* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
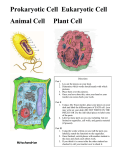
Developed the first microscope. He built over 240 microscopes He was the first to describe living cells Examined a slice of cork from the bark of an oak tree. He observed that cork was composed of tiny hollow boxes. He called these boxes cells. His descriptions led other scientists to look for evidence of cells. Concluded that all plants are made of cells. Concluded that all animals are made of cells. 1. All organisms are composed Cells Multicellular are the of one or more cells. “bricks” 2. The cell is the basic unit of of life. organization of organisms. 3. All cells come from preexisting cells. Unicellular There are two basic types of cells. 1. Prokaryotes – Have NO membrane-bound organelles. 2. Eukaryotes – DO have membrane-bound organelles. A prokaryote is an organism with a cell that lacks organelles surrounded by a membrane. An organelle is a small, membrane-bound structure in the cell. (little organs) The most obvious organelle is the nucleus. A eukaryote is an organism that has membrane bound organelles (like a nucleus), which allow different parts of the cell to specialize in different functions. Eukaryotes are either unicellular or multicellular. ORGANELLES The nucleus is only found in eukaryotic cells. It is the organelle that controls all cell functions. It is surrounded by a double, layered membrane called the nuclear membrane. The nuclear membrane will control what moves in and out of the nucleus. The nucleus is an organelle that contains DNA. (deoxyribonucleic acid) The nucleus also contains the nucleolus. It is a dark structure in the nucleus composed of proteins and RNA (ribonucleic acid) It is the site where ribosomes are made. The ER is a complex network of membranes that form channels, canals, and tubes that are found throughout the cytoplasm. It functions as a transport system moving materials throughout the cell. ER contains enzymes that aid in the synthesis of lipids. Rough ER is covered in ribosomes and is involved in protein synthesis. will not contain any ribosomes and is NOT involved in protein synthesis.. Is a series of closely stacked, flattened membrane sacs. - packages the new proteins & lipids it receives from the ER into organelles called vesicles. It may also temporarily store these materials if they are not needed at that time. PLANT CELL ANIMAL CELL VACUOLES It is a sac of fluid surrounded by a membrane. It’s main function is to store food, water, enzymes, and other materials needed by the cell. It is a small membranebordered organelle that contains digestive enzymes. Its function is to digest excess or worn out cell part, food particles, and invading viruses or bacteria. They are also known as suicide sacs because they sometimes digest the cell that contains them. lysosome Is a membrane-bound organelle that changes food molecules into usable energy (ATP). The cristae of the inner membrane provide a large surface area in a small place where energy-storing molecules are produced. Transforms light energy into usable chemical energy and stores the energy in food molecules. Is an organelle that can be found in plants and some protists. They contain molecules of chlorophyll, a green pigment that traps the energy from sunlight and gives the organism a green color. Other Cell Structures Also called the PLASMA MEMBRANE It serves as a flexible boundary between the cell and the external environment. It also controls the movement of materials that enter and exit the cell through a process called selective permeability. The cell membrane is a bilayer made up of lipid molecules (lipids are fats and oils). Protein molecules are also embedded in the lipid layer. Protein molecules Lipid bilayer Is located outside the cell membrane and gives the cell rigidity. It is a porous structure that allows substances to pass through it easily. Organisms with a cell wall can be found in 5 of the 6 Kingdoms of life: Eubacteria, Archeabacteria, Fungi, some Protista and Plants. It is the area between the cell membrane and the nucleus. It provides shape and support for the cell and it’s organelles. The Cytoplasm also contains a network of thin, fibrous elements called a cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton is mainly composed of hollow cylinders called microtubules and solid protein fibers called microfilaments. Shortcut to Brief_History_of_the_Cell_4.21.lnk Are involved in the production of enzymes and other proteins (protein synthesis) according to the directions of the DNA. Proteins Ribosome mRNA They can be found throughout the entire cell, but they are commonly associated with the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Animal cells will contain a pair of centrioles that lie just outside the nucleus. The centrioles are important when the cell is dividing. Cells can contain cilia or flagella, which are made of microtubules. In single-celled organisms, cilia and flagella are the major means of locomotion. cilia flagellum Are short, numerous, hairlike projections from the plasma membrane. Are long projections from the cell membrane that move with a whip-like motion.