* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Modern Genetics Notes
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
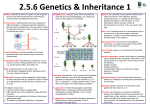
Question: Why do some traits exhibit a large number of phenotypes? COMPLEX PATTERNS OF INHERITANCE Incomplete dominance — when neither allele of the parents is completely dominant, the phenotype of the heterozygous offspring is a mix of parents. Ex. red snapdragons x white snapdragons pink snapdragons Codominant alleles — both alleles show equally Ex. black chicken x white chicken speckled chicken Multiple alleles — there are more than two alleles for a genetic trait Ex. a rabbit’s coat color — four possible colors Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes. 22 pairs of homologous chromosomes are called autosomes. The 23rd pair is called the sex chromosomes, which are indicated by X for females and Y for males. Sex — linked traits — traits controlled by genes located on sex chromosomes. Ex. color blindness Polygenic inheritance — inheritance pattern of a trait that is controlled by two or more genes. Ex. skin color and height *Nutrition, light, chemicals, and infectious agents such as bacteria, fungi, parasites and viruses can all influence how genes are expressed. Question: What does mRNA and tRNA stand for? THE GENETIC CODE Gene — a section of a DNA molecule that contains the information to code for one specific protein. The order of the nitrogen bases (guanine, cytosine, adenine and thymine) along a gene forms a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be produced. RNA — (ribonucleic acid) genetic “messenger” which carries genetic code from the DNA inside the nucleus into the cytoplasm Messenger RNA — copies coded message from DNA and carries message to ribosome in the cytoplasm. Transfer RNA — carries amino acids to the ribosome and adds them to growing protein # Strands SUGAR NITROGEN BASES DNA 2 deoxyribose A, G, C, T vs. RNA 1 ribose A, G, C, U (Uracil) Mutation — any change in a gene or chromosome Let’s say…original DNA sequence reads: THE RED HAT substitution THE RED CAT deletion THE REC AT Question: How are genetic disorders diagnosed? addition THE READ HAT HUMAN GENETIC DISORDERS Genetic disorder — an abnormal condition that a person inherits through genes or chromosomes that are caused by: 1. mutations in the DNA of genes 2. changes in the overall structure or number of chromosomes Pedigree — diagram or family tree of genetic inheritance used by geneticists to map genetic traits Karyotype — photograph of a person’s chromosome arranged in pairs and can reveal whether a person has correct number of chromosomes SOME GENETIC DISORDER CAUSED BY ABNORMAL CHROMOSOME # DISORDER CHROMOSOME DESCRIPTION Down Syndrome or Trisomy 21 # 21 47 chromosomes, intellectual disability, heart defects, respiratory infections Edward’s Syndrome or Trisomy 18 # 18 47 chromosomes, severe intellectual disability, characteristic malformations Turner’s Syndrome Single X in female 45 chromosomes, females only, are infertile, no secondary sex characteristics Klinefelter’s Syndrome Extra X in male 45 chromosomes, males only, sterile, small testicles, otherwise normal appearance Question: Can you give an example of selective breeding? ADVANCES IN GENETICS Selective breeding — process of selecting organisms with desired traits to be parents of next generation—two techniques include: Inbreeding — involves crossing two individuals that have similar characteristics Hybridization — breeders cross two genetically different individuals in hopes of offspring having best traits from both parents Clone — organism that has exactly the same genes as the organism from which it was produced Genetic Engineering — genes from one organism are transferred into the DNA of another organism (ex. bacteria producing insulin or cows producing milk with blood— clotting protein for hemophiliacs) Gene Therapy — involves inserting copies of a gene directly into a person’s cell The Human Genome Project — project to identify the DNA sequence of every gene in the human genome Genome — all the DNA in one cell of an organism