* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7th grade Ch. 5 section 2 and 3 Notes
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
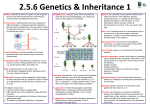
Genetic Disorders Ch. 5 section 2 Causes • Genetic Disorder: an abnormal condition that a person inherits through genes or chromosomes. • Some are caused by mutations in DNA. • Others by the changes in structure or Number of chromosomes. Cystic Fibrosis • The body produces abnormally thick mucus in the lungs and the intestines. • Mucus makes it hard to breath. • The recessive allele is a result of a mutation in which 3 bases are removed. Sickle Cell Disease • Affects the hemoglobin in red blood cells that carry oxygen. • When oxygen levels are low the red blood cell has a sickle shape. • Blot clots are common with this disease. Hemophilia • Disorder where a person’s blood clots very slowly. • Occurs more in males than females. • People bleed a lot just from a small cut. Downs Syndrome • A person’s cells carry an extra copy of chromosome 21. • Instead of a pair of chromosomes they have 3 in the 21st set. • People with DS have a degree of mental retardation and heart defect are also common. Pedigrees • An important tool that geneticists use to trace inheritance of traits in humans. • Chart or “family tree” that track which family member has a particular trait. Karyotypes • Picture of all the chromosomes in a cell. • Can help reveal if a person has the correct number of chromosomes in his or her cells. Dealing with genetic disorders • People with disorders face serious challenges. • Medical care and treatments can help people with some of these disorders. • Most genetic disorders do not prevent people from living active and productive lives. CH. 5 section 3 • Selective Breeding: selecting organisms with desired traits to be parents of the next generation. • Inbreeding: crossing 2 individuals that have similar characteristics. (usually very similar) • Hybridization: cross 2 genetically different individuals. Cloning • Can be used to produce offspring with desired traits. • Clone: organism that has the exact same genes as the organism in which it was produced by. • Researchers have cloned sheep and pigs. Genetic Engineering • Genes from one organism are transferred into the DNA of another. • One type of Bacteria is genetically engineered to produce insulin that is used for people with Diabetes. Gene Therapy • Involves inserting copies of a gene directly into a person’s cells. Concerns • Long term effects are still in question. • could cause health problems or environmental problems. Human Genome project • Genome: all the DNA in one cell of an organism. • Goal is to identify the DNA sequence of every gene in the human genome. • Humans contain at least 30,000 genes. • Average gene has about 3,000 bases.