* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
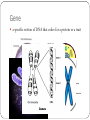
Genetics and Reproduction Vocabulary Sexual reproduction A form of reproduction that involves the fusion of both male and female cells (gametes) to create unique and different offspring. DNA exchange takes place Asexual reproduction A form of reproduction where only one parent is needed, and the offspring is an exact or identical copy of the parent. There is no exchange of DNA and no variety Types of Asexual Reproduction: Binary Fission When one cell splits into 2 parts and each new cell contains identical copies of DNA http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rgLJrvoX_qo Types of asexual reproduction: Budding The formation of a growth of an organism that can separate and become a new individual organism Why be asexual? Fast reproduction Don’t have to spend time or energy looking for a mate If you live in a place without a lot of mate options you don’t have to worry if you can reproduce Lots of offspring (kids) in short period of time Why reproduce sexually Offspring will all be genetically different The variation of offspring will allow them to survive in different situations and environments Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction # of parents 1 (no gender or female) 2: male and female Genes of offspring Identical Clone of parent Mixture of both parents Time Many kids very quickly (minutes) 1 or few kids very slowly (months) Cells required 1 cell turns to 2 2 cells merge into 1 Why Beneficial Fast, and no need for mates Not a lot of energy Offspring more likely to survive in different environements DAY 2 Trait A characteristic, quality, or feature of something Inherited trait traits that were inherited in an organism’s genes and DNA. They were received from their parents Acquired Trait A trait that is learned, acquired or developed by an organism- Not resulting from genes Inherited Vs. Acquired Inherited Both Acquired Allergies intelligence weight Cancer Height Cold or flu Eye color Personality Skin color Talents Blood Type Amputation ABO/AB (lost limb) DAY 3 Gene a specific section of DNA that codes for a protein or a trait Allele an alternative form of a gene (an option for a gene) Gene= eye color Allele= blue, green, brown, gray Gene= Hairline Allele= Striaght, widow’s peak Dominant allele The allele that will always show up in the Physical appearance if it is present Represented by a capital letter (R) Recessive Allele The allele that will only show up in the phenotype if there is not dominant allele Represented by a lowercase letter (r) Genotype The combination of alleles- or the genes an organism possesses 3 possibilities Two dominant (1 from Dad 1from mom= RR) Two Recessive (1 from Dad 1 from mom = rr) 1 of each (1 from either mom or dad Rr) Phenotype The physical appearance of an organism’s genes