* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
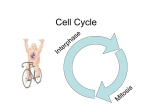
Download The phases of Mitosis
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
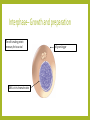
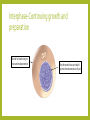
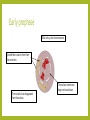
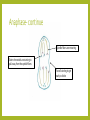
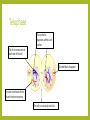
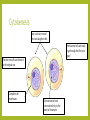
THE PHASES OF MITOSIS Claire Stevens Interphase– Growth and preparation The cell is making protein necessary for its survival DNA is in its chromatin state Cell grows bigger Interphase--Replication It may not look like anything has changed in the cell but…. An enzyme separates the DNA into two stands here DNA unwinds The original DNA strand is a sort of template for a new side to form around Most organelles will be replicated during this stage Interphase-Continuing growth and preparation The cell is continuing to grow and make proteins The chromatin has not coiled up into chromosomes as of yet Early prophase DNA coils up into chromosomes Spindle fibers start to form from the centrioles The nucleolus has disappeared from the nucleus The nuclear membrane begins to break down Early prophase-continue The nuclear membrane continues to break down The centrioles with the spindle fibers move towards the poles of the cell Early prophase- continue The centrioles and spindle fibers are now almost at the poles of the cell The cell membrane has almost completely disintegrated Late prophase The centrioles are completely at the poles The spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes at the centromere The spindle fibers are now fully formed. The nuclear membrane has completely disappeared Late prophase- continue The spindle fibers are starting to pull the chromosomes into a line across the equator of the cell Late prophase- continue The chromosomes are continuing to straighten out Metaphase The spindle fibers pull the chromosomes into a line across the middle of the cell Metaphase- continue The spindle fibers are starting to retract The chromosomes are starting to be pulled apart at the centromere Metaphase- continue The spindle fibers continue to retract The centromere is close to breaking Anaphase Spindle fibers are continuing to retract and pull back towards the centrioles Chromosomes break apart at the centromere and the sister chromatids are pull toward opposite poles of the cell Anaphase- continue Spindle fibers are retracting Sister chromatids are starting to pull away from the spindle fibers The cell starting to get ready to divide Anaphase- continue Nuclear membrane starts to form around each set of sister chromatids Spindle fibers are almost completely retracted into the centriole Sister chromatids detach from the spindle fibers and come together with their partners Telophase The nucleolus reappears within each nucleus Set of chromosomes at each end of the cell Spindle fibers disappear A nuclear membrane forms around the chromosomes The cell is now ready to divide Telophase- continue The cell is getting closer and closer to division The chromosomes are starting to uncoil into chromatin Telophase- continue The cell is ready to split in two The cell membrane is getting stronger and more complete The chromosomes uncoil further and are now almost entirely in the chromatin state Cytokenesis Two nuclei are moved into two daughter cells The two new cells are ready to go through the life cycle again! The two new cells are identical to the original one Complete cell membrane Chromosomes have returned entirely to the state of chromatin Bibliography • http://ineedmoving.com/siteadmin/interphase-cell-diagram • http://www.macroevolution.net/prophase-i.html • http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/meiosis/teloi.html • http://morganterhune3a.edublogs.org/2011/11/14/cell-cycle-sequencing/ • http://www.flickr.com/photos/26457459@N02/3264922970/ • http://seximexibio3.blogspot.ca/ • http://s322991969.websitehome.co.uk/wsb5822978901/interphase-labeleddiagram • http://www.ied.edu.hk/biotech/eng/classrm/class_gene2.html