* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Chromosome Mutations
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
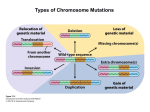
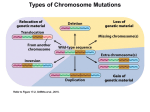
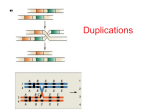
Types of Chromosome Mutations Refer to Figure 17-2, Griffiths et al., 2015. Chromosome Mutations Deletion/ Deficiency Duplication Inversion A B C D E F A C D E F A B C D E F A B B C A B C D E F A E D C B F A B C D E F A B C D J K G H J K G H E F D E F Translocation I I Reciprocal Translocation Reciprocal translocation heterozygotes are semisterile. 50% of gametes are genetically unbalanced. In plants, these gametes are not viable. In animals, zygotes that are formed by these gametes are not viable. Adjacent segregation produces genetically unbalanced gametes. Alternate segregation produces genetically balanced gametes. Down Syndrome and Translocation Heterozygote • Down syndrome is caused by trisomy 21 (3 copies of chromosome 21). • 95% of Down syndrome cases are associated with nondisjunction and shows no familial recurrence. • The other 5% (familial Down syndrome) is attributed to Robertsonian translocation between chromosome 21 and chromosome 14. Chromatin and Gene Expression Heterochromatin • Contains methylated histones (H3) • Associated with heterochromatin protein-1 (HP-1) Transcriptionally Active Euchromatin • Contains hyperacetylated histones Prevention of Heterochromatin Formation • DNA elements (barrier insulators) promote binding of histone acteyltransferase Gene Silencing is Caused by the Spread of Heterochromatin When a chromosome mutation places a gene next to heterochromatin, the gene can become inactivated. Inversion, deletion, duplication, and translocation can place a gene next to heterochromatin. Refer to Figure 12-23, Griffiths et al., 2015. Heterochromatin May Spread Farther in Some Cells Than in Others Refer to Figure 12-25, Griffiths et al., 2015. Position-effect Variegation A heterozygote for a gene and a translocation can show variegated phenotype for that gene. Position-effect variegation is exhibited by this w+/w heterozygote. Wild-type allele is no longer wild-type in its expression in some of the eye facets. Any chromosomal change that places a locus next to heterochromatin can result in inactivation of that gene. A tissue or organ that is comprised of a mixture of cells that express one or the other phenotype exhibit this variegation. Types of Chromosome Mutations Refer to Figure 17-2, Griffiths et al., 2015. The fates of a million implanted human zygotes 50% of spontaneous abortions are associated with chromosome abnormalities. Over half of these are trisomics, with trisomy 21 accounting for 9% of them. 18% of abnormalities are the Turner condition. ~ 0.6% of birthed infants have chromosome abnormalities. ~ 36% of birthed infants with chromosome abnormalities are aneuploidy of sex chromosome. Refer to Figure 17-37, Griffiths et al., 2015. ~ 23% of birthed infants with chromosome abnormalities are trisomics. Molecular Basis for Relationship between Genotype and Phenotype genotype DNA DNA sequence transcription RNA translation protein function phenotype organism amino acid sequence