* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reciprocal Translocation
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
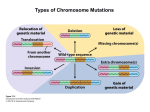
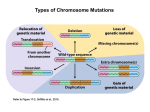
Types of Chromosome Mutations Chromosome Mutations Deletion/ Deficiency Duplication Inversion A B C D E F A C D E F A B C D E F A B B C A B C D E F A E D C B F A B C D E F A B C D J K G H J K G H E F D E F Translocation I I Inversions A B C D E F G H A B F E D C G H F H pericentric inversion A B C D E F G H A B C D E G paracentric inversion A heterozygote for a normal chromosome and an inversion will form an inversion loop during meiosis. The number of recombinant products is reduced in inversion heterozygotes by: 1) elimination of crossing over products within the inversion loop, and 2) inhibition of pairing between homologues in the region of the inversion. Pairing in paracentric inversion heterozygotes and resulting meiotic products. Anaphase bridge results in random breakage of chromosomal material. 2 of 4 meiotic products are not genetically balanced and will not produce viable gametes. Pairing in pericentric inversion heterozygotes and resulting meiotic products. Possible effects of inversion at the molecular level No disruption of any gene. Chromosomal rearrangement is the only result. Disruption of one gene by chromosomal breakage. Disruption of two genes and fusion of those two genes. Chromosome Mutations Deletion/ Deficiency Duplication Inversion A B C D E F A C D E F A B C D E F A B B C A B C D E F A E D C B F A B C D E F A B C D J K G H J K G H E F D E F Translocation I I Translocation In reciprocal translocation, exchange of chromosomal segments between two nonhomologous chromosomes establishes new linkage groups. A B C D E F G H G C D E F A B H In Robertsonian translocation, long arms of two acrocentric chromosomes are combined to form one large chromosome and one small chromosome. If the short metacentric chromosome does not contain essential genetic information, it could be lost without any consequence to viability. Reciprocal Translocation Reciprocal translocation heterozygotes are semisterile. 50% of gametes are genetically unbalanced. In plants, these gametes are not viable. In animals, zygotes that are formed by these gametes are not viable. Adjacent segregation produces genetically unbalanced gametes. Alternate segregation produces genetically balanced gametes. Down Syndrome and Translocation Heterozygote • Down syndrome is caused by trisomy 21 (3 copies of chromosome 21). • 95% of Down syndrome cases are associated with nondisjunction and shows no familial recurrence. • The other 5% (familial Down syndrome) is attributed to Robertsonian translocation between chromosome 21 and chromosome 14. Chromatin and Gene Expression Heterochromatin • Contains methylated histones (H3) • Associated with heterochromatin protein-1 (HP-1) Transcriptionally Active Euchromatin • Contains hyperacetylated histones Prevention of Heterochromatin Formation • DNA elements (barrier insulators) promote binding of histone acteyltransferase Gene Silencing is Caused by the Spread of Heterochromatin When a chromosome mutation places a gene next to heterochromatin, the gene can become inactivated. Inversion, deletion, duplication, and translocation can place a gene next to heterochromatin. Heterochromatin May Spread Farther in Some Cells Than in Others Position-effect Variegation A heterozygote for a gene and a translocation can show variegated phenotype for that gene. Position-effect variegation is exhibited by this w+/w heterozygote. Wild-type allele is no longer wild-type in its expression in some of the eye facets. Any chromosomal change that places a locus next to heterochromatin can result in inactivation of that gene. A tissue or organ that is comprised of a mixture of cells that express one or the other phenotype exhibit this variegation.