* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells - singhscience
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
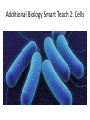
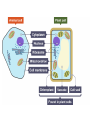
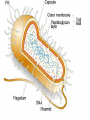
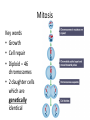
Additional Biology Smart Teach 2: Cells Animal, Plant and Bacteria Cell Organelle Nucleus Cell Membrane Cell Wall Sap Vacuole Flagellum/Pili Plasmid Chloroplast Plant Cell Animal Cell Bacteria Cell Plant and Animal Cells Plant and animal cells can be studies in greater detail using a light microscope. Light passes through a thin slice of the specimen. Lenses magnify the specimen many times. 7 Organelles Function Cell Membrane Controls movement into and out of the cell. Nucleus Contains DNA. Controls the cell Cytoplasm Where chemical reactions take place. Mitochondria Where respiration occurs. Cell Wall Made of CELLULOSE. Supports the cell. Vacuole Contains CELL SAP. Helps support the plant by keeping the cell rigid Chloroplast Contains CHLOROPHYLL. Absorbs LIGHT. Where photosynthesis takes place Differences between the cell Plant Animal Bacteria Nucleus Nucleus No nucleus – chromosomal DNA and Plasmids Cell wall No cell wall Cell wall Chloroplasts No Chloroplasts No chloroplasts Mitochondria Mitochondria No Mitochondria No Slime coat/capsule No Slime coat/capsule Slime coat/capsule No pili No pili pili No flagellum flagellum flagellum Cell division • Two types resulting in different cells: – Mitosis – Meiosis • You could be asked to compare and contrast the two processes, or you could be asked to describe in detail one process with a diagram. Copy the table and use the information on the following slides to compare mitosis and meiosis Mitosis Meiosis Mitosis Key words • Growth • Cell repair • Diploid – 46 chromosomes • 2 daughter cells which are genetically identical Meiosis Keywords • Gametes • Haploid – 23 chromosomes • 4 genetically different daughter cells Now lets have a look at an exam question about this.......... Questions Q1. Corals are animals that live on the sea bed. The photograph shows some species of coral. After fertilisation, mitosis takes place to form an embryo. The embryo develops into new coral. (i) Describe mitosis. (3) Answer (i) Acceptable Mark answers A description credit correct including three of reference to stages the following of mitosis: points: DNA replication / cell divides chromosomes / cell division / cell duplicate (1) splits(1) Chromosomes two cells line up along the produced (1) equator / middle of (both) the cell (1) diploid (1) chromosomes (both) cells pulled to either end are genetically of cell (1) identical (1) cytokinesis / cytoplasm splits (1) (3) Cloning • Process by which organisms are copied exactly. – Can apply to plants (taking a cutting) – Can apply to animals • You could be asked to describe the stages of cloning, or evaluate cloning. Evaluating means giving the advantages and disadvantages. Stages of cloning – Nuclear transfer • Remove the nucleus from an unfertilised egg cell. • Transfer the nucleus from the adult body cell (somatic cell) of the organism you wish to clone into the egg cell. • Apply an electric shock to cause the egg cell to begin to divide • Implant the embryo cells into a host mother. Dolly the Sheep – First cloned mammal Advantages and disadvantages Advantage or disadvantage Advantage Advantage Disadvantage Disadvantage Cloning situation All the new organisms are genetically identical – they will all have the desired characteristics. Organisms that are difficult or slow to breed normally can be reproduced quickly. If a clone is susceptible to disease or changes in environment, then all the clones will be susceptible. It will lead to less variation, and less opportunity to create new varieties in the future. Now lets have a look at an exam question about this.......... *(ii) A cloned animal contains genetic information that is identical to its parent. Describe the stages in the production of a cloned mammal. (6) Did you get all these points into your answer? A description including · use of body cell · nucleus removed from body / parent cell · use of egg cell · nucleus removed from egg cell/enucleated egg · nucleus (from body cell) transferred to enucleated egg · electric shock; · to stimulate cell division · mitosis · formation of embryo; · embryo implanted · into surrogate 1-2 Limited description of 2 of the stages involved in cloning and the sequence of events is confused the answer communicates ideas using simple language and uses limited scientific terminology spelling, punctuation and grammar are used with limited accuracy 3-4 a simple description of 3 or more of the stages involved in cloning but some of the steps may be missing or out of sequence the answer communicates ideas showing some evidence of clarity and organisation and uses scientific terminology appropriately spelling, punctuation and grammar are used with some accuracy 5-6 a detailed description of 5 or more of the stages involved in cloning but the sequence is largely in order and complete the answer communicates ideas clearly and coherently uses a range of scientific terminology accurately spelling, punctuation and grammar are used with few errors Genetic engineering • This is altering an organisms genetic code to give desired characteristics such as resistance to disease in crops or producing desirable products such as insulin. • You could be asked about the stages of genetic engineering and give examples. Examples of GM organisms • GM insulin • Golden rice that produce extra beta carotene that is used to make Vitamin A • Herbicide resistant crop plants Stages of genetic engineering • Select the desired characteristic. • Isolate the gene responsible for the characteristic. • Insert that gene into another organism usually by using a bacterium as a vector. • Replicate the transgenic organism. Now lets have a look at an exam question about this.......... Organisms can be genetically engineered to make them more useful to humans. Suggest how wheat could be genetically engineered to allow it to grow in wet, marshy land. (3) Question number Answer Mark an answer describing the process that includes three of the following: identify gene that allows plant to grow in wet or marshy area (1) extract/cut out the gene with a restriction (endonuclease)/enzyme (1) use vector/agrobacterium/ plasmid/to put desired gene into wheat/crop (1) (3)