* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Transport
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
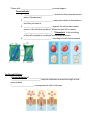
Chapter 5 Homeostasis and Cell Transport Section 1 Vocabulary Pretest 1. Passive Transport 2. Diffusion 3. Concentration gradient 4. Equilibrium 5. Osmosis 6. Hypotonic 7. Hypertonic 8. Isotonic 9. Contractile vacuole 10. Turgor pressure 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Plasmolysis Cytolysis Facilitated diffusion Carrier protein Ion channel Types of Transport *Cells transport molecules using different types of ______________________________ *These differ from each other by whether or not cells must use ___________________ Passive = ______________________ Active = _______________________ Passive transport—movement of ____________________________________________that requires ____________________ *Types of Passive Transport: a. ___________________--movement of molecules from ___________________ _______________________________________________ b. ___________________--movement of __________ from high to low concentration c. ________________________--assisted diffusion of large or insoluble molecules ____________________________________ d. ___________________________--movement of ____________ from high to low concentration Diffusion *Simplest type of ____________________________ *Moves molecules from ________________________________________ a. They have ______________________ and are in ______________________ b. Spread out because they “ ___________” into each other c. Move from where they are ___________________________ d. This is called ___________________________________________________ (Concentration gradient is the difference in concentration of molecules across a distance) e. Diffusion can happen in a _____________________________________ f. It can happen in a ____________________________________________ g. It is how most molecules pass into and out of ___________________________ h. It continues until ______________________ is reached. (Equilibrium--the concentration of molecules is the same throughout the space they occupy) Note: Even at equilibrium the _______________________ of molecules _______________ but the net movement in one direction does not. *Cell membranes are ____________________________ a. Depends on _______________ and ___________________________ of the molecule b. Passing ____________________ through the membrane is called __________________________________ Examples: Osmosis *Diffusion of _________________ from high to low concentration *Direction of _________________________ depends on the relative concentration of ________________ inside and outside the cell. *Review a. Solute--_______________________________________________________ b. Solvent--______________________ *______________________________--a solution outside the cell that has a ___________concentration of _________________________ than the concentration inside the cell. Ex: (less salt outside the cell) a. This means that there is a _______________________________ of solvent outside the cell. (more water outside the cell) b. So water will ________________________ the cell by osmosis. *____________________________--a solution outside the cell that has a ___________ concentration of ________________________ than the concentration inside the cell. Ex: (more salt outside the cell). a. This means that there is a _____________________________ of solvent inside the cell. Ex: (more water inside the cell) b. So water will ____________________ of the cell by osmosis. *____________________________concentrations of solute are ____________ on both inside and outside of the cell. a. Water will move in ________________________ in even amounts. *Some cells _______________________________to some degree. Three methods: 1. ____________________________---structures that pump out excess water. (Paramecium) 2. ____________________________--pump out solutes so that water is less likely to move in. 3. ___________________________--support the cell so when water moves in the cell does not burst. When vacuoles fill is creates “__________________________”. “Plasmolysis” is the shrinking of the cells cytoplasm, creating a loss of turgor pressure. 4. ___________________________—bursting of a cell due to osmosis Facilitated Diffusion *Assisted diffusion of __________________________________________________ *____________________________--help the molecules to move from high to low concentration *______________________ is transported to cells in this way. Ion Channel Diffusion *Several ions are vital to cells but cannot pass through the cell membrane because they are not soluble in lipids. They are: __________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ *They require specific _________________________ to pass through membranes. *Many ion channels have _____________ that close or open in response to 3 stimuli: a. ________________________________ b. ________________________________ c. ________________________________ Section 2 Vocabulary Pretest 1. Active Transport 2. Sodium-potassium pump 3. Endocytosis 4. Vesicle 5. Pinocytosis 6. Phagocytosis 7. Phagocyte 8. Exocytosis Active Transport *Active Transport—movement of substances through a cell membrane that ______________________________. *Molecules move from _______________________________________________ (“up” their _________________________________________) *The Carrier Proteins involved require energy from ______________ and are called _____________________________________________ *Example: ______________________________________ *The sodium-potassium pump is important in animals to maintain the normal function of many cells including __________________________. *The exchange of ______________________ for _________________________ creates an ________________________________. The outside of the cell becomes ______________________ and the inside becomes _________________ *This helps nerve cells to __________________________________________ Endocytosis *Movement of _______________________________ into a cell. The cell membrane pinches off to trap the particle inside a _______________ which can then transport it throughout the cell. *Types: a. ____________________--movement of large particles or whole cells b. ____________________--movement of fluids Exocytosis *Movement of _______________________________out of a cell. Vesicles bring particles to the cell membrane to be released.