* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
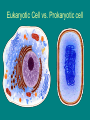
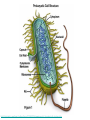
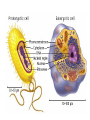
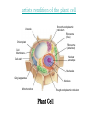
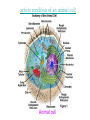
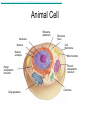
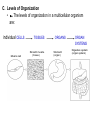
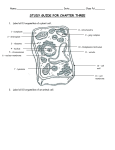
CHAPTER 7: CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Scanning Electron Microscope: Specimen Cells http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/java/electronmicroscopy/magnify1/index.html Fat cells Nerve Cells Red Blood Cells More Cells More Cells! 7-1 Life Is Cellular A. The Discovery of the Cell 1. Early Microscopes • Robert Hooke- Used compound microscope to look at a slice of cork • Anton van Leeuwenhoek- Observed tiny living things in pond water 2. The Cell Theory • Mathias Schleiden-Concluded all plants are made of cells • Theodor Schwann- Stated all animals are made of cells • Rudolf Virchow- Concluded new cells come from existing cells Cell Theory: • All living things are composed of _____ cells • Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things • New cells are produced from Existing cells ____________ B. Exploring the Cell 1. Electron Microscope (TEM & SEM) -Specimen placed in a vacuum http://www.mos.org/sln/sem/ 2. Scanning Probe Microscope -1990 development of fine probe microscope ordinary air -operates in _______________ -can even show samples in solution C. Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes 0.2 micrometers • cells vary in size from _________________1000 micrometers ___________________ • viruses are not cells Prokaryotic cell Cell membrane Eukaryotic cell Cytoplasm Cell membrane Organelles Cytoplasm Nucleus Prokaryotes Common to Both before pro=__________ contain DNA __________ karyote= kernel (nucleus) Cell generally smaller membrane less complicated no Membrane bound organelles Ex: Kingdom Monera - Eubacteria - Archaea Eukaryotes true Eu= ___________ Karyote=kernel (nucleus) Generally larger Contain membrane bound organelles (“little organs”) Ex: Plants, animals, fungi, and protists Eukaryotic Cell vs. Prokaryotic cell http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cell_structure/cell_structure.htm artists rendition of the plant cell Section 7-2 Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Vacuole Ribosome (free) Chloroplast Ribosome (attached) Cell Membrane Nuclear envelope Cell wall Nucleolus Golgi apparatus Nucleus Mitochondrion Rough endoplasmic reticulum Plant Cell artists rendition of an animal cell Animal cell http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cell_structure/cell_structure.htm Animal Cell Ribosome (attached) Nucleolus Nucleus Nuclear envelope Rough endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Ribosome (free) Cell Membrane Mitochondrion Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Centrioles 7-4 The Diversity of Cellular Life A. Unicellular Organisms (single celled) • Unicellular organisms _________ outnumber multicellular organisms • Examples: Yeast, algae, bacteria B. Multicellular Organisms (many celled) • Cells become ___________ specialized to perform different tasks • Cells need to communicate and cooperate C. Levels of Organization • The levels of organization in a multicellular organism are: individual CELLS TISSUES ORGANS Section Muscle cell Smooth muscle ( ti ssue) Stomach (organ) ORGAN SYSTEMS Digesti ve system (organ system) 1. Tissues= Group of similar cells that perform a particular function • Four types of tissue: - muscle - epithelial - nervous - connective 2. Organs= Groups of tissues • Ex. bicep muscle is mad of muscle, connective, and nervous tissue 3. Organ Systems= Group of organs that work together to perform a specific function.