* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plasma Membrane
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
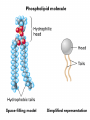
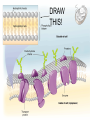
Plasma Membrane Responsible for homeostasis Plasma membrane • Thin, flexible boundary between a cell and its environment. Allows nutrients in and allows waste to leave cell • Plasma membranes have Selective permeability: allows some substances to pass through while keeping others out. • A cell membrane is called a fluid mosaic because it behaves more like a liquid than a solid. Structure of Plasma Membrane • Cell membranes are made of a lipid bi-layer. (double layer) • A single phospholipid molecule has two different ends: a head and a tail. • The head end contains a phosphate group and is hydrophilic. This means that it likes or is attracted to water molecules. • Phosphate group makes the head polar and is attracted to water ( water also polar) Structure of Plasma Membrane • The tail end is made up of two strings of hydrogen and carbon atoms called fatty acid chains. • The tail is hydrophobic or do not like to mingle with water molecules • 2 fatty acid tails are nonpolar and are repelled by water • Inside Plasma Membrane Cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates move among the phospholipids. • Proteins: transmit signals, anchor the cells • Transport protein: tunnel for certain substances to enter and leave cell( aid movement of substances) • Cholesterol: helps the fatty acid tails from sticking together. ( structure) • Carbohydrate chain: define cells characteristics and help cells identify chemical signals(recognition marker) • Enzymes: biochemical reactions within the cell DRAW THIS!