________________________________________ 4. Golgi Apparatus ____________________________________________________________ 5. Lysosome _________________________________________________________________ 6. Microtubule _______________________________________________________________ 7. Mitochondria ______________________________________________________________ 8. Nucleus ___________________________________________________________________ Cells Alive- Internet Lesson URL: www.cellsalive.com Objective: You will look at computer models of cells; learn the functions and the descriptions of the cells and their components. Navigating the site: Cells Alive has a navigation bar at the left. After accessing the page, click on CELL BIOLOGY on the left side navigation bar. From here, you will access the links: "How Big", the animal cell model, the plant cell model, and the bacterial cell model. Part A. "HOW BIG” Here you will look at objects found on the head of a pin. Your job is to rank them in order of size on the chart. The line in the bottom right corner of the screen is used to help you estimate. Object Red Blood Cells Rank Size (1 for smallest, 8 for largest) Rhinovirus QUESTIONS – For each, determine what units of measurement you would use: Human hair 1. A virus: ( nanometers | micrometers | millimeters ) - circle Rank Size #1-8 Ebola virus 2. A red blood cell: ( nanometers | micrometers | millimeters ) 3. An E. Coli bacteria: ( nanometers | micrometers | millimeters ) 4. The length of a strand of hair: ( centimeters | micrometers | millimeters ) - circle The width of a strand of hair: ( centimeters | micrometers | millimeters ) - circle Staphylococcus E. coli Dust Mite Ragweed Part B: Bacterial Cell Model - (you will need to go to the “cell models" link and find the prokaryote or bacteria cell). Label the drawing. Part C; Animal Cell Model - (you will need to return to the "Cell Biology" link to access this page, or hit your back button). For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there. 1. What do mitochondria do? Sketch each of the following. Mitochondria 2. How big are mitochondria? 3. What does the Golgi Apparatus do? Lysosome 4. What is the difference between smooth and rough ER? 5. Where is the nucleolus found? 6. What does the nucleolus do? Golgi Apparatus 7. What does the cytoskeleton do? 8. Cytosol goes by what other name? Rough ER 9. What is the function of the cytosol? 10. What is the function of the lysosome? Part D: Plant Cell Model - (you will need to return to the "Cell Models" link to access this page, or hit your back button) 1. What other type of cell has a cell wall? Sketch the following Chloroplast 2. What makes the plant cells green? 3. In plant cells, what does the vacuole do? Vacuole Part E: Overview For the chart below, place a check in the box if the cell has that component. Plant Chloroplast Vacuole Ribosome Mitochondria DNA Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Wall Golgi Apparatus Animal Bacteria After soaking height After soaking height After soaking height Create a bar graph representing the before and after measurements. Make sure to put the mass, width, and height on the X axis and the numbers on the Y axis. DON’T FORGET TO PUT THE UNITS FOR EACH MEASUREMENT! Diffusion Virtual Lab Station Go to: http://tinyurl.com/4lujflm Answer the following questions by going through the lab step by step. Questions are in order of appearance: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Describe the difference you see between side A and B: _____________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ What kind of energy do molecules use to move randomly around? _____________________ _______________________________________________________________ What is net diffusion? ___________________________________________ What direction does net diffusion move? __________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Molecules will move back and forth across the membrane until _________________________ is reached. What happens if the temperature is raised? ________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ What happens if the temperature is lowered? _______________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ Osmosis Virtual Lab Station Answer the following questions by going through the lab step by step. Questions are in order of appearance: Go to http://tinyurl.com/4pomaql 1. Define osmosis: _____________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 2. What happens to the solute and solvent in the beaker pictured (watch for a little bit): ___________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 3. In your own words, write down the three things we are assuming in this lab: a. ______________________________________________________________________ b. ______________________________________________________________________ c. ______________________________________________________________________ 4. Why don’t the solute molecules (red) move across the membrane? ______________________ 5. What happens if the large molecules are removed from both sides of the beaker?__________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 6. When the large (red) molecules are placed back into the water, what happens to the water and why? _______________________________________________________________________ 7. What kind of solution are living cells bathed in? _____________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 8. What happens when cells are placed in a hypertonic solution? _________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 9. Why? ______________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 10. What happens when cells are placed in a hypotonic solution? _________________________ 11. Why? _______________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ Biology ~ Cell Project DUE DATE: ____________ Floating around in the cytoplasm are small structures called organelles. Like the organs in your own body, each one carries out a specific function necessary for the cell to survive. Our goal in this project will be to understand how these structures work together to help the cell do its work. In this project you will have 2 choices in creating a model of the cell. 1. 3-D model 2. Pamphlet All options need to include labels for all the cells organelles as well as descriptions of their functions. You can choose either a plant cell or an animal cell. You will be graded on the following criteria: Criteria Clearly and correctly labeled organelles Key with correct functions of organelles Name, period and label (plant or animal cell) Correct approximate sizes of organelles Effort in neatness and creativity Possible points 15 points Points earned 20 points 5 points 5 points 15 points TOTAL POINTS : _____/ 60 Ch. 7 - Study Guide 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Who discovered cells? _______________________________________________. What was he looking at when he named them cells? _______________________. ______________________________________ stated all ________________________made of cells. _______________________________________stated all _________________________ made of cells. _______________________________________stated only ____________________ are produced from______________________________________________________________. Name the three parts of the cell theory: _____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Describe a PROKARYOTE: ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Describe a EUKARYOTE: ______________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ A cell membrane supports the cell and holds in all of the organelles; what does a cell wall do and do plants or animals have them? ___________________________________________________________ List the organelles you learned below, list their function and if found in plants or animals: Organelle Function Plant or Animal 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. Osmosis is the movement of ____________________ across a semi-permeable membrane. 25. Is energy needed for osmosis to occur? _________________. 26. Diffusion is the movement of ___________________ from a ________________concentration to a ______________________ concentration. 27. Is energy needed for diffusion to occur? __________________. 28. Facilitated diffusion uses a ____________________ to get material across a semi-permeable membrane. 29. Is energy needed for Facilitated diffusion to occur? __________________. 30. Active transport is the process of moving material from an area of _____________ concentration to an area of ___________________ concentration.