* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Student Objectives
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
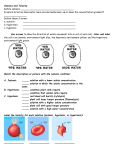
Student Objectives Cells Upon completion of this unit, you should be able to: 1. List ten cell processes and explain each. 2. Define the following terms: cell, diffusion, osmosis, cytolysis, plasmolysis, turgor pressure, hypotonic solution, hypertonic solution, isotonic solution, exocytosis, endocytosis, phagocytosis, homeostasis, mitosis, meiosis. 3. Compare and contrast the effects of hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic solutions on cells. 4. Outline the levels of organization in multicellular organisms: (tissues, organs, systems) 5. List five phases of mitosis and discuss the events that take place in each. Compare these with the phases of meiosis. 6. Clearly tell the difference between a chromatid and a chromosome. 7. Identify the centriole as the organelle that forms spindles to separate chromatids during anaphase. 8. Identify the following organelles from drawings: nucleus, nucleolus, mitochondrion, and chloroplast. 9. Match the following terms with their descriptions: cell, nucleus, nucleolus, cytoplasm, vacuole, mitochondrion, ribosome, rough E.R., golgi complex, phagocytosis, lysosome, chloroplast, cell membrane, and cell wall. 10. Compare plant cells with animal cells. 11. Write and compare the chemical reactions of photosynthesis and respiration, and name the organelles where these two processes take place. 12. Outline the energy pathway of photosynthesis. 13. Compare prokaryotic cells with eukaryotic cells. 1. Nutrition, Excretion, Respiration, Digestion, Secretion, Biosynthesis, Absorption, Response, Photosynthesis, Reproduction. See the NERSDSBARPR handout for explanation of each. 2. Terms and definitions: o Cell: basic structural unit of life o Diffusion: the dispersal of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration due to molecular movement and collisions o Osmosis: the diffusion of water through a cell membrane o Cytolysis (cyto=cell + lysis=breaking): rupture of a cell when water enters faster than it leaves. This happens to cells that lack a cell wall when they are placed in a hypotonic solution. o Plasmolysis (plasma= fluid + lysis=breaking): shriveling of a cell when water leaves faster than it enters. This happens to any cell placed in a hypertonic solution. o Turgor: water pressure inside a cell with cell walls. A plant cell or bacterial cell placed in a hypotonic solution takes up water by osmosis until the turgor pressure inside equals the osmotic pressure of the solution. Plants wilt without this water-pressure inside their cells. o Hypotonic solution (under salted) (hypo=under): a solution that is less concentrated in dissolved materials than another solution. Pure water is hypotonic to a cell; it has less dissolved salt, etc.. Hypotonic solutions tend to inject cells with water creating turgor pressure in cells with cell walls or cytolysis where cell walls are absent. o Hypertonic solution (over salted) (hyper=too much): a solution that is more concentrated in dissolved materials than another solution. Hypertonic solutions tend to dehydrate cells causing plasmolysis. o Isotonic (iso=the same + tonic=pressure): a solution that has the same concentration of dissolved materials as another solution. Cells are neither dehydrated nor injected by such a solution. Isotonic physiological saline is used for intravenous injections, and as a wetting agent for contact lenses. o Exocytosis (exo=exit + cyto=cell + osis=process): the use of energy by cells to pump out unwanted materials against diffusion pressure. o Endocytosis (endo=enter + cyto=cell + osis=process): the use of energy to take in more needed materials than would normally enter by diffusion. o Phagocytosis: (phago=to eat + ctyo=cell + osis=process): the capture of a particle or another cell too large to be taken in by normal endocytosis. The particle is surrounded and drawn into a vacuole by the cell. o Homeostasis (homeo=the same + stasis=state): a steady state maintained by living cells. o mitosis: cell division that results in two diploid cells. In humans, each new cell receives 23 pairs or 46 chromosomes. o meiosis: the division of a cell into four haploid gametes (sperm or egg cells). In humans, each new cell receives 23 chromosomes. 3. see above 4. In multi-cellular organisms, specialized cells are organized into tissues, which are organized into organs, which are organized into systems, which are organized into the organism. For example: The digestive system is made out of several organs: teeth, tongue, esophagus, stomach, intestine, colon etc. The stomach, is an organ made out of several kinds of tissues. One of those is smooth muscle tissue. Smooth muscle is made out of special smooth muscle cells. 5. Interphase: normal cell processes, growth, etc. chromosomes duplicate themselves just prior to the next phase. Prophase: the DNA coils up and chromosomes appear. Nuclear membrane dissolves. Metaphase: chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. Anaphase: chromatids separate and migrate to opposite ends (poles) of the cell. Telophase: formation of new nuclear membranes Cytokinesis: the cell cleave into two. 6. Chromosome: two identical strands of DNA coiled up and ready for cell division Chromatid: half of a chromosome, one strand of DNA. 7. The Centriole forms spindles and separates chromatids. 8. Nucleus Nucleolus Mitochondrion Chloroplast 9. Match the terms the definitions. nucleus, cell, nucleolus, cytoplasm, vacuole, mitochondrion, ribosome, rough E.R., golgi complex, phagocytosis, lysosome, chloroplast, cell membrane, cell wall _____________________ basic structural unit of life _____________________ surrounds the cell, acts as a gate _____________________ contains DNA, controls the cell _____________________ site of protein synthesis _____________________ system of ribosome filled canals _____________________ contains protein digesting enzymes _____________________ cell fluids outside the nucleus _____________________ site of cell respiration _____________________ endocytosis of large particles _____________________ fluid filled cavity for storage _____________________ site of photosynthesis _____________________ found inside nucleus, makes RNA _____________________ packages proteins for secretion 10. Plant cells have cell walls and plastids like chloroplasts, leucoplasts, and chromoplasts, which animal cells do not have. 11. 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 C6H12O6 + 6O2 Phoptosynthesis in Chloroplasts 6CO2 + 6H2O Respiration in Mitochondria 12. Sun Chlorophyll ATP NADH Glucose 13. Prokaryotes like bacteria have no visible nucleus or organelles Eukayotes like plant and animal cells have a visible nucleus and organelles